Create a trigger that runs a pipeline on a tumbling window
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
This article provides steps to create, start, and monitor a tumbling window trigger. For general information about triggers and the supported types, see Pipeline execution and triggers.
Tumbling window triggers are a type of trigger that fires at a periodic time interval from a specified start time, while retaining state. Tumbling windows are a series of fixed-sized, nonoverlapping, and contiguous time intervals. A tumbling window trigger has a one-to-one relationship with a pipeline and can only reference a singular pipeline.
A tumbling window trigger is a more heavyweight alternative for a schedule trigger. It offers a suite of features for complex scenarios like (dependency on other tumbling window triggers, rerunning a failed job, and setting user retry for pipelines). To further understand the difference between a schedule trigger and a tumbling window trigger, see Trigger type comparison.
Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse portal experience
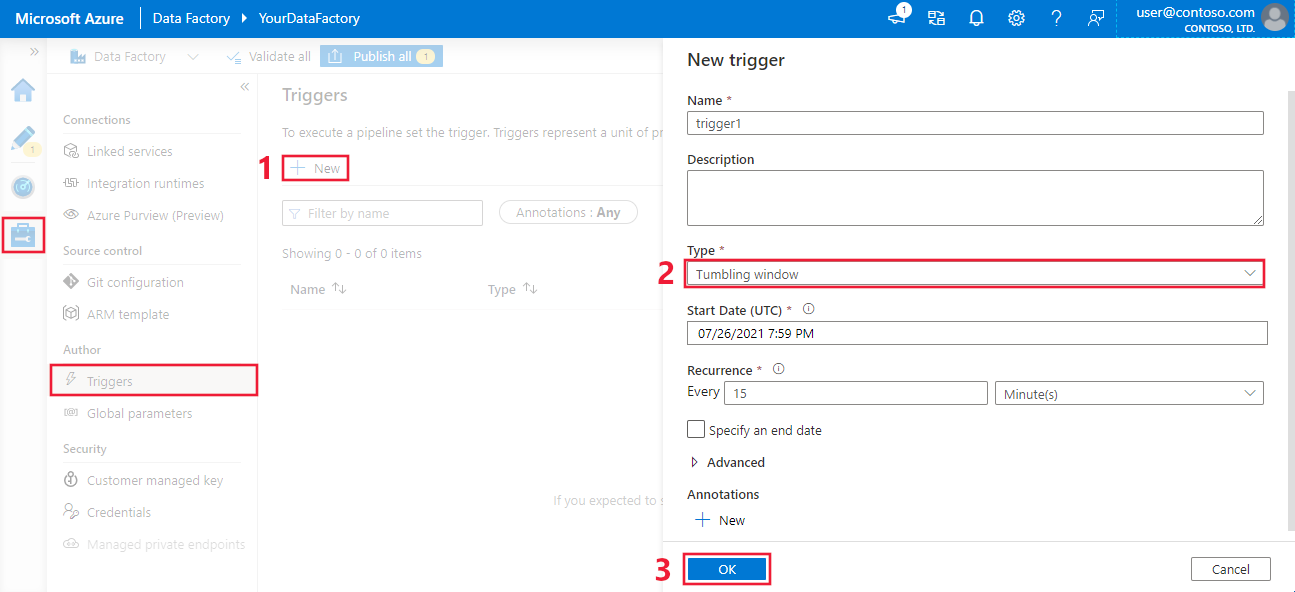
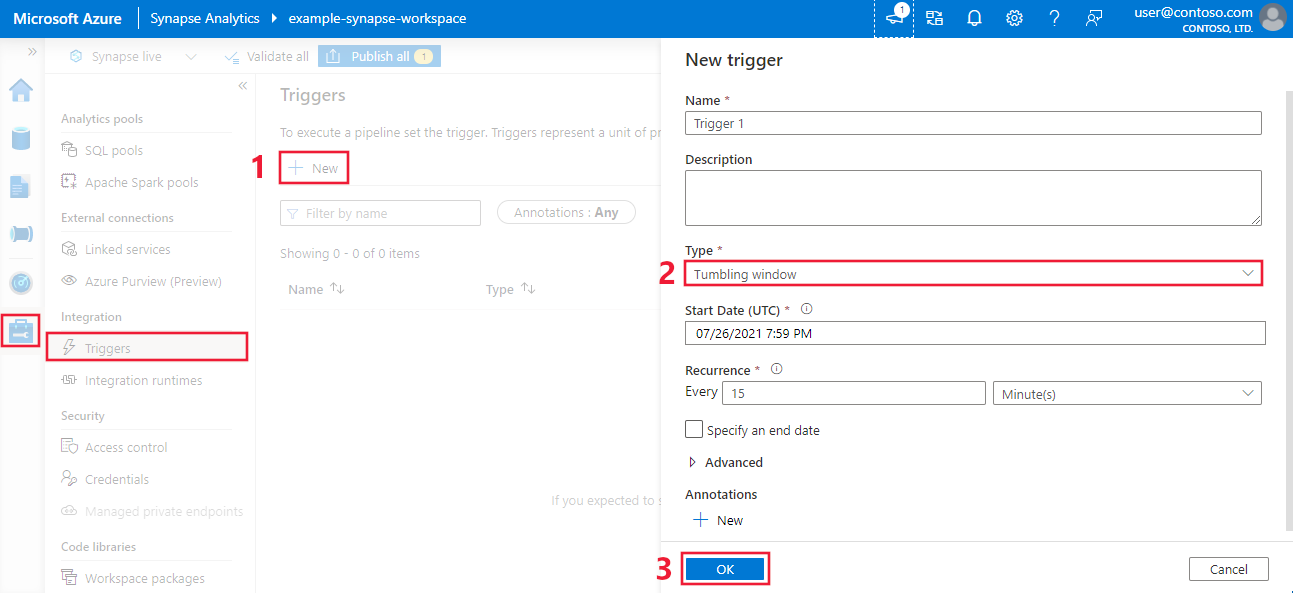
- To create a tumbling window trigger in the Azure portal, select the Triggers tab, and then select New.
- After the trigger configuration pane opens, select Tumbling window. Then define your tumbling window trigger properties.
- When you're finished, select Save.
Tumbling window trigger type properties
A tumbling window has the following trigger type properties:
{
"name": "MyTriggerName",
"properties": {
"type": "TumblingWindowTrigger",
"runtimeState": "<<Started/Stopped/Disabled - readonly>>",
"typeProperties": {
"frequency": <<Minute/Hour>>,
"interval": <<int>>,
"startTime": "<<datetime>>",
"endTime": <<datetime - optional>>,
"delay": <<timespan - optional>>,
"maxConcurrency": <<int>> (required, max allowed: 50),
"retryPolicy": {
"count": <<int - optional, default: 0>>,
"intervalInSeconds": <<int>>,
},
"dependsOn": [
{
"type": "TumblingWindowTriggerDependencyReference",
"size": <<timespan - optional>>,
"offset": <<timespan - optional>>,
"referenceTrigger": {
"referenceName": "MyTumblingWindowDependency1",
"type": "TriggerReference"
}
},
{
"type": "SelfDependencyTumblingWindowTriggerReference",
"size": <<timespan - optional>>,
"offset": <<timespan>>
}
]
},
"pipeline": {
"pipelineReference": {
"type": "PipelineReference",
"referenceName": "MyPipelineName"
},
"parameters": {
"parameter1": {
"type": "Expression",
"value": "@{concat('output',formatDateTime(trigger().outputs.windowStartTime,'-dd-MM-yyyy-HH-mm-ss-ffff'))}"
},
"parameter2": {
"type": "Expression",
"value": "@{concat('output',formatDateTime(trigger().outputs.windowEndTime,'-dd-MM-yyyy-HH-mm-ss-ffff'))}"
},
"parameter3": "https://mydemo.chinacloudsites.cn/api/demoapi"
}
}
}
}
The following table provides a high-level overview of the major JSON elements that are related to recurrence and scheduling of a tumbling window trigger.
| JSON element | Description | Type | Allowed values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
type |
The type of the trigger. The type is the fixed value TumblingWindowTrigger. |
String |
TumblingWindowTrigger |
Yes |
runtimeState |
The current state of the trigger run time. This element is <readOnly>. |
String |
Started, Stopped, Disabled |
Yes |
frequency |
A string that represents the frequency unit (minutes, hours, or months) at which the trigger recurs. If the startTime date values are more granular than the frequency value, the startTime dates are considered when the window boundaries are computed. For example, if the frequency value is hourly and the startTime value is 2017-09-01T10:10:10Z, the first window is (2017-09-01T10:10:10Z, 2017-09-01T11:10:10Z). |
String |
Minute, Hour, Month |
Yes |
interval |
A positive integer that denotes the interval for the frequency value, which determines how often the trigger runs. For example, if the interval is 3 and the frequency is hour, the trigger recurs every 3 hours. The minimum window interval is 5 minutes. |
Integer |
A positive integer. | Yes |
startTime |
The first occurrence, which can be in the past. The first trigger interval is (startTime, startTime + interval). |
DateTime |
A DateTime value. |
Yes |
endTime |
The last occurrence, which can be in the past. | DateTime |
A DateTime value. |
Yes |
delay |
The amount of time to delay the start of data processing for the window. The pipeline run is started after the expected execution time plus the amount of delay. The delay defines how long the trigger waits past the due time before triggering a new run. The delay doesn't alter the window startTime. For example, a delay value of 00:10:00 implies a delay of 10 minutes. |
Timespan(hh:mm:ss) |
A timespan value where the default is 00:00:00. |
No |
maxConcurrency |
The number of simultaneous trigger runs that are fired for windows that are ready. For example, to backfill hourly runs for yesterday results in 24 windows. If maxConcurrency = 10, trigger events are fired only for the first 10 windows (00:00-01:00 - 09:00-10:00). After the first 10 triggered pipeline runs are complete, trigger runs are fired for the next 10 windows (10:00-11:00 - 19:00-20:00). Continuing with this example of maxConcurrency = 10, if there are 10 windows ready, there are 10 total pipeline runs. If only one window is ready, only one pipeline runs. |
Integer |
An integer between 1 and 50. | Yes |
retryPolicy: Count |
The number of retries before the pipeline run is marked as Failed. |
Integer |
An integer, where the default is 0 (no retries). | No |
retryPolicy: intervalInSeconds |
The delay between retry attempts specified in seconds. | Integer |
The number of seconds, where the default is 30. The minimum value is 30. |
No |
dependsOn: type |
The type of TumblingWindowTriggerReference. Required if a dependency is set. |
String |
TumblingWindowTriggerDependencyReference, SelfDependencyTumblingWindowTriggerReference |
No |
dependsOn: size |
The size of the dependency tumbling window. | Timespan(hh:mm:ss) |
A positive timespan value where the default is the window size of the child trigger. |
No |
dependsOn: offset |
The offset of the dependency trigger. | Timespan(hh:mm:ss) |
A timespan value that must be negative in a self-dependency. If no value is specified, the window is the same as the trigger itself. |
Self-Dependency: Yes Other: No |
Note
After a tumbling window trigger is published, the interval and frequency values can't be edited.
WindowStart and WindowEnd system variables
You can use the WindowStart and WindowEnd system variables of the tumbling window trigger in your pipeline definition (that is, for part of a query). Pass the system variables as parameters to your pipeline in the trigger definition. The following example shows you how to pass these variables as parameters.
{
"name": "MyTriggerName",
"properties": {
"type": "TumblingWindowTrigger",
...
"pipeline": {
"pipelineReference": {
"type": "PipelineReference",
"referenceName": "MyPipelineName"
},
"parameters": {
"MyWindowStart": {
"type": "Expression",
"value": "@{concat('output',formatDateTime(trigger().outputs.windowStartTime,'-dd-MM-yyyy-HH-mm-ss-ffff'))}"
},
"MyWindowEnd": {
"type": "Expression",
"value": "@{concat('output',formatDateTime(trigger().outputs.windowEndTime,'-dd-MM-yyyy-HH-mm-ss-ffff'))}"
}
}
}
}
}
To use the WindowStart and WindowEnd system variable values in the pipeline definition, use your MyWindowStart and MyWindowEnd parameters, accordingly.
Execution order of windows in a backfill scenario
If the trigger startTime is in the past, then based on the formula M=(CurrentTime- TriggerStartTime)/TumblingWindowSize, the trigger generates {M} backfill(past) runs in parallel, honoring trigger concurrency, before executing the future runs. The order of execution for windows is deterministic, from oldest to newest intervals. Currently, this behavior can't be modified.
Note
In this scenario, all runs from the selected startTime are run before executing future runs. If you need to backfill a long period of time, we recommend doing an initial historical load.
Existing TriggerResource elements
The following points apply to updating existing TriggerResource elements:
- The value for the
frequencyelement (or window size) of the trigger along with theintervalelement can't be changed after the trigger is created. This restriction is required for proper functioning oftriggerRunreruns and dependency evaluations. - If the value for the
endTimeelement of the trigger changes (by adding or updating), the state of the windows that are already processed is not reset. The trigger honors the newendTimevalue. If the newendTimevalue is before the windows that are already executed, the trigger stops. Otherwise, the trigger stops when the newendTimevalue is encountered.
User-assigned retries of pipelines
In the case of pipeline failures, a tumbling window trigger can retry the execution of the referenced pipeline automatically by using the same input parameters, without user intervention. Use the retryPolicy property in the trigger definition to specify this action.
Tumbling window trigger dependency
If you want to make sure that a tumbling window trigger is executed only after the successful execution of another tumbling window trigger in the data factory, create a tumbling window trigger dependency.
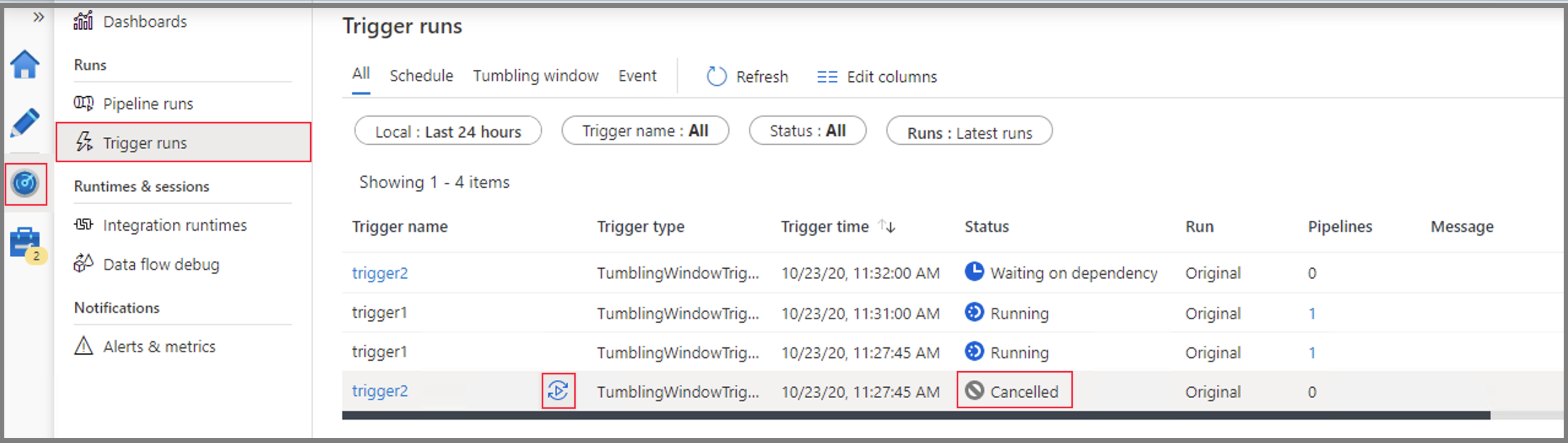
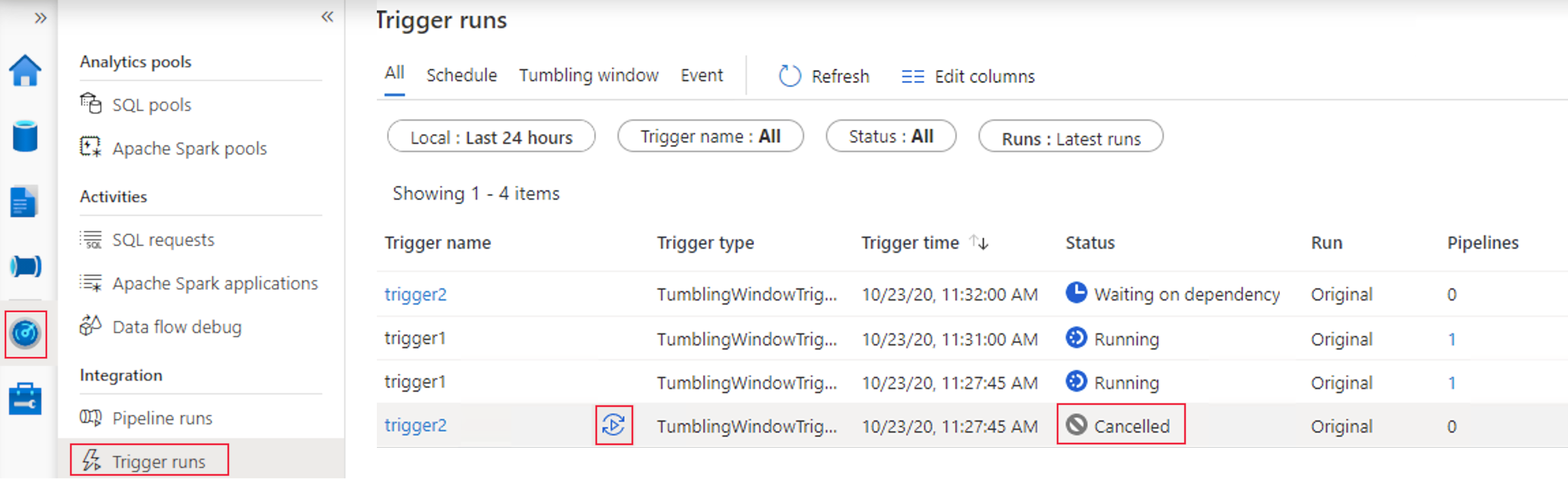
Cancel a tumbling window run
You can cancel runs for a tumbling window trigger if the specific window is in a Waiting, Waiting on dependency, or Running state:
- If the window is in a Running state, cancel the associated Pipeline Run, and the trigger run is marked as Canceled afterwards.
- If the window is in a Waiting or Waiting on dependency state, you can cancel the window from Monitoring.
You can also rerun a canceled window. The rerun takes the latest published definitions of the trigger. Dependencies for the specified window are reevaluated upon rerun.
Sample for Azure PowerShell and the Azure CLI
This section shows you how to use Azure PowerShell to create, start, and monitor a trigger.
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. See Install Azure PowerShell to get started. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial account before you begin.
- Azure PowerShell. Follow the instructions in Install Azure PowerShell on Windows with PowerShellGet.
- Azure Data Factory: Follow the instructions in Create an Azure Data Factory by using PowerShell to create a data factory and a pipeline.
Sample code
Create a JSON file named MyTrigger.json in the C:\ADFv2QuickStartPSH\ folder with the following content:
Important
Before you save the JSON file, set the value of the
startTimeelement to the current Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) time. Set the value of theendTimeelement to one hour past the current UTC time.{ "name": "PerfTWTrigger", "properties": { "type": "TumblingWindowTrigger", "typeProperties": { "frequency": "Minute", "interval": "15", "startTime": "2017-09-08T05:30:00Z", "endTime" : "2017-09-08T06:30:00Z", "delay": "00:00:01", "retryPolicy": { "count": 2, "intervalInSeconds": 30 }, "maxConcurrency": 50 }, "pipeline": { "pipelineReference": { "type": "PipelineReference", "referenceName": "DynamicsToBlobPerfPipeline" }, "parameters": { "windowStart": "@trigger().outputs.windowStartTime", "windowEnd": "@trigger().outputs.windowEndTime" } }, "runtimeState": "Started" } }Create a trigger by using the Set-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger cmdlet:
Set-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -DataFactoryName $DataFactoryName -Name "MyTrigger" -DefinitionFile "C:\ADFv2QuickStartPSH\MyTrigger.json"Confirm that the status of the trigger is Stopped by using the Get-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger cmdlet:
Get-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -DataFactoryName $DataFactoryName -Name "MyTrigger"Start the trigger by using the Start-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger cmdlet:
Start-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -DataFactoryName $DataFactoryName -Name "MyTrigger"Confirm that the status of the trigger is Started by using the Get-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger cmdlet:
Get-AzDataFactoryV2Trigger -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -DataFactoryName $DataFactoryName -Name "MyTrigger"Get the trigger runs in Azure PowerShell by using the Get-AzDataFactoryV2TriggerRun cmdlet. To get information about the trigger runs, execute the following command periodically. Update the
TriggerRunStartedAfterandTriggerRunStartedBeforevalues to match the values in your trigger definition:Get-AzDataFactoryV2TriggerRun -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -DataFactoryName $DataFactoryName -TriggerName "MyTrigger" -TriggerRunStartedAfter "2017-12-08T00:00:00" -TriggerRunStartedBefore "2017-12-08T01:00:00"
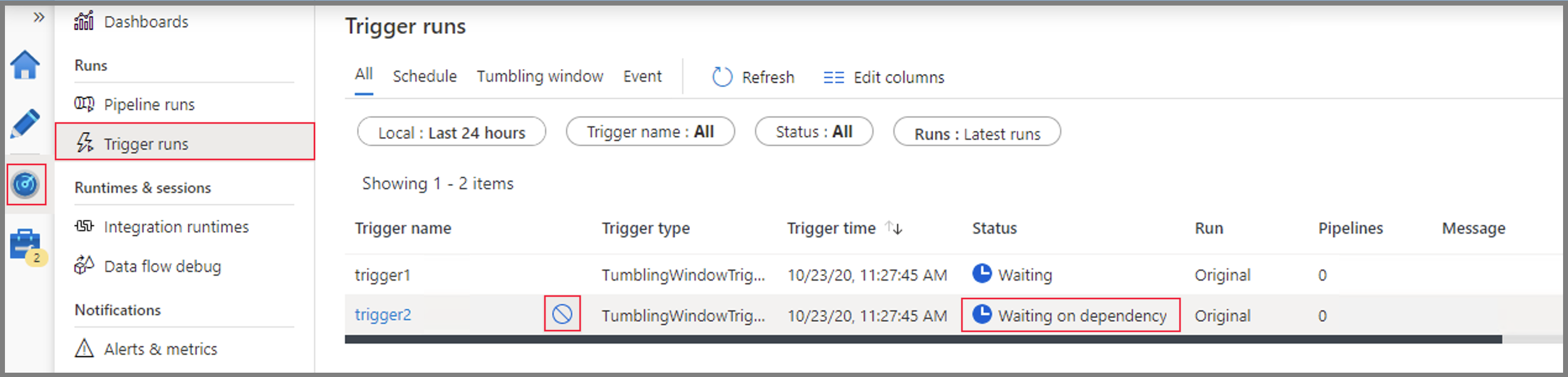
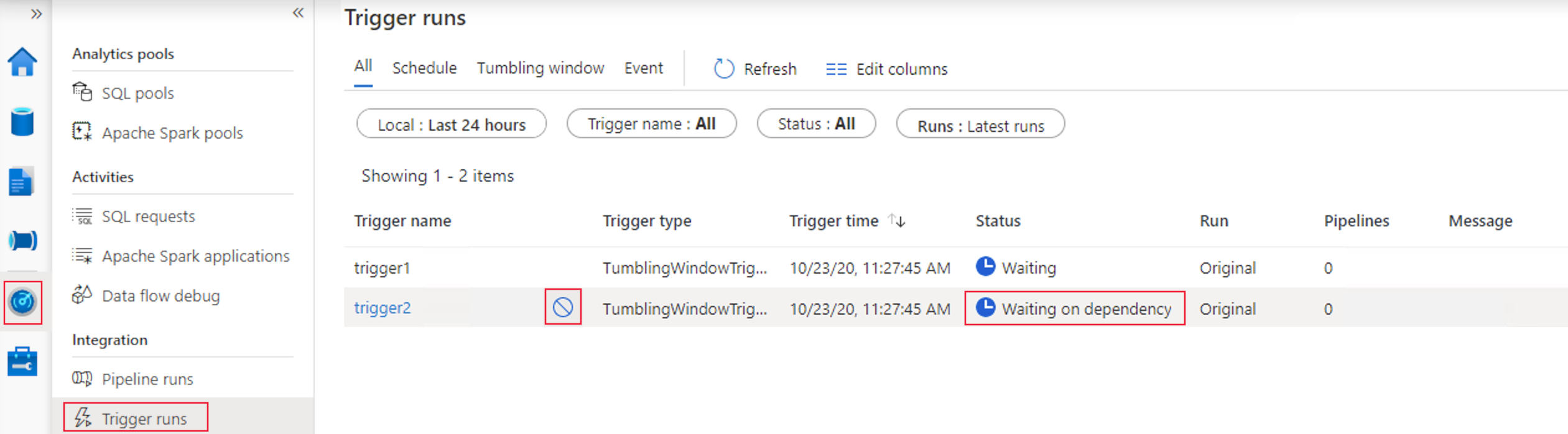
To monitor trigger runs and pipeline runs in the Azure portal, see Monitor pipeline runs.