Azure Synapse 中适用于专用 SQL 池的具体化视图为复杂的分析查询提供一种低维护的方法来加速查询性能,且无需对查询进行任何更改。 本文讨论了使用具体化视图的一般指南。
具体化视图与标准视图
Azure Synapse 中的专用 SQL 池支持标准视图和具体化视图。 两者都是用 SELECT 表达式创建并以逻辑表的形式呈现给查询的虚拟表。 视图封装了常见数据计算的复杂性,并为计算更改添加了一个抽象层,因此无需重写查询。
每次使用标准视图时,该视图都会计算其数据。 磁盘上不存储任何数据。 用户通常使用标准视图作为一个有助于组织专用 SQL 池中的逻辑对象和查询的工具。 若要使用标准视图,查询需要直接引用它。
和表一样,具体化视图在专用 SQL 池中预先计算、存储和维护其数据。 每次使用具体化视图时都不需要重新计算。 这就是为什么使用具体化视图中的全部或部分数据的查询可以获得更快的性能。 更有利的是,查询可以使用具体化视图而无需直接引用它,因此不需要更改应用程序代码。
标准视图上的大多数要求仍然适用于具体化视图。 有关具体化视图语法和其他要求的详细信息,请参阅 CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW AS SELECT
| 比较 | 视图 | 具体化视图 |
|---|---|---|
| 查看定义 | 存储在专用 SQL 池中。 | 存储在专用 SQL 池中。 |
| 查看内容 | 在每次使用视图时生成。 | 在创建视图期间进行预处理并存储在专用 SQL 池中。 随着数据添加到基础表中而更新。 |
| 数据刷新 | 始终更新 | 始终更新 |
| 从复杂查询检索视图数据的速度 | 慢 | 快速 |
| 额外存储 | 否 | 是 |
| 语法 | CREATE VIEW | CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW AS SELECT |
使用具体化视图的优点
设计合理的具体化视图具有以下优势:
- 使用联接和聚合函数减少复杂查询的执行时间。 查询越复杂,就越有可能节省执行时间。 当查询的计算成本很高而生成的数据集很小时,可以获得最大的优势。
- 专用 SQL 池中的优化器可以自动使用部署的具体化视图来改善查询执行计划。 此过程对提供更快查询性能的用户是透明的,并且不需要查询直接引用具体化视图。
- 需要对视图进行低维护。 所有来自基表的增量数据更改将以同步方式自动添加到具体化视图中,这意味着基表和具体化视图在相同事务中进行更新。 这种设计可以使查询具体化视图后返回的数据与直接查询基表后返回的数据相同。
- 具体化视图中的数据可以采用与基表不同的方式分发。
- 具体化视图中的数据与常规表中的数据具有相同的高可用性和复原优势。
在专用 SQL 池中实现的具体化视图还提供以下优势:
与其他数据仓库提供程序相比,在专用 SQL 池中实现的具体化视图还提供以下优势:
- 广泛的聚合函数支持。 请参阅 CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW AS SELECT (Transact-SQL)。
- 支持查询特定的具体化视图建议。 请参阅 EXPLAIN (Transact-SQL)。
- 根据基表中的数据更改,自动、同步刷新数据。 不需要任何用户操作。
常见方案
在以下场景中,往往会使用具体化视图:
需要提高大规模数据的复杂分析查询的性能
复杂的分析查询往往使用更多的聚合函数和表联接,导致更多的计算密集型操作,例如查询执行中的随机排布和联接。 因此,复杂的分析查询需要更长时间才能完成,尤其是针对大型表执行时。
用户可以针对从常见查询计算返回的数据创建具体化视图,因此,当查询需要此数据时无需重新计算,从而可以降低计算成本,并加快查询响应速度。
在没有或只有少量查询更改的情况下需要更快的性能
为了支持常规的 ETL 操作和报告,往往会尽量在专用 SQL 池中保留最少量的架构和查询更改。 如果查询性能的提高可以弥补视图所产生的成本,则可以使用具体化视图来对查询性能进行优化。
与其他优化选项(例如缩放和统计信息管理)相比,创建和维护具体化视图带来的变化对生产造成的影响更小,并且性能提升的潜力也更高。
- 创建或维护具体化视图不会影响对基表运行的查询。
- 查询优化器可以自动使用已部署的具体化视图,而无需在查询中直接引用视图。 此功能减少了性能优化中查询更改的需要。
需要不同的数据分布策略来提高查询性能
专用 SQL 池是一种分布式查询处理系统。 SQL 表中的数据使用三种分布策略(哈希、round_robin 或复制)之一分布在多达 60 个节点中。
数据分布在表创建时进行指定,并且在删除表之前保持不变。 作为磁盘上的虚拟表,具体化视图支持哈希和 round_robin 数据分布。 用户可以选择与基表不同的、但对于使用视图的查询性能最有利的数据分布方式。
设计指南
下面是关于使用具体化视图提高查询性能的一般指南:
针对工作负载设计
在开始创建具体化视图之前,必须从查询模式、重要性、频率和生成的数据大小等方面深入了解工作负载。
用户可以针对查询优化器建议的具体化视图运行 EXPLAIN WITH_RECOMMENDATIONS <SQL_statement>。 由于这些建议特定于查询,因此对一个查询有利的具体化视图可能并不适合同一工作负载中的其他查询。
评估这些建议时应考虑工作负载需要。 理想的具体化视图是那些有利于工作负载性能的视图。
注意快速查询和成本之间的权衡
每个具体化视图都有相应的数据存储成本和视图维护成本。 当基表中的数据更改时,具体化视图的大小会增加,其物理结构也会改变。 为了避免查询性能下降,每个具体化视图会由 SQL 引擎单独维护。
当具体化视图和基表更改的数量增加时,维护工作负载会增加。 用户应该检查查询性能的提高是否可以弥补所有具体化视图所产生的成本。
可运行以下查询来生成专用 SQL 池中的具体化视图列表:
SELECT V.name as materialized_view, V.object_id
FROM sys.views V
JOIN sys.indexes I ON V.object_id= I.object_id AND I.index_id < 2;
减少具体化视图数量的选项:
确定工作负载中的复杂查询经常使用的常见数据集。 创建具体化视图来存储这些数据集,以便优化器可以在创建执行计划时将它们用作构建基块。
删除使用率低或不再需要的具体化视图。 禁用的具体化视图不会得到维护,但仍会产生存储成本。
合并在相同或相似基表上创建的具体化视图,即使它们的数据没有重叠。 合并具体化视图可能导致视图的大小大于单独视图的总和,但是视图维护成本应该会降低。 例如:
-- Query 1 would benefit from having a materialized view created with this SELECT statement
SELECT A, SUM(B)
FROM T
GROUP BY A
-- Query 2 would benefit from having a materialized view created with this SELECT statement
SELECT C, SUM(D)
FROM T
GROUP BY C
-- You could create a single materialized view of this form
SELECT A, C, SUM(B), SUM(D)
FROM T
GROUP BY A, C
并非所有性能优化都需要更改查询
SQL 查询优化器可以自动使用部署的具体化视图来改善查询性能。 此支持透明地应用于不引用视图的查询和使用具体化视图创建中不支持的聚合的查询。 无需更改任何查询。 可以检查查询的预估执行计划,确认是否使用了具体化视图。
监视具体化视图
与使用聚集列存储索引 (CCI) 的表一样,具体化视图存储在专用 SQL 池中。 从具体化视图读取数据包括扫描 CCI 索引段和应用基表中的任何增量更改。 当增量更改的数量太多时,从具体化视图解析查询可能比直接查询基表花费更长的时间。
为了避免查询性能下降,最佳做法是运行 DBCC PDW_SHOWMATERIALIZEDVIEWOVERHEAD 来监视视图的 overhead_ratio (total_rows / max(1, base_view_row))。 如果具体化视图的 overhead_ratio 过高,则用户应重新生成该视图。
具体化视图和结果集缓存
专用 SQL 池中的这两项功能用于优化查询性能。 结果集缓存用于获得高并发性,使针对静态数据的重复查询快速返回响应。
为使用缓存结果,请求缓存的查询的形式必须与生成缓存的查询匹配。 此外,缓存的结果必须应用于整个查询。
具体化视图允许基表中的数据更改。 具体化视图中的数据可以应用于查询的一部分。 借助这一支持,使用相同的某些计算的不同查询可使用相同的具体化视图,以获得更快的性能。
示例
本例使用类似 TPCDS 的查询,查找通过目录支出比在商店花费更多资金的客户,确定首选客户及其原产国家/地区。 查询包括从涉及 SUM() 和 GROUP BY 的三个子 SELECT 语句的并集中选择前 100 条记录。
WITH year_total AS (
SELECT c_customer_id customer_id
,c_first_name customer_first_name
,c_last_name customer_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag customer_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country customer_birth_country
,c_login customer_login
,c_email_address customer_email_address
,d_year dyear
,sum(isnull(ss_ext_list_price-ss_ext_wholesale_cost-ss_ext_discount_amt+ss_ext_sales_price, 0)/2) year_total
,'s' sale_type
FROM customer
,store_sales
,date_dim
WHERE c_customer_sk = ss_customer_sk
AND ss_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk
GROUP BY c_customer_id
,c_first_name
,c_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country
,c_login
,c_email_address
,d_year
UNION ALL
SELECT c_customer_id customer_id
,c_first_name customer_first_name
,c_last_name customer_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag customer_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country customer_birth_country
,c_login customer_login
,c_email_address customer_email_address
,d_year dyear
,sum(isnull(cs_ext_list_price-cs_ext_wholesale_cost-cs_ext_discount_amt+cs_ext_sales_price, 0)/2) year_total
,'c' sale_type
FROM customer
,catalog_sales
,date_dim
WHERE c_customer_sk = cs_bill_customer_sk
AND cs_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk
GROUP BY c_customer_id
,c_first_name
,c_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country
,c_login
,c_email_address
,d_year
UNION ALL
SELECT c_customer_id customer_id
,c_first_name customer_first_name
,c_last_name customer_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag customer_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country customer_birth_country
,c_login customer_login
,c_email_address customer_email_address
,d_year dyear
,sum(isnull(ws_ext_list_price-ws_ext_wholesale_cost-ws_ext_discount_amt+ws_ext_sales_price, 0)/2) year_total
,'w' sale_type
FROM customer
,web_sales
,date_dim
WHERE c_customer_sk = ws_bill_customer_sk
AND ws_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk
GROUP BY c_customer_id
,c_first_name
,c_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country
,c_login
,c_email_address
,d_year
)
SELECT TOP 100
t_s_secyear.customer_id
,t_s_secyear.customer_first_name
,t_s_secyear.customer_last_name
,t_s_secyear.customer_birth_country
FROM year_total t_s_firstyear
,year_total t_s_secyear
,year_total t_c_firstyear
,year_total t_c_secyear
,year_total t_w_firstyear
,year_total t_w_secyear
WHERE t_s_secyear.customer_id = t_s_firstyear.customer_id
AND t_s_firstyear.customer_id = t_c_secyear.customer_id
AND t_s_firstyear.customer_id = t_c_firstyear.customer_id
AND t_s_firstyear.customer_id = t_w_firstyear.customer_id
AND t_s_firstyear.customer_id = t_w_secyear.customer_id
AND t_s_firstyear.sale_type = 's'
AND t_c_firstyear.sale_type = 'c'
AND t_w_firstyear.sale_type = 'w'
AND t_s_secyear.sale_type = 's'
AND t_c_secyear.sale_type = 'c'
AND t_w_secyear.sale_type = 'w'
AND t_s_firstyear.dyear+0 = 1999
AND t_s_secyear.dyear+0 = 1999+1
AND t_c_firstyear.dyear+0 = 1999
AND t_c_secyear.dyear+0 = 1999+1
AND t_w_firstyear.dyear+0 = 1999
AND t_w_secyear.dyear+0 = 1999+1
AND t_s_firstyear.year_total > 0
AND t_c_firstyear.year_total > 0
AND t_w_firstyear.year_total > 0
AND CASE WHEN t_c_firstyear.year_total > 0 THEN t_c_secyear.year_total / t_c_firstyear.year_total ELSE NULL END
> CASE WHEN t_s_firstyear.year_total > 0 THEN t_s_secyear.year_total / t_s_firstyear.year_total ELSE NULL END
AND CASE WHEN t_c_firstyear.year_total > 0 THEN t_c_secyear.year_total / t_c_firstyear.year_total ELSE NULL END
> CASE WHEN t_w_firstyear.year_total > 0 THEN t_w_secyear.year_total / t_w_firstyear.year_total ELSE NULL END
ORDER BY t_s_secyear.customer_id
,t_s_secyear.customer_first_name
,t_s_secyear.customer_last_name
,t_s_secyear.customer_birth_country
OPTION ( LABEL = 'Query04-af359846-253-3');
检查查询的预估执行计划。 共有 18 个随机排布和 17 个联接操作,执行这些操作需要更多的时间。 现在让我们为三个子 SELECT 语句分别创建一个具体化视图。
CREATE materialized view nbViewSS WITH (DISTRIBUTION=HASH(customer_id)) AS
SELECT c_customer_id customer_id
,c_first_name customer_first_name
,c_last_name customer_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag customer_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country customer_birth_country
,c_login customer_login
,c_email_address customer_email_address
,d_year dyear
,sum(isnull(ss_ext_list_price-ss_ext_wholesale_cost-ss_ext_discount_amt+ss_ext_sales_price, 0)/2) year_total
, count_big(*) AS cb
FROM dbo.customer
,dbo.store_sales
,dbo.date_dim
WHERE c_customer_sk = ss_customer_sk
AND ss_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk
GROUP BY c_customer_id
,c_first_name
,c_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country
,c_login
,c_email_address
,d_year
GO
CREATE materialized view nbViewCS WITH (DISTRIBUTION=HASH(customer_id)) AS
SELECT c_customer_id customer_id
,c_first_name customer_first_name
,c_last_name customer_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag customer_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country customer_birth_country
,c_login customer_login
,c_email_address customer_email_address
,d_year dyear
,sum(isnull(cs_ext_list_price-cs_ext_wholesale_cost-cs_ext_discount_amt+cs_ext_sales_price, 0)/2) year_total
, count_big(*) as cb
FROM dbo.customer
,dbo.catalog_sales
,dbo.date_dim
WHERE c_customer_sk = cs_bill_customer_sk
AND cs_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk
GROUP BY c_customer_id
,c_first_name
,c_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country
,c_login
,c_email_address
,d_year
GO
CREATE materialized view nbViewWS WITH (DISTRIBUTION=HASH(customer_id)) AS
SELECT c_customer_id customer_id
,c_first_name customer_first_name
,c_last_name customer_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag customer_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country customer_birth_country
,c_login customer_login
,c_email_address customer_email_address
,d_year dyear
,sum(isnull(ws_ext_list_price-ws_ext_wholesale_cost-ws_ext_discount_amt+ws_ext_sales_price, 0)/2) year_total
, count_big(*) AS cb
FROM dbo.customer
,dbo.web_sales
,dbo.date_dim
WHERE c_customer_sk = ws_bill_customer_sk
AND ws_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk
GROUP BY c_customer_id
,c_first_name
,c_last_name
,c_preferred_cust_flag
,c_birth_country
,c_login
,c_email_address
,d_year
再次检查原始查询的执行计划。 现在,联接数从 17 个更改为 5 个,并且没有随机排布。 选择计划中的“筛选操作”图标,其“输出列表”将显示已从具体化视图而不是基表读取了数据。
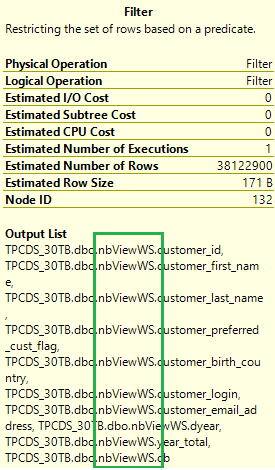
使用具体化视图时,同一查询的运行速度更快,且无需进行任何代码更改。
后续步骤
有关更多开发技巧,请参阅专用 SQL 池开发概述。