Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
- Starting 1st April 2025, all jobs running on agent-based Hybrid Worker will be stopped.
- Azure Automation Agent-based User Hybrid Runbook Worker (Windows and Linux) has retired on 31 August 2024 and is no longer supported. Follow the guidelines on how to migrate from an existing Agent-based User Hybrid Runbook Workers to Extension-based Hybrid Workers.
You can use the user Hybrid Runbook Worker feature of Azure Automation to run runbooks directly on an Azure or non-Azure machine, including servers registered with Azure Arc-enabled servers. From the machine or server that's hosting the role, you can run runbooks directly against it and against resources in the environment to manage those local resources.
Azure Automation stores and manages runbooks and then delivers them to one or more chosen machines. This article describes how to deploy a user Hybrid Runbook Worker on a Windows machine, how to remove the worker, and how to remove a Hybrid Runbook Worker group. For user Hybrid Runbook Workers, see also Deploy an extension-based Windows or Linux user Hybrid Runbook Worker in Automation
After you successfully deploy a runbook worker, review Run runbooks on a Hybrid Runbook Worker to learn how to configure your runbooks to automate processes in your on-premises datacenter or other cloud environment.
Note
A hybrid worker can co-exist with both platforms: Agent based (V1) and Extension based (V2). If you install Extension based (V2)on a hybrid worker already running Agent based (V1), then you would see two entries of the Hybrid Runbook Worker in the group. One with Platform Extension based (V2) and the other Agent based (V1). Learn more.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have the following.
A Log Analytics workspace
The Hybrid Runbook Worker role depends on an Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace to install and configure the role. You can create it through Azure Resource Manager, through PowerShell, or in the Azure portal.
If you don't have an Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace, review the Azure Monitor Log design guidance before you create the workspace.
Log Analytics agent
The Hybrid Runbook Worker role requires the Log Analytics agent for the supported Windows operating system. For servers or machines hosted outside of Azure, you can install the Log Analytics agent using Azure Arc-enabled servers.
Supported Windows operating system
The Hybrid Runbook Worker feature supports the following operating systems:
- Windows Server 2022 (including Server Core)
- Windows Server 2019 (including Server Core)
- Windows Server 2016, version 1709 and 1803 (excluding Server Core)
- Windows Server 2012, 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2008 SP2 (x64), 2008 R2
- Windows 10 Enterprise (including multi-session) and Pro
- Windows 8 Enterprise and Pro
- Windows 7 SP1
Note
Hybrid Worker would follow support timelines of the OS vendor.
Minimum requirements
The minimum requirements for a Windows system and user Hybrid Runbook Worker are:
- Windows PowerShell 5.1 (download WMF 5.1). PowerShell Core isn't supported.
- .NET Framework 4.6.2 or later
- Two cores
- 4 GB of RAM
- Port 443 (outbound)
Network configuration
For networking requirements for the Hybrid Runbook Worker, see Configuring your network.
Adding a machine to a Hybrid Runbook Worker group
You can add the worker machine to a Hybrid Runbook Worker group in one of your Automation accounts. For machines hosting the system Hybrid Runbook worker managed by Update Management, they can be added to a Hybrid Runbook Worker group. But you must use the same Automation account for both Update Management and the Hybrid Runbook Worker group membership.
Note
Azure Automation Update Management automatically installs the system Hybrid Runbook Worker on an Azure or non-Azure machine that's enabled for Update Management. However, this worker is not registered with any Hybrid Runbook Worker groups in your Automation account. To run your runbooks on those machines, you need to add them to a Hybrid Runbook Worker group. Follow step 6 under the section Manual deployment to add it to a group.
Enable for management with Azure Automation State Configuration
For information about enabling machines for management with Azure Automation State Configuration, see Enable machines for management by Azure Automation State Configuration.
Note
To manage the configuration of machines that support the Hybrid Runbook Worker role with Desired State Configuration (DSC), you must add the machines as DSC nodes.
Installation options
To install and configure a Windows user Hybrid Runbook Worker, you can use one of the following methods.
- Use a provided PowerShell script to completely automate the process of configuring one or more Windows machines. This is the recommended method for machines in your datacenter or another cloud environment.
- Manually import the Automation solution, install the Log Analytics agent for Windows, and configure the worker role on the machine.
- Agent-based hybrid worker uses MMA proxy setting. You have to pass the proxy setting while installing the log analytics extension(MMA) and this setting will be stored under MMA configuration(registry) on VM.
Automated deployment
There are two methods to automatically deploy a Hybrid Runbook Worker. You can import a runbook from the Runbook Gallery in the Azure portal and run it, or you can manually download a script from the PowerShell Gallery.
Importing a runbook from the Runbook Gallery
The import procedure is described in detail in Import runbooks from GitHub with the Azure portal. The name of the runbook to import is Create Automation Windows HybridWorker.
The runbook uses the following parameters.
| Parameter | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
Location |
Mandatory | The Location of the automation account in which the script is executed. |
ResourceGroupName |
Mandatory | The resource group for your Automation account. |
AccountName |
Mandatory | The Automation account name in which the Hybrid Run Worker will be registered. |
CreateLA |
Mandatory | If true, uses the value of WorkspaceName to create a Log Analytics workspace. If false, the value of WorkspaceName must refer to an existing workspace. |
LAlocation |
Optional | The location where the Log Analytics workspace will be created, or where it already exists. |
WorkspaceName |
Optional | The name of the Log Analytics workspace to use. |
CreateVM |
Mandatory | If true, use the value of VMName as the name of a new VM. If false, use VMName to find and register existing VM. |
VMName |
Optional | The name of the virtual machine that's either created or registered, depending on the value of CreateVM. |
VMImage |
Optional | The name of the VM image to be created. |
VMlocation |
Optional | Location of the VM that's either created or registered. If this location isn't specified, the value of LAlocation is used. |
RegisterHW |
Mandatory | If true, register the VM as a hybrid worker. |
WorkerGroupName |
Mandatory | Name of the Hybrid Worker Group. |
Download a script from the PowerShell Gallery
This automated deployment method uses the PowerShell script New-OnPremiseHybridWorker.ps1 to automate and configure the Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker role. It performs the following:
- Installs the necessary modules
- Signs in with your Azure account
- Verifies the existence of specified resource group and Automation account
- Creates references to Automation account attributes
- Creates an Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace if not specified
- Enable the Azure Automation solution in the workspace
- Download and install the Log Analytics agent for Windows
- Register the machine as Hybrid Runbook Worker
Perform the following steps to install the role on your Windows machine using the script.
Download the New-OnPremiseHybridWorker.ps1 script from the PowerShell Gallery. After you've downloaded the script, copy or run it on the target machine. The script uses the following parameters.
Parameter Status Description AAResourceGroupNameMandatory The name of the resource group that's associated with your Automation account. AutomationAccountNameMandatory The name of your Automation account. CredentialOptional The credentials to use when logging in to the Azure environment. HybridGroupNameMandatory The name of a Hybrid Runbook Worker group that you specify as a target for the runbooks that support this scenario. OMSResourceGroupNameOptional The name of the resource group for the Log Analytics workspace. If this resource group isn't specified, the value of AAResourceGroupNameis used.SubscriptionIDMandatory The identifier of the Azure subscription associated with your Automation account. TenantIDOptional The identifier of the tenant organization associated with your Automation account. WorkspaceNameOptional The Log Analytics workspace name. If you don't have a Log Analytics workspace, the script creates and configures one. Open an elevated 64-bit PowerShell command prompt.
From the PowerShell command prompt, browse to the folder that contains the script that you downloaded. Change the values for the parameters
AutomationAccountName,AAResourceGroupName,OMSResourceGroupName,HybridGroupName,SubscriptionID, andWorkspaceName. Then run the script.You're prompted to authenticate with Azure after you run the script. You must sign in with an account that's a member of the Subscription Admins role and co-administrator of the subscription.
$NewOnPremiseHybridWorkerParameters = @{ AutomationAccountName = <nameOfAutomationAccount> AAResourceGroupName = <nameOfResourceGroup> OMSResourceGroupName = <nameOfResourceGroup> HybridGroupName = <nameOfHRWGroup> SubscriptionID = <subscriptionId> WorkspaceName = <nameOfLogAnalyticsWorkspace> } .\New-OnPremiseHybridWorker.ps1 @NewOnPremiseHybridWorkerParametersYou're prompted to agree to install NuGet, and to authenticate with your Azure credentials. If you don't have the latest NuGet version, you can download it from Available NuGet Distribution Versions.
Verify the deployment after the script is finished. From the Hybrid Runbook Worker Groups page in your Automation account, under the User hybrid runbook workers group tab, it shows the new group and the number of members. If it's an existing group, the number of members is incremented. You can select the group from the list on the page, from the left-hand menu choose Hybrid Workers . On the Hybrid Workers page, you can see each member of the group listed.
Manual deployment
To install and configure a Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker, perform the following steps.
Enable the Azure Automation solution in your Log Analytics workspace by running the following command in an elevated PowerShell command prompt.
Set-AzOperationalInsightsIntelligencePack -ResourceGroupName <resourceGroupName> -WorkspaceName <workspaceName> -IntelligencePackName "AzureAutomation" -Enabled $trueDeploy the Log Analytics agent to the target machine.
For Azure VMs, install the Log Analytics agent for Windows using the virtual machine extension for Windows. The extension installs the Log Analytics agent on Azure virtual machines, and enrolls virtual machines into an existing Log Analytics workspace. You can use an Azure Resource Manager template, PowerShell, or Azure Policy to assign the Deploy Log Analytics agent for Linux or Windows VMs built-in policy definition. Once the agent is installed, the machine can be added to a Hybrid Runbook Worker group in your Automation account.
For non-Azure machines, you can install the Log Analytics agent using Azure Arc-enabled servers. Azure Arc-enabled servers support deploying the Log Analytics agent using the following methods:
Using the VM extensions framework.
This feature in Azure Arc-enabled servers allows you to deploy the Log Analytics agent VM extension to a non-Azure Windows or Linux server. VM extensions can be managed using the following methods on your hybrid machines or servers managed by Arc-enabled servers:
- The Azure portal
- The Azure CLI
- Azure PowerShell
- Azure Resource Manager templates
Verify agent is reporting to workspace
The Log Analytics agent for Windows connects machines to an Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace. When you install the agent on your machine and connect it to your workspace, it automatically downloads the components that are required for the Hybrid Runbook Worker.
When the agent has successfully connected to your Log Analytics workspace after a few minutes, you can run the following query to verify that it's sending heartbeat data to the workspace.
Heartbeat | where Category == "Direct Agent" | where TimeGenerated > ago(30m)In the search results, you should see heartbeat records for the machine, indicating that it's connected and reporting to the service. By default, every agent forwards a heartbeat record to its assigned workspace. Use the following steps to complete the agent installation and setup.
Confirm the version of the Hybrid Runbook Worker on the machine hosting the Log Analytics agent, browse to
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Monitoring Agent\Agent\AzureAutomation\and note the version subfolder. This folder will appear on the machine several minutes after the solution is enabled in the workspace.Install the runbook environment and connect to Azure Automation. When you configure an agent to report to a Log Analytics workspace and import the Automation solution, the solution pushes down the
HybridRegistrationPowerShell module. This module contains theAdd-HybridRunbookWorkercmdlet. Use this cmdlet to install the runbook environment on the machine and register it with Azure Automation.Open a PowerShell session in Administrator mode and run the following commands to import the module.
cd "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Monitoring Agent\Agent\AzureAutomation\<version>\HybridRegistration" Import-Module .\HybridRegistration.psd1Run the
Add-HybridRunbookWorkercmdlet specifying the values for the parametersUrl,Key, andGroupName.Add-HybridRunbookWorker -GroupName <String> -Url <Url> -Key <String>You can get the information required for the parameters
UrlandKeyfrom the Keys page in your Automation account. Select Keys under the Account settings section from the left-hand side of the page.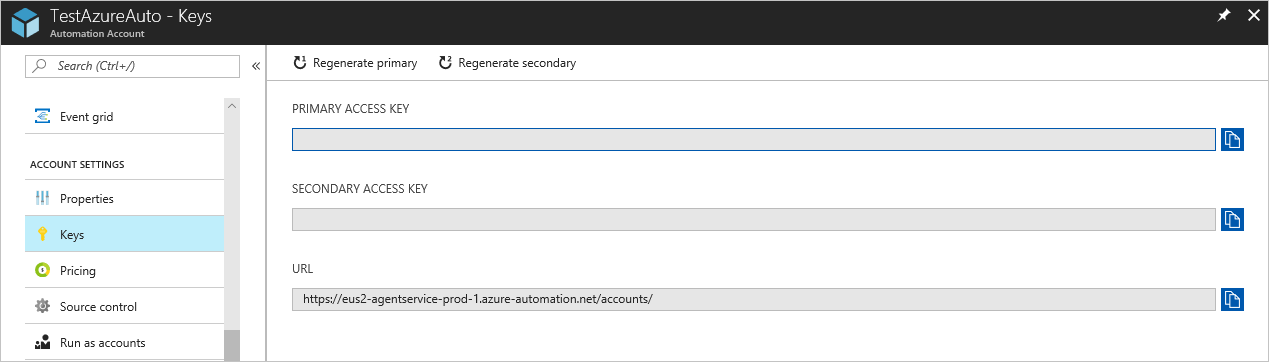
For the
Urlparameter, copy the value for URL.For the
Keyparameter, copy the value for PRIMARY ACCESS KEY.For the
GroupNameparameter, use the name of the Hybrid Runbook Worker group. If this group already exists in the Automation account, the current machine is added to it. If this group doesn't exist, it's added.If necessary, set the
Verboseparameter to receive details about the installation.
Verify the deployment after the command is completed. From the Hybrid Runbook Worker Groups page in your Automation account, under the User hybrid runbook workers group tab, it shows the new or existing group and the number of members. If it's an existing group, the number of members is incremented. You can select the group from the list on the page, from the left-hand menu choose Hybrid Workers. On the Hybrid Workers page, you can see each member of the group listed.
Install PowerShell modules
Runbooks can use any of the activities and cmdlets defined in the modules installed in your Azure Automation environment. As these modules aren't automatically deployed to on-premises machines, you must install them manually. The exception is the Azure module. This module is installed by default and provides access to cmdlets for all Azure services and activities for Azure Automation.
Because the primary purpose of the Hybrid Runbook Worker is to manage local resources, you most likely need to install the modules that support these resources, particularly the PowerShellGet module. For information on installing Windows PowerShell modules, see Windows PowerShell.
Modules that are installed must be in a location referenced by the PSModulePath environment variable so that the hybrid worker can automatically import them. For more information, see Install Modules in PSModulePath.
Remove the Hybrid Runbook Worker
Open PowerShell session in Administrator mode and run the following command:
Remove-Item -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\HybridRunbookWorker\<AutomationAccountID>\<HybridWorkerGroupName>" -Force -VerboseUnder Process Automation, select Hybrid worker groups and then your hybrid worker group to go to the Hybrid Worker Group page.
Under Hybrid worker group, select Hybrid Workers.
Select the checkbox next to the machine(s) you want to delete from the hybrid worker group.
Select Delete to remove the agent-based Windows Hybrid Worker.
Note
- After you disable the Private Link in your Automation account, it might take up to 60 minutes to remove the Hybrid Runbook worker.
- After you remove the Hybrid Worker, the Hybrid Worker authentication certificate on the machine is valid for 45 minutes.
Remove a Hybrid Worker group
To remove a Hybrid Runbook Worker group, you first need to remove the Hybrid Runbook Worker from every machine that is a member of the group. Then use the following steps to remove the group:
Open the Automation account in the Azure portal.
Select Hybrid worker groups under Process Automation. Select the group that you want to delete. The properties page for that group appears.
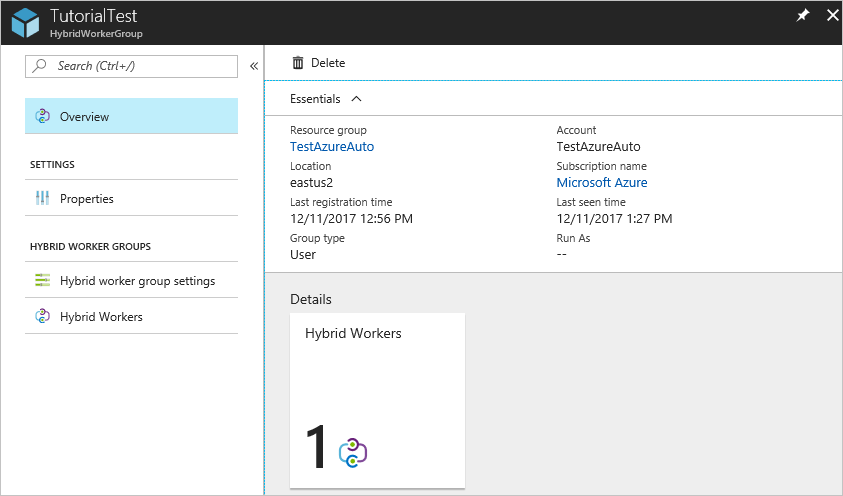
On the properties page for the selected group, select Delete. A warning message appears to remove any machines that are defined as hybrid workers in the hybrid worker group. If there's already a worker added to the group, you'll first have to delete the worker from the group.
Select Yes if you're sure that you want to continue.
This process can take several seconds to finish. You can track its progress under Notifications from the menu.
Manage Role permissions for Hybrid Worker Groups and Hybrid Workers
You can create custom Azure Automation roles and grant following permissions to Hybrid Worker Groups and Hybrid Workers. To learn more about how to create Azure Automation custom roles, see Azure custom roles
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/read | Reads a Hybrid Runbook Worker Group. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/write | Creates a Hybrid Runbook Worker Group. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/delete | Deletes a Hybrid Runbook Worker Group. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/hybridRunbookWorkers/read | Reads a Hybrid Runbook Worker. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/hybridRunbookWorkers/delete | Deletes a Hybrid Runbook Worker. |
Check version of Hybrid Worker
To check version of agent-based Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker, go to the following path:
C:\ProgramFiles\Microsoft Monitoring Agent\Agent\AzureAutomation\
The Azure Automation folder has a sub-folder with the version number as the name of the sub-folder.
Update Log Analytics agent to latest version
Azure Automation Agent-based User Hybrid Runbook Worker (V1) requires the Log Analytics agent (also known as MMA agent) during the installation of the Hybrid Worker. We recommend you to update the Log Analytics agent to the latest version to reduce security vulnerabilities and benefit from bug fixes.
Log Analytics agent versions prior to 10.20.18053 (bundle) and 1.0.18053.0 (extension) use an older method of certificate handling, and hence it is not recommended. Hybrid Workers on the outdated agents will not be able to connect to Azure, and Azure Automation jobs executed by these Hybrid Workers will stop.
You must update the Log Analytics agent to the latest version by following the below steps:
- Check the current version of the Log Analytics agent for your Windows Hybrid Worker: Go to the installation path - C:\ProgramFiles\Microsoft Monitoring Agent\Agent and right-click HealthService.exe to check Properties. The field Product version provides the version number of the Log Analytics agent.
- If your Log Analytics agent version is prior to 10.20.18053 (bundle) and 1.0.18053.0 (extension), upgrade to the latest version of the Windows Log Analytics agent, following these guidelines.
Note
Any Azure Automation jobs running on the Hybrid Worker during the upgrade process might stop. Ensure that there aren't any jobs running or scheduled during the Log Analytics agent upgrade.
Next steps
To learn how to configure your runbooks to automate processes in your on-premises datacenter or other cloud environment, see Run runbooks on a Hybrid Runbook Worker.
To learn how to troubleshoot your Hybrid Runbook Workers, see Troubleshoot Hybrid Runbook Worker issues.