教程:使用适用于 NoSQL 的 Azure Cosmos DB 开发 .NET 控制台应用程序
适用范围: NoSQL
使用 Azure SDK for .NET,你可以通过异步单个操作或事务批处理的方式向 API for NoSQL 容器添加数据。 本教程逐步讲解如何创建一个可将多个项添加到容器的新 .NET 控制台应用程序。
本教程介绍如何执行下列操作:
- 使用 API for NoSQL 创建数据库
- 创建 .NET 控制台应用程序并添加用于 .NET 的 Azure SDK
- 将单个项添加到 API for NoSQL 容器
- 从 API for NoSQL 容器中有效检索项
- 为 API for NoSQL 容器创建包含批处理更改的事务
先决条件
- 一个现有的适用于 NoSQL 的 Azure Cosmos DB 帐户。
- Visual Studio Code
- .NET 8 或更高版本
- 有编写 C# 应用程序的经验。
创建 API for NoSQL 资源
首先,在现有的 API for NoSQL 帐户中创建一个空数据库。 稍后使用用于 .NET 的 Azure SDK 创建容器。
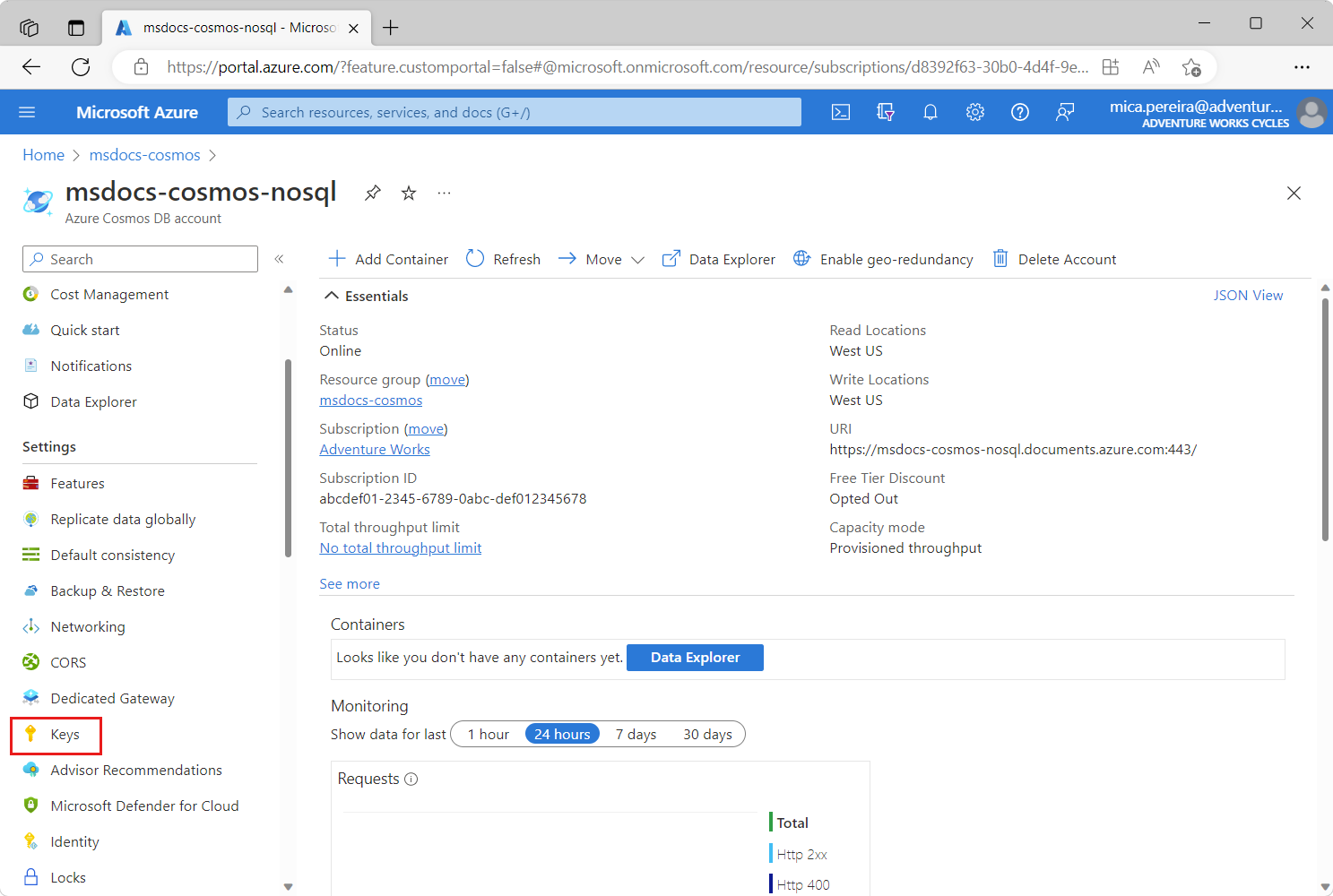
在 Azure 门户中导航到现有的 API for NoSQL 帐户。
在资源菜单中选择“密钥”。
在“密钥”页上,找到并记下“URI”和“主密钥”字段的值。 这些值会在整个教程中使用。
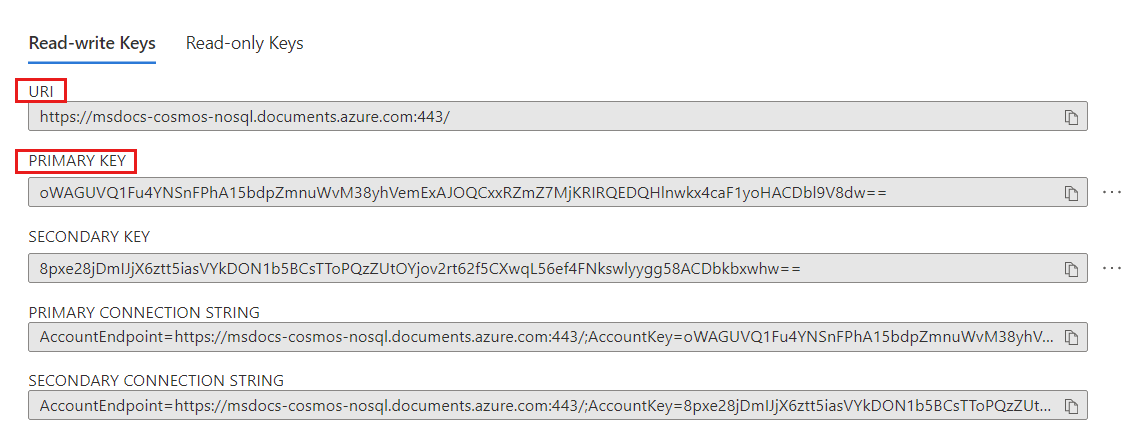
在资源菜单中,选择“数据资源管理器”。
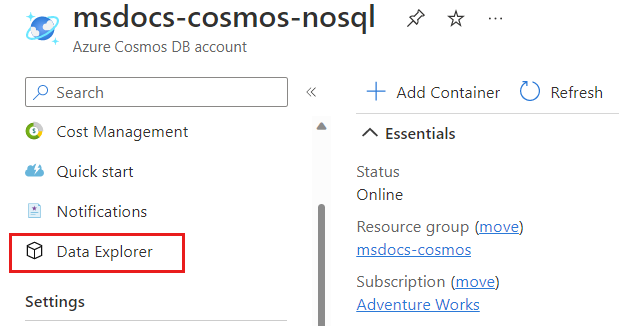
在“数据资源管理器”页上,选择命令栏中的“新建数据库”选项。
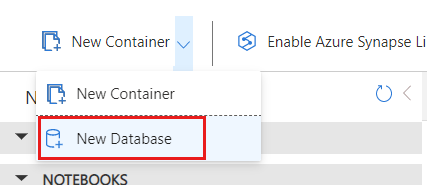
在“新建数据库”对话框中,使用以下设置创建新容器:
值 数据库 ID cosmicworks数据库吞吐量类型 手动 数据库吞吐量 400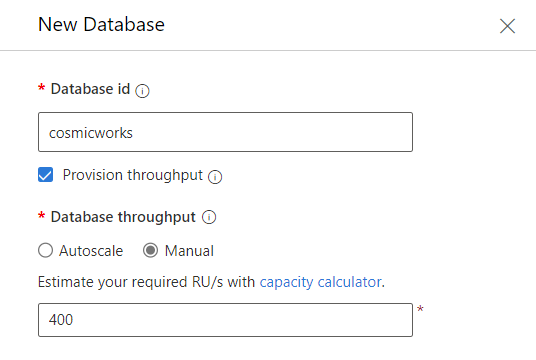
选择“确定”以创建数据库。
创建 .NET 控制台应用程序
现在,请创建一个新的 .NET 控制台应用程序,并从 NuGet 使用 Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos 库导入用于 .NET 的 Azure SDK。
在空目录中打开终端。
使用
console内置模板创建新的控制台应用程序dotnet new console --langVersion preview从 NuGet 添加 3.31.1-preview 版本的
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos包。dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos --version 3.31.1-preview另外,从 NuGet 添加 pre-release 版本的
System.CommandLine包。dotnet add package System.CommandLine --prerelease另外,从 NuGet 添加
Humanizer包。dotnet add package Humanizer生成控制台应用程序项目。
dotnet build使用当前项目文件夹作为工作区打开 Visual Studio Code。
提示
可以在终端中运行
code .,以打开 Visual Studio Code 并自动打开作为当前工作区的工作目录。导航到 Program.cs 文件并将其打开。 删除该文件中的所有现有代码。
将以下代码添加到该文件,以使用 System.CommandLine 库来分析命令行中通过
--first和--last选项传入的两个字符串。using System.CommandLine; var command = new RootCommand(); var nameOption = new Option<string>("--name") { IsRequired = true }; var emailOption = new Option<string>("--email"); var stateOption = new Option<string>("--state") { IsRequired = true }; var countryOption = new Option<string>("--country") { IsRequired = true }; command.AddOption(nameOption); command.AddOption(emailOption); command.AddOption(stateOption); command.AddOption(countryOption); command.SetHandler( handle: CosmosHandler.ManageCustomerAsync, nameOption, emailOption, stateOption, countryOption ); await command.InvokeAsync(args);注意
对于本教程,你是否了解命令行分析程序的工作原理并不十分重要。 运行应用程序时,可为分析程序指定四个选项。 其中三个选项是必需的,因为它们用于构造 ID 和分区键字段。
由于你尚未定义静态
CosmosHandler.ManageCustomerAsync方法,因此项目此时不会生成。保存 Program.cs 文件。
使用 SDK 将项添加到容器
接下来,请使用单独的操作将项添加到 API for NoSQL 容器中。 在本部分,请定义 CosmosHandler.ManageCustomerAsync 方法。
创建新的 CosmosHandler.cs 文件。
在 CosmosHandler.cs 文件中,为
Humanizer和Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos命名空间添加新的 using 指令。using Humanizer; using Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos;创建名为
CosmosHandler的新静态类。public static class CosmosHandler { }创建静态
ManageCustomerAsync方法的简短实现以输出命令行输入,目的只是为了验证此应用是否正常工作。public static async Task ManageCustomerAsync(string name, string email, string state, string country) { await Console.Out.WriteLineAsync($"Hello {name} of {state}, {country}!"); }保存 CosmosHandler.cs 文件。
回到终端并运行应用程序。
dotnet run -- --name 'Mica Pereira' --state 'Washington' --country 'United States'命令的输出应是一段有趣的问候。
Hello Mica Pereira of Washington, United States!返回到 CosmosHandler.cs 文件。
在静态 CosmosHandler 类中,添加一个名为
_client、类型为CosmosClient的新private static readonly成员。private static readonly CosmosClient _client;为
CosmosHandler类创建新的静态构造函数。static CosmosHandler() { }在该构造函数中,创建
CosmosClient类的新实例并传入两个字符串参数,其中包含前面你在实验中记下的“URI”和“主密钥”值。 将此新实例存储在_client成员中。static CosmosHandler() { _client = new CosmosClient( accountEndpoint: "<uri>", authKeyOrResourceToken: "<primary-key>" ); }回到静态 CosmosHandler 类,创建一个名为
GetContainerAsync的新异步方法,该方法返回Container。private static async Task<Container> GetContainerAsync() { }对于后续步骤,请在
GetContainerAsync方法中添加此代码。获取
cosmicworks数据库并将其存储在名为database的变量中。Database database = _client.GetDatabase("cosmicworks");在分层分区键路径列表中创建
string值的新泛型List<>,并将其存储在名为keyPaths的变量中。List<string> keyPaths = new() { "/address/country", "/address/state" };使用容器名称 (
customers) 和分区键路径列表创建新的ContainerProperties变量。ContainerProperties properties = new( id: "customers", partitionKeyPaths: keyPaths );使用
CreateContainerIfNotExistsAsync方法提供容器属性并检索容器。 如果数据库中尚不存在该容器,则此方法将根据名称以异步方式创建该容器。 返回结果,即GetContainerAsync方法的输出。return await database.CreateContainerIfNotExistsAsync( containerProperties: properties );
删除
ManageCustomerAsync方法中的所有代码。对于后续步骤,请在
ManageCustomerAsync方法中添加此代码。以异步方式调用
GetContainerAsync方法并将结果存储在名为container的变量中。Container container = await GetContainerAsync();创建一个名为
id的新变量,该变量使用 Humanizer 中的Kebaberize方法来转换name方法参数。string id = name.Kebaberize();注意
Kebaberize方法会将所有空格替换为连字符,并将文本转换为小写。使用
name、state和country方法参数以及id变量创建一个新的匿名类型项。 将该项存储为名为customer的变量。var customer = new { id = id, name = name, address = new { state = state, country = country } };使用容器的异步
CreateItemAsync方法在容器中创建一个新项,并将 HTTP 响应元数据分配到名为response的变量。var response = await container.CreateItemAsync(customer);将
response变量的StatusCode和RequestCharge属性值写入控制台。 另外,写入id变量的值。Console.WriteLine($"[{response.StatusCode}]\t{id}\t{response.RequestCharge} RUs");
保存 CosmosHandler.cs 文件。
回到终端并再次运行应用程序。
dotnet run -- --name 'Mica Pereira' --state 'Washington' --country 'United States'命令的输出应包含操作的状态和请求费用。
[Created] mica-pereira 7.05 RUs注意
你的请求费用可能与此不同。
再次运行应用程序。
dotnet run -- --name 'Mica Pereira' --state 'Washington' --country 'United States'这一次,程序应会崩溃。 如果你滚动浏览错误消息的话,则会看到崩溃原因是项的唯一标识符有冲突。
Unhandled exception: Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.CosmosException : Response status code does not indicate success: Conflict (409);Reason: ( Errors : [ "Resource with specified id or name already exists." ] );
使用 SDK 检索项
在容器中创建第一个项后,可以使用相同的 SDK 来检索该项。 在此处,你将查询该项并对其进行点读取,以比较请求单位 (RU) 消耗量的差异。
返回到 CosmosHandler.cs 文件或将其打开。
从
ManageCustomerAsync方法中删除除前两行之外的所有代码行。public static async Task ManageCustomerAsync(string name, string email, string state, string country) { Container container = await GetContainerAsync(); string id = name.Kebaberize(); }对于后续步骤,请在
ManageCustomerAsync方法中添加此代码。使用容器的异步
CreateItemAsync方法在容器中创建一个新项,并将 HTTP 响应元数据分配到名为response的变量。var response = await container.CreateItemAsync(customer);使用 SQL 查询创建名为
sql的新字符串,以检索筛选器 (@id) 匹配的项。string sql = @" SELECT * FROM customers c WHERE c.id = @id ";创建名为
query的新QueryDefinition变量,并传入sql字符串作为唯一一个查询参数。 另外,使用WithParameterfluid 方法将变量id的值应用于@id参数。var query = new QueryDefinition( query: sql ) .WithParameter("@id", id);使用
GetItemQueryIterator<>泛型方法和query变量创建从 Azure Cosmos DB 获取数据的迭代器。 将该迭代器存储在名为feed的变量中。 将整个表达式包装在 using 语句中,以便稍后释放该迭代器。using var feed = container.GetItemQueryIterator<dynamic>( queryDefinition: query );以异步方式调用
feed变量的ReadNextAsync方法并将结果存储在名为response的变量中。var response = await feed.ReadNextAsync();将
response变量的StatusCode和RequestCharge属性值写入控制台。 另外,写入id变量的值。Console.WriteLine($"[{response.StatusCode}]\t{id}\t{response.RequestCharge} RUs");
保存 CosmosHandler.cs 文件。
回到终端,运行应用程序以使用 SQL 查询读取单个项。
dotnet run -- --name 'Mica Pereira' --state 'Shanghai' --country 'China'命令的输出应指示查询需要多个请求单位 (RU)。
[OK] mica-pereira 2.82 RUs回到 CosmosHandler.cs 文件,再次从
ManageCustomerAsync方法中删除除前两行之外的所有代码行。public static async Task ManageCustomerAsync(string name, string email, string state, string country) { Container container = await GetContainerAsync(); string id = name.Kebaberize(); }对于后续步骤,请在
ManageCustomerAsync方法中添加此代码。通过将
state和country参数添加为多部分分区键值来创建PartitionKeyBuilder的新实例。var partitionKey = new PartitionKeyBuilder() .Add(country) .Add(state) .Build();使用容器的
ReadItemAsync<>方法通过id和partitionKey变量对容器中的项进行点读取。 将结果保存在名为response的变量中。var response = await container.ReadItemAsync<dynamic>( id: id, partitionKey: partitionKey );将
response变量的StatusCode和RequestCharge属性值写入控制台。 另外,写入id变量的值。Console.WriteLine($"[{response.StatusCode}]\t{id}\t{response.RequestCharge} RU");
再次保存 CosmosHandler.cs 文件。
回到终端,再次运行应用程序以便对单个项进行点读取。
dotnet run -- --name 'Mica Pereira' --state 'Washington' --country 'United States'命令的输出应指示查询需要单个 RU。
[OK] mica-pereira 1 RUs
使用 SDK 创建事务
最后,你获取创建的项,读取该项,并使用用于 .NET 的 Azure SDK 创建另一个相关项作为单个事务的一部分。
返回到 CosmosHandler.cs 文件或将其打开。
从
ManageCustomerAsync方法中删除以下代码行。var response = await container.ReadItemAsync<dynamic>( id: id, partitionKey: partitionKey ); Console.WriteLine($"[{response.StatusCode}]\t{id}\t{response.RequestCharge} RUs");对于后续步骤,请在
ManageCustomerAsync方法中添加此新代码。使用
name、state和country方法参数以及id变量创建一个新的匿名类型项。 将该项存储为名为customerCart的变量。 此项代表客户的实时购物车,它当前是空的。var customerCart = new { id = $"{Guid.NewGuid()}", customerId = id, items = new string[] {}, address = new { state = state, country = country } };使用
name、state和country方法参数以及id变量创建另一个新的匿名类型项。 将该项存储为名为customerCart的变量。 此项代表客户的发货和联系信息。var customerContactInfo = new { id = $"{id}-contact", customerId = id, email = email, location = $"{state}, {country}", address = new { state = state, country = country } };使用容器的
CreateTransactionalBatch方法并传入partitionKey变量来创建一个新的批处理。 将该批处理存储在名为batch的变量中。 使用 fluent 方法执行以下操作:方法 参数 ReadItemid字符串变量CreateItemcustomerCart匿名类型变量CreateItemcustomerContactInfo匿名类型变量var batch = container.CreateTransactionalBatch(partitionKey) .ReadItem(id) .CreateItem(customerCart) .CreateItem(customerContactInfo);使用批处理的
ExecuteAsync方法启动事务。 将结果保存在名为response的变量中。using var response = await batch.ExecuteAsync();将
response变量的StatusCode和RequestCharge属性值写入控制台。 另外,写入id变量的值。Console.WriteLine($"[{response.StatusCode}]\t{response.RequestCharge} RUs");
再次保存 CosmosHandler.cs 文件。
回到终端,再次运行应用程序以便对单个项进行点读取。
dotnet run -- --name 'Mica Pereira' --state 'Washington' --country 'United States'命令的输出应显示整个事务使用的请求单位数。
[OK] 16.05 RUs注意
你的请求费用可能与此不同。
验证数据资源管理器中的最终数据
最后,使用 Azure 门户中的数据资源管理器来查看你在本教程中创建的数据和容器。
在 Azure 门户中导航到现有的 API for NoSQL 帐户。
在资源菜单中,选择“数据资源管理器”。

在“数据资源管理器”页上展开
cosmicworks数据库,然后选择customers容器。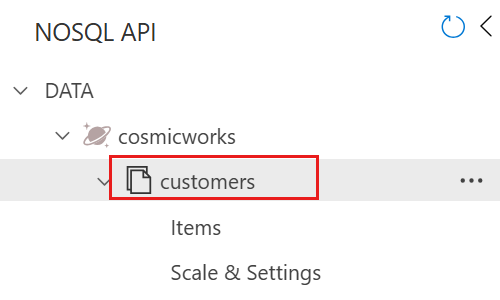
在命令栏中,选择“新建 SQL 查询”。
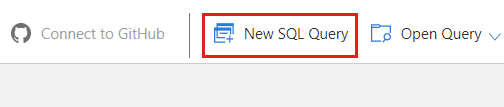
在查询编辑器中找到以下 SQL 查询字符串。
SELECT * FROM c选择“执行查询”以运行该查询并观察结果。
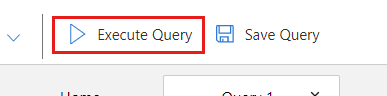
结果应包含一个 JSON 数组,其中包含本教程中创建的三个项。 可以看到,所有项具有相同的分层分区键值,但 ID 字段值是唯一的。 为简洁起见,包含的示例输出已截断。
[ { "id": "mica-pereira", "name": "Mica Pereira", "address": { "state": "Washington", "country": "United States" }, ... }, { "id": "33d03318-6302-4559-b5c0-f3cc643b2f38", "customerId": "mica-pereira", "items": [], "address": { "state": "Washington", "country": "United States" }, ... }, { "id": "mica-pereira-contact", "customerId": "mica-pereira", "email": null, "location": "Washington, United States", "address": { "state": "Washington", "country": "United States" }, ... } ]
清理资源
今后不再需要本教程中使用的数据库时,请将其删除。 为此,请导航到帐户页,选择“数据资源管理器”,选择 cosmicworks 数据库,然后选择“删除”。