Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In IoT Hub, under each device identity, you can create up to 50 module identities. Each module identity implicitly generates a module twin. Similar to device twins, module twins are JSON documents that store module state information including metadata, configurations, and conditions. Azure IoT Hub maintains a module twin for each module that you connect to IoT Hub.
This article assumes that you read Understand and use device twins in IoT Hub first.
On the device side, the IoT Hub device software development kits (SDKs) enable you to create modules where each one opens an independent connection to IoT Hub. This functionality enables you to use separate namespaces for different components on your device. For example, you have a vending machine that has three different sensors. Different departments in your company control each sensor. You can create a module for each sensor so that a department is only able to send jobs or direct methods to the sensor that they control, avoiding conflicts and user errors.
Module identity and module twin provide the same capabilities as device identity and device twin but at a finer granularity. This finer granularity enables capable devices, such as operating system-based devices or firmware devices managing multiple components, to isolate configuration and conditions for each of those components. Module identity and module twins provide a management separation of concerns when working with IoT devices that have modular software components. We aim at supporting all the device twin functionality at module twin level by module twin general availability.
Note
The features described in this article are available only in the standard tier of IoT Hub. For more information about the basic and standard/free IoT Hub tiers, see Choose the right IoT Hub tier for your solution.
This article describes:
- The structure of the module twin: tags, desired and reported properties.
- The operations that the modules and back ends can perform on module twins.
Refer to Device-to-cloud communication guidance for guidance on using reported properties, device-to-cloud messages, or file upload.
Refer to Cloud-to-device communication guidance for guidance on using desired properties, direct methods, or cloud-to-device messages.
Module twins
Module twins store module-related information that:
Modules on the device and IoT Hub can use to synchronize module conditions and configuration.
The solution back end can use to query and target long-running operations.
The lifecycle of a module twin is linked to the corresponding module identity. Modules twins are implicitly created and deleted when a module identity is created or deleted in IoT Hub.
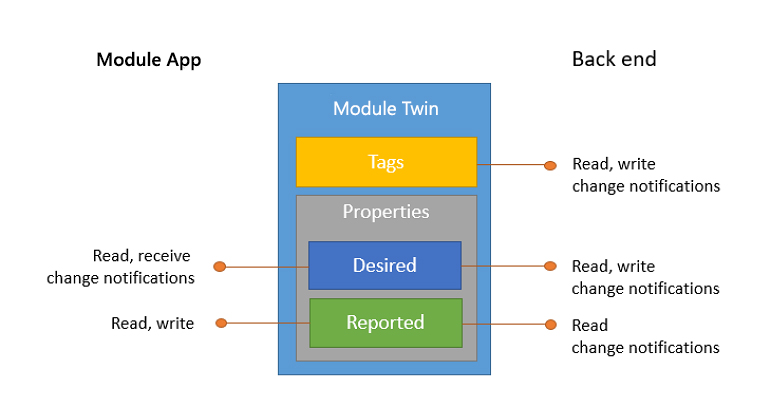
A module twin is a JSON document that includes:
Tags. A section of the JSON document that back-end apps can read from and write to. Tags aren't visible to modules on the device. Tags are set for querying purpose.
Desired properties. Used along with reported properties to synchronize module configuration or conditions. Back-end apps can set desired properties, and the module app can read them. The module app can also receive notifications of changes in the desired properties.
Reported properties. Used along with desired properties to synchronize module configuration or conditions. The module app can set reported properties, and back-end apps can read and query them.
Module identity properties. The root of the module twin JSON document contains the read-only properties from the corresponding module identity stored in the identity registry.
The following example shows a module twin JSON document:
{
"deviceId": "devA",
"moduleId": "moduleA",
"etag": "AAAAAAAAAAc=",
"status": "enabled",
"statusReason": "provisioned",
"statusUpdateTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00",
"connectionState": "connected",
"lastActivityTime": "2015-02-30T16:24:48.789Z",
"cloudToDeviceMessageCount": 0,
"authenticationType": "sas",
"x509Thumbprint": {
"primaryThumbprint": null,
"secondaryThumbprint": null
},
"version": 2,
"tags": {
"deploymentLocation": {
"building": "43",
"floor": "1"
}
},
"properties": {
"desired": {
"telemetryConfig": {
"sendFrequency": "5m"
},
"$metadata" : {...},
"$version": 1
},
"reported": {
"telemetryConfig": {
"sendFrequency": "5m",
"status": "success"
},
"batteryLevel": 55,
"$metadata" : {...},
"$version": 4
}
}
}
At the top level, a module twin object contains the module identity properties and container objects for tags and both reported and desired properties. The properties container contains some read-only elements ($metadata and $version) described in the Module twin metadata and Optimistic concurrency sections.
Reported property example
In the previous example, the module twin contains a batteryLevel reported property. This property makes it possible to query and operate on modules based on the last reported battery level. Other examples include the module app reporting module capabilities or connectivity options.
Note
Reported properties simplify scenarios where you're interested in the last known value of a property. Use device-to-cloud messages if you want to process module telemetry in sequences of timestamped events, such as time series.
Desired property example
In the previous example, the telemetryConfig module twin desired and reported properties are used by the back-end apps and the module app to synchronize the telemetry configuration for this module. For example:
A back-end app sets the desired property with the desired configuration value. Here's the portion of the document with the desired property set:
... "desired": { "telemetryConfig": { "sendFrequency": "5m" }, ... }, ...The module app is notified of the change immediately if the module is connected. If it's not connected, the module app follows the module reconnection flow when it connects. The module app then reports the updated configuration (or an error condition using the
statusproperty). Here's the portion of the reported properties:"reported": { "telemetryConfig": { "sendFrequency": "5m", "status": "success" } ... }A back-end app can track the results of the configuration operation across many modules, by querying module twins.
Note
The preceding snippets are examples, optimized for readability, of one way to encode a module configuration and its status. IoT Hub does not impose a specific schema for the module twin desired and reported properties in the module twins.
Back-end operations
Back-end apps operate on the module twin using the following atomic operations, exposed through HTTPS:
Retrieve module twin by ID. This operation returns the module twin document, including tags and desired and reported system properties.
Partially update module twin. This operation partially updates the tags or desired properties in a module twin. The partial update is expressed as a JSON document that adds or updates any property. Properties set to
nullare removed. The following example creates a new desired property with value{"newProperty": "newValue"}, overwrites the existing value ofexistingPropertywith"otherNewValue", and removesotherOldProperty. No other changes are made to existing desired properties or tags:{ "properties": { "desired": { "newProperty": { "nestedProperty": "newValue" }, "existingProperty": "otherNewValue", "otherOldProperty": null } } }Replace desired properties. This operation completely overwrites all existing desired properties and substitutes a new JSON document for
properties/desired.Replace tags. This operation completely overwrites all existing tags and substitutes a new JSON document for
tags.Receive twin notifications. This operation notifies when the twin is modified. To receive module twin change notifications, your IoT solution needs to create a route and to set the Data Source equal to twinChangeEvents. By default, no such route exists, so no twin notifications are sent. If the rate of change is too high, or for other reasons such as internal failures, the IoT Hub might send only one notification that contains all changes. Therefore, if your application needs reliable auditing and logging of all intermediate states, you should use device-to-cloud messages. To learn more about the properties and body returned in the twin notification message, see Non-telemetry event schemas.
All the preceding operations support Optimistic concurrency and require the ServiceConnect permission, as defined in the Control Access to IoT Hub article.
In addition to these operations, back-end apps can query the module twins using the SQL-like IoT Hub query language.
Module operations
The module app operates on the module twin using the following atomic operations:
Retrieve module twin. This operation returns the module twin document (including desired and reported system properties) for the currently connected module.
Partially update reported properties. This operation enables the partial update of the reported properties of the currently connected module.
Observe desired properties. The currently connected module can choose to be notified of updates to the desired properties when they happen.
All the preceding operations require the DeviceConnect permission, as defined in the Control Access to IoT Hub article.
The Azure IoT device SDKs make it easy to use the preceding operations from many languages and platforms.
Tags and properties format
Tags, desired properties, and reported properties are JSON objects with the following restrictions:
Keys: All keys in JSON objects are UTF-8 encoded, case-sensitive, and up-to 1 KB in length. Allowed characters exclude UNICODE control characters (segments C0 and C1), and
.,$, and SP.Values: All values in JSON objects can be of the following JSON types: boolean, number, string, object. Arrays are also supported.
Integers can have a minimum value of -4503599627370496 and a maximum value of 4503599627370495.
String values are UTF-8 encoded and can have a maximum length of 4 KB.
Depth: The maximum depth of JSON objects in tags, desired properties, and reported properties is 10. For example, the following object is valid:
{ ... "tags": { "one": { "two": { "three": { "four": { "five": { "six": { "seven": { "eight": { "nine": { "ten": { "property": "value" } } } } } } } } } } }, ... }
Module twin size
IoT Hub enforces an 8-KB size limit on the value of tags, and a 32-KB size limit each on the value of properties/desired and properties/reported. These totals are exclusive of read-only elements like $version and $metadata/$lastUpdated.
Twin size is computed as follows:
IoT Hub cumulatively computes and adds the length of each property's key and value.
Property keys are considered as UTF8-encoded strings.
Simple property values are considered as UTF8-encoded strings, numeric values (8 Bytes), or Boolean values (4 Bytes).
The size of UTF8-encoded strings is computed by counting all characters, excluding UNICODE control characters (segments C0 and C1).
Complex property values (nested objects) are computed based on the aggregate size of the property keys and property values that they contain.
IoT Hub rejects with an error all operations that would increase the size of those documents above the limit.
Module twin metadata
IoT Hub maintains the timestamp of the last update for each JSON object in module twin desired and reported properties. The timestamps are in UTC and encoded in the ISO8601 format YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.mmmZ.
For example:
{
...
"properties": {
"desired": {
"telemetryConfig": {
"sendFrequency": "5m"
},
"$metadata": {
"telemetryConfig": {
"sendFrequency": {
"$lastUpdated": "2016-03-30T16:24:48.789Z"
},
"$lastUpdated": "2016-03-30T16:24:48.789Z"
},
"$lastUpdated": "2016-03-30T16:24:48.789Z"
},
"$version": 23
},
"reported": {
"telemetryConfig": {
"sendFrequency": "5m",
"status": "success"
},
"batteryLevel": "55%",
"$metadata": {
"telemetryConfig": {
"sendFrequency": "5m",
"status": {
"$lastUpdated": "2016-03-31T16:35:48.789Z"
},
"$lastUpdated": "2016-03-31T16:35:48.789Z"
},
"batteryLevel": {
"$lastUpdated": "2016-04-01T16:35:48.789Z"
},
"$lastUpdated": "2016-04-01T16:24:48.789Z"
},
"$version": 123
}
}
...
}
This information is kept at every level (not just the leaves of the JSON structure) to preserve updates that remove object keys.
Optimistic concurrency
Tags, desired properties, and reported properties all support optimistic concurrency. If you need to guarantee order of twin property updates, consider implementing synchronization at the application level by waiting for reported properties callback before sending the next update.
Module twins have an ETag (etag property), as per RFC7232, that represents the twin's JSON representation. You can use the etag property in conditional update operations from back-end apps to ensure consistency. This option ensures consistency in operations that involve the tags container.
Module twin desired and reported properties also have a $version value that is guaranteed to be incremental. Similarly to an ETag, you can use the version value to enforce consistency of updates. For example, a module app for a reported property or a back-end app for a desired property.
Versions are also useful when an observing agent (such as the module app observing the desired properties) must reconcile races between the result of a retrieve operation and an update notification. The section Module reconnection flow provides more information.
Module reconnection flow
IoT Hub doesn't preserve desired properties update notifications for disconnected modules. It follows that a module that is connecting must retrieve the full desired properties document, in addition to subscribing for update notifications. Given the possibility of races between update notifications and full retrieval, the following flow must be ensured:
- Module app connects to an IoT hub.
- Module app subscribes for desired properties update notifications.
- Module app retrieves the full document for desired properties.
The module app can ignore all notifications with $version less or equal than the version of the full retrieved document. This approach is possible because IoT Hub guarantees that versions always increment.
Next steps
To try out some of the concepts described in this article, see the following IoT Hub tutorials: