Reference trigger metadata in pipeline runs
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
This article describes how trigger metadata, such as the trigger start time, can be used in a pipeline run.
A pipeline sometimes needs to understand and read metadata from the trigger that invokes it. For instance, with a tumbling window trigger run, based on the window start and end time, the pipeline processes different data slices or folders. In Azure Data Factory, we use parameterization and system variables to pass metadata from triggers to pipelines.
This pattern is especially useful for tumbling window triggers, where the trigger provides the window start and end time, and custom event triggers, where the trigger parses and processes values in a custom-defined data field.
Note
Different trigger types provide different metadata information. For more information, see System variables.
Data Factory UI
This section shows you how to pass metadata information from triggers to pipelines, within the Data Factory user interface (UI).
Go to the Authoring Canvas and edit a pipeline.
Select the blank canvas to bring up pipeline settings. Don't select any activity. You might need to pull up the setting pane from the bottom of the canvas because it might be collapsed.
Select the Parameters tab and select + New to add parameters.
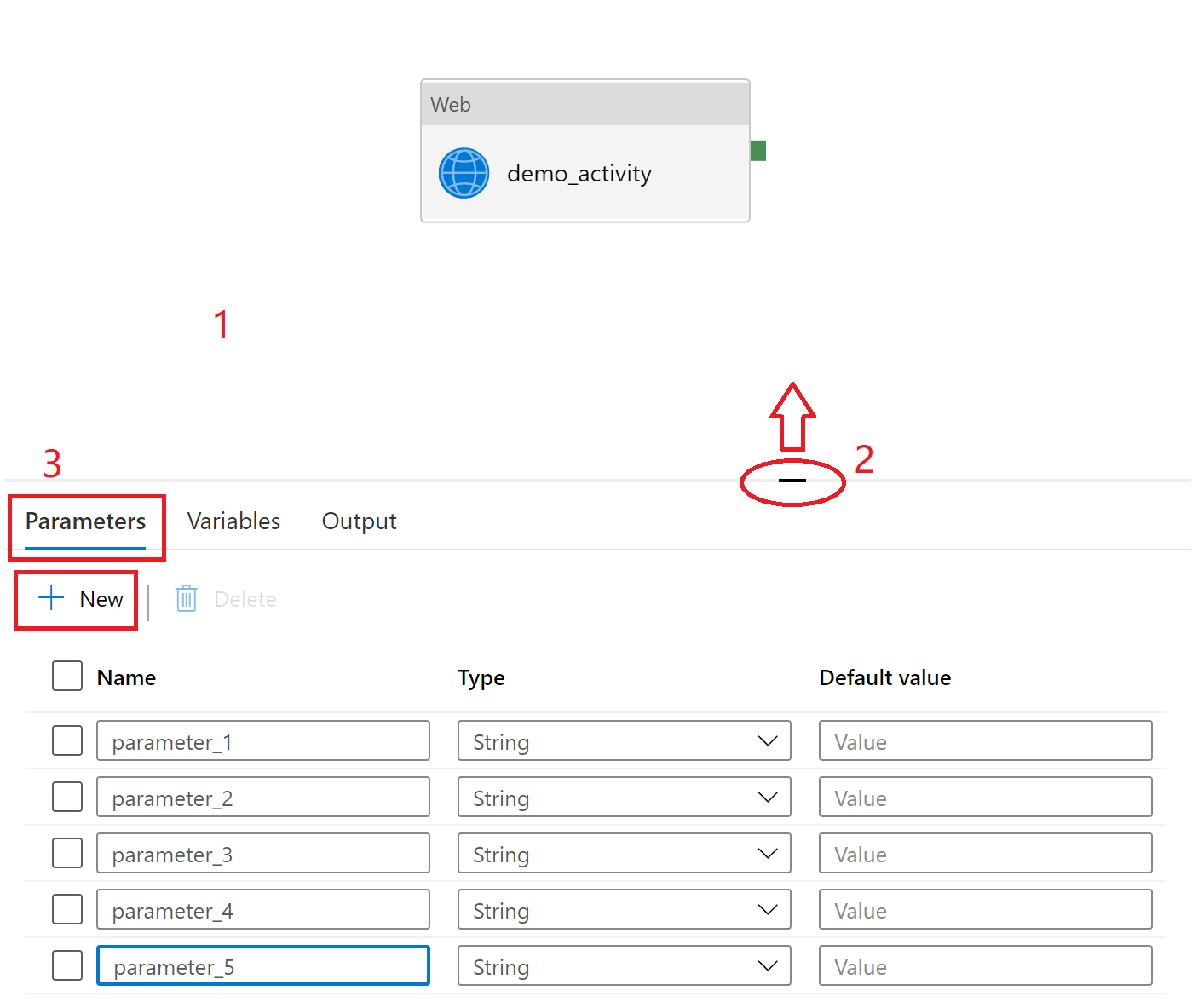
Add triggers to the pipeline by selecting + Trigger.
Create or attach a trigger to the pipeline and select OK.
After you select OK, another New trigger page appears with a list of the parameters specified for the pipeline, as shown in the following screenshot. On that page, fill in the trigger metadata for each parameter. Use the format defined in System variables to retrieve trigger information. You don't need to fill in the information for all parameters. Just fill in the ones that will assume trigger metadata values. For instance, here we assign the trigger run start time to
parameter_1.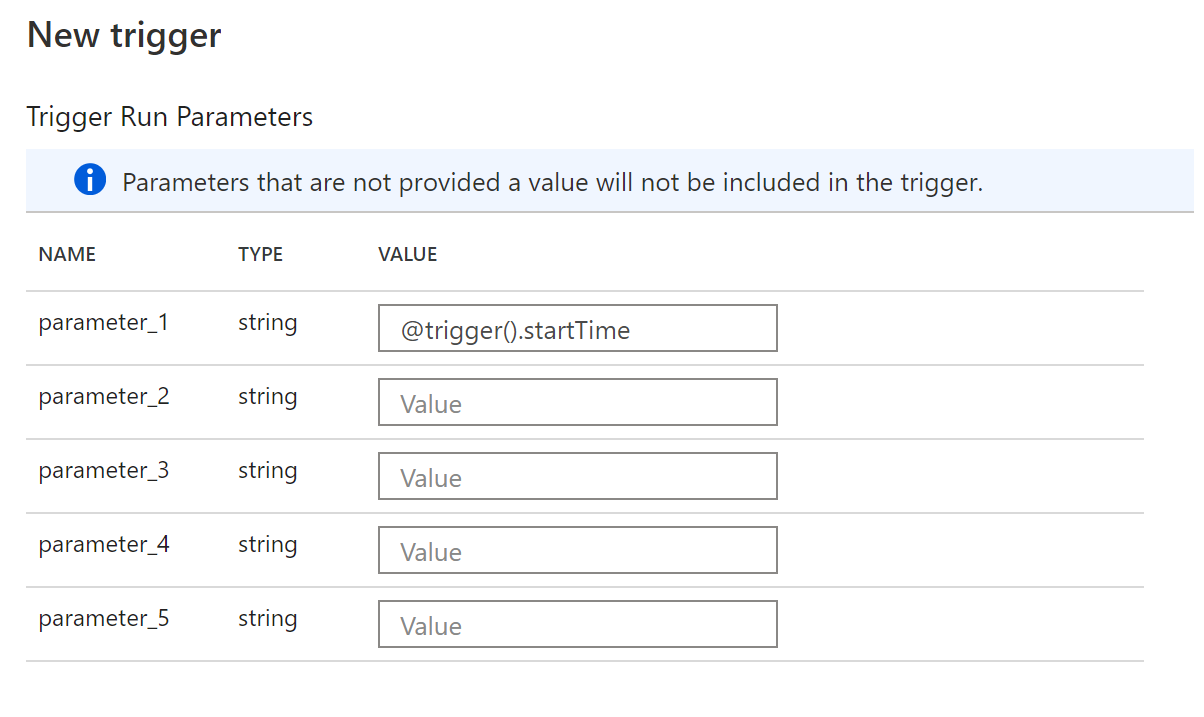
To use the values in the pipeline, utilize parameters, like
@pipeline().parameters.parameterName, not system variables, in pipeline definitions. For instance, in this case, to read the trigger start time, we reference@pipeline().parameters.parameter_1.
JSON schema
To pass in trigger information to pipeline runs, both the trigger and the pipeline JSON need to be updated with the parameters section.
Pipeline definition
Under the properties section, add parameter definitions to the parameters section.
{
"name": "demo_pipeline",
"properties": {
"activities": [
{
"name": "demo_activity",
"type": "WebActivity",
"dependsOn": [],
"policy": {
"timeout": "7.00:00:00",
"retry": 0,
"retryIntervalInSeconds": 30,
"secureOutput": false,
"secureInput": false
},
"userProperties": [],
"typeProperties": {
"url": {
"value": "@pipeline().parameters.parameter_2",
"type": "Expression"
},
"method": "GET"
}
}
],
"parameters": {
"parameter_1": {
"type": "string"
},
"parameter_2": {
"type": "string"
},
"parameter_3": {
"type": "string"
},
"parameter_4": {
"type": "string"
},
"parameter_5": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"annotations": [],
"lastPublishTime": "2021-02-24T03:06:23Z"
},
"type": "Microsoft.DataFactory/factories/pipelines"
}
Trigger definition
Under the pipelines section, assign parameter values in the parameters section. You don't need to fill in the information for all parameters. Just fill in the ones that will assume trigger metadata values.
{
"name": "trigger1",
"properties": {
"annotations": [],
"runtimeState": "Started",
"pipelines": [
{
"pipelineReference": {
"referenceName": "demo_pipeline",
"type": "PipelineReference"
},
"parameters": {
"parameter_1": "@trigger().startTime"
}
}
],
"type": "ScheduleTrigger",
"typeProperties": {
"recurrence": {
"frequency": "Minute",
"interval": 15,
"startTime": "2021-03-03T04:38:00Z",
"timeZone": "UTC"
}
}
}
}
Use trigger information in a pipeline
To use the values in a pipeline, utilize parameters, like @pipeline().parameters.parameterName, not system variables, in pipeline definitions.
Related content
For more information about triggers, see Pipeline execution and triggers.