“执行 R 脚本”组件
本文介绍如何使用“执行 R 脚本”组件在 Azure 机器学习设计器管道中运行 R 代码。
使用 R,你可以执行现有组件不支持的任务,例如:
- 创建自定义数据转换
- 使用你自己的指标来评估预测
- 使用在设计器中未作为独立组件实现的算法来构建模型
R 版本支持
Azure 机器学习设计器使用 R 的 CRAN(综合 R 存档网络)分发。当前使用的版本为 CRAN 3.5.1。
支持的 R 包
R 环境预装有 100 多个包。 有关完整列表,请参阅预安装的 R 包部分。
你还可以将以下代码添加到任何“执行 R 脚本”组件,以查看已安装的包。
azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){
print("R script run.")
dataframe1 <- data.frame(installed.packages())
return(list(dataset1=dataframe1, dataset2=dataframe2))
}
注意
如果你的管道包含需要不在预安装列表中的包的多个“执行 R 脚本”组件,请在每个组件中安装这些包。
安装 R 程序包
若要安装其他 R 包,请使用 install.packages() 方法。 将为每个“执行 R 脚本”组件安装包。 这些包不会在其他“执行 R 脚本”组件之间共享。
注意
建议不要从脚本包安装 R 包。 建议直接在脚本编辑器中安装包。
在安装包时,请指定 CRAN 存储库,例如 install.packages("zoo",repos = "https://cloud.r-project.org")。
警告
“执行 R 脚本”组件不支持安装需要本机编译的包,比如需要 Java 的 qdap 包和需要 C++ 的 drc 包。 这是因为该组件是在具有非管理员权限的预安装环境中执行的。
请勿安装在 Windows 上预先构建/针对 Windows 预先构建的包,因为设计器组件在 Ubuntu 上运行。 若要检查一个包是否是在 windows 上预建的包,可以转到 CRAN 并搜索该包,根据 OS 下载一个二进制文件,然后检查 DESCRIPTION 文件中的“Built:”部分。 下面是一个示例: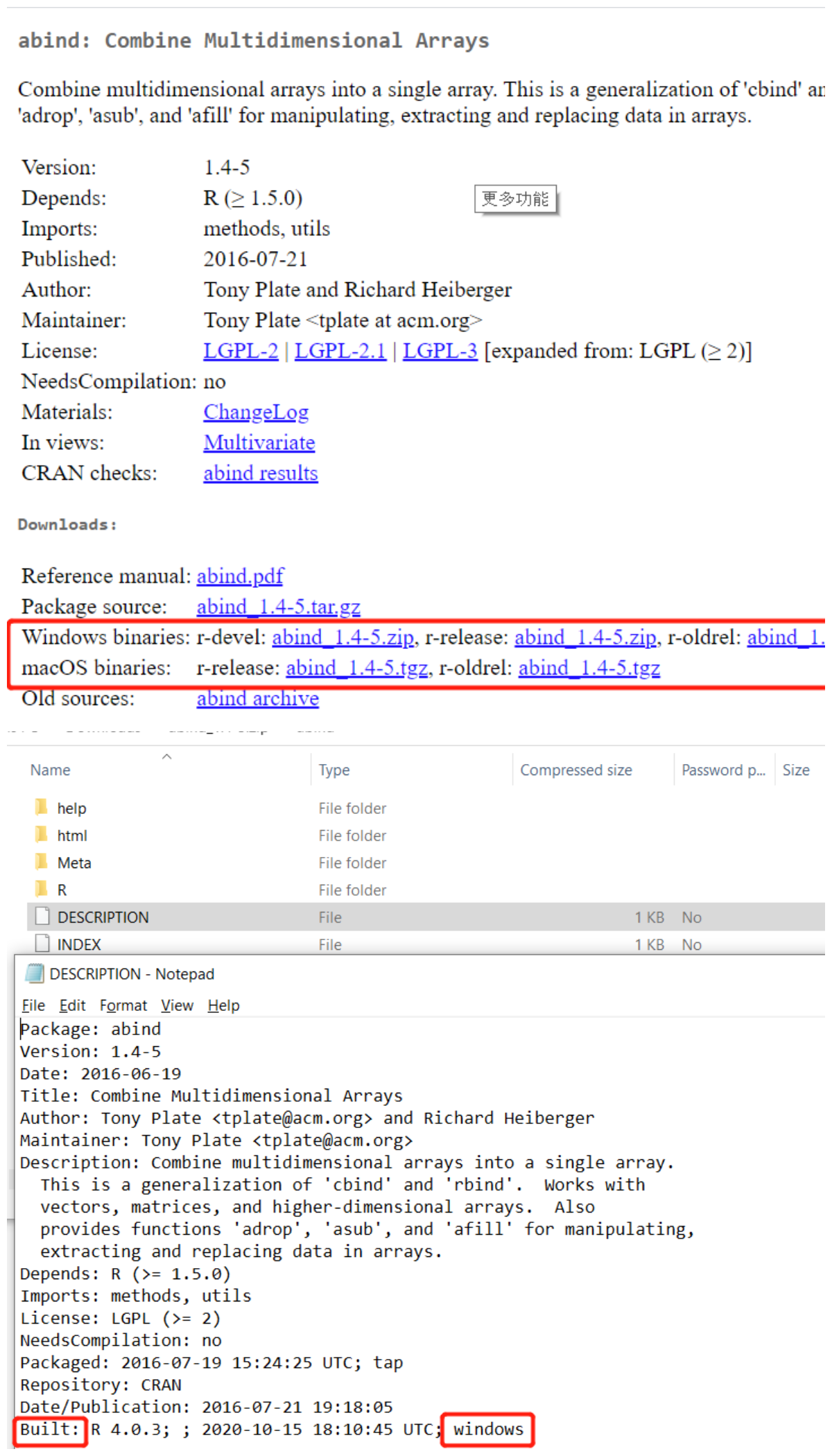
此示例演示如何安装 Zoo:
# R version: 3.5.1
# The script MUST contain a function named azureml_main,
# which is the entry point for this component.
# Note that functions dependent on the X11 library,
# such as "View," are not supported because the X11 library
# is not preinstalled.
# The entry point function MUST have two input arguments.
# If the input port is not connected, the corresponding
# dataframe argument will be null.
# Param<dataframe1>: a R DataFrame
# Param<dataframe2>: a R DataFrame
azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){
print("R script run.")
if(!require(zoo)) install.packages("zoo",repos = "https://cloud.r-project.org")
library(zoo)
# Return datasets as a Named List
return(list(dataset1=dataframe1, dataset2=dataframe2))
}
注意
安装包之前,请检查它是否已经存在,以避免重复安装。 重复安装可能会导致 Web 服务请求超时。
访问已注册的数据集
可以参阅以下示例代码,在工作区中访问已注册的数据集:
azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){
print("R script run.")
run = get_current_run()
ws = run$experiment$workspace
dataset = azureml$core$dataset$Dataset$get_by_name(ws, "YOUR DATASET NAME")
dataframe2 <- dataset$to_pandas_dataframe()
# Return datasets as a Named List
return(list(dataset1=dataframe1, dataset2=dataframe2))
}
如何配置“执行 R 脚本”
“执行 R 脚本”组件包含示例代码作为起点。
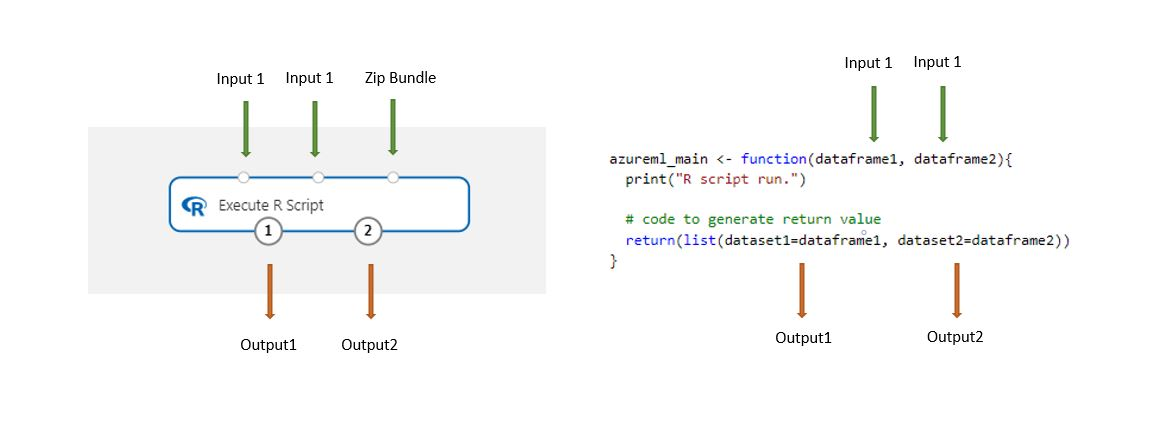
使用此组件加载时,存储在设计器中的数据集会自动转换为 R 数据帧。
将“执行 R 脚本”组件添加到管道中。
连接该脚本需要的任何输入。 输入是可选的,可以包含数据和其他 R 代码。
Dataset1:引用第一个输入作为
dataframe1。 输入数据集必须是 CSV、TSV 或 ARFF 格式的文件。 或者可以连接 Azure 机器学习数据集。Dataset2:引用第二个输入作为
dataframe2。 此数据集也必须是 CSV、TSV、ARFF 格式的文件,或者是 Azure 机器学习数据集。脚本包:第三个输入接受 .zip 文件。 压缩文件可以包含多个文件和多种文件类型。
在“R 脚本”文本框中,键入或粘贴有效的 R 脚本。
注意
编写脚本时请细致谨慎。 确保没有语法错误,例如使用未声明的变量或未导入的组件或函数。 请特别注意本文结尾处的预安装包列表。 若要使用未列出的包,请通过脚本安装它们。 例如
install.packages("zoo",repos = "https://cloud.r-project.org")。为了帮助你入门,“R 脚本”文本框中预填充了可编辑或替换的代码示例。
# R version: 3.5.1 # The script MUST contain a function named azureml_main, # which is the entry point for this component. # Note that functions dependent on the X11 library, # such as "View," are not supported because the X11 library # is not preinstalled. # The entry point function MUST have two input arguments. # If the input port is not connected, the corresponding # dataframe argument will be null. # Param<dataframe1>: a R DataFrame # Param<dataframe2>: a R DataFrame azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){ print("R script run.") # If a .zip file is connected to the third input port, it's # unzipped under "./Script Bundle". This directory is added # to sys.path. # Return datasets as a Named List return(list(dataset1=dataframe1, dataset2=dataframe2)) }入口点函数必须有输入参数
Param<dataframe1>和Param<dataframe2>,即使该函数中没有使用这些参数。注意
传递给“执行 R 脚本”组件的数据将作为
dataframe1和dataframe2被引用,这与 Azure 机器学习设计器不同(设计器以dataset1和dataset2形式来引用)。 请确保脚本中正确引用了输入数据。注意
现有 R 代码可能需要稍做更改才能在设计器管道中运行。 例如,以 CSV 格式提供的输入数据应显式转换为数据集,然后才能在代码中使用。 R 语言中使用的数据和列类型与在设计器中使用的数据和列类型在某些方面也有所不同。
如果脚本大于 16 KB,请使用“脚本绑定”端口以避免错误,如“命令行超过 16597 个字符的限制”。
- 将脚本和其他自定义资源捆绑到一个 zip 文件中。
- 将 zip 文件作为“文件数据集”上传到工作室。
- 从设计器创作页面左侧组件窗格中的“数据集”列表中拖动数据集组件。
- 将数据集组件连接到“执行 R 脚本”组件的“脚本捆绑”端口。
下面是使用脚本包中的脚本的示例代码:
azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){ # Source the custom R script: my_script.R source("./Script Bundle/my_script.R") # Use the function that defined in my_script.R dataframe1 <- my_func(dataframe1) sample <- readLines("./Script Bundle/my_sample.txt") return (list(dataset1=dataframe1, dataset2=data.frame("Sample"=sample))) }对于“随机种子”,请输入要在 R 环境中用作随机种子值的值。 此参数相当于在 R 代码中调用
set.seed(value)。提交管道。
结果
“执行 R 脚本”组件可以返回多个输出,但这些输出必须作为 R 数据帧提供。 设计器自动将数据帧转换为数据集,以与其他组件兼容。
R 生成的标准消息和错误将返回到组件的日志中。
如果需要在 R 脚本中打印结果,可以在组件右侧面板的“输出+日志”选项卡下的 70_driver_log 中找到打印的结果。
示例脚本
通过使用自定义 R 脚本来扩展管道的方法有多种。 本部分提供常见任务的示例代码。
添加 R 脚本作为输入
“执行 R 脚本”组件支持任意 R 脚本文件作为输入。 要使用这些文件,必须将它们作为 .zip 文件的一部分上传到工作区。
若要将包含 R 代码的 .zip 文件上传到工作区,请转到“数据集”资产页。 选择“创建数据集”,然后选择“从本地文件”和“文件”数据集类型选项 。
验证压缩文件是否出现在左侧组件树中“数据集”类别下的“我的数据集”中。
将数据集连接到“脚本包”输入端口。
该 .zip 文件中的所有文件在管道运行时都是可用的。
如果脚本包文件中已包含目录结构,则会保留结构。 但是,必须更改代码,以将目录“./Script Bundle”追加到路径前面。
处理数据
以下示例演示如何缩放和规范化输入数据:
# R version: 3.5.1
# The script MUST contain a function named azureml_main,
# which is the entry point for this component.
# Note that functions dependent on the X11 library,
# such as "View," are not supported because the X11 library
# is not preinstalled.
# The entry point function MUST have two input arguments.
# If the input port is not connected, the corresponding
# dataframe argument will be null.
# Param<dataframe1>: a R DataFrame
# Param<dataframe2>: a R DataFrame
azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){
print("R script run.")
# If a .zip file is connected to the third input port, it's
# unzipped under "./Script Bundle". This directory is added
# to sys.path.
series <- dataframe1$width
# Find the maximum and minimum values of the width column in dataframe1
max_v <- max(series)
min_v <- min(series)
# Calculate the scale and bias
scale <- max_v - min_v
bias <- min_v / dis
# Apply min-max normalizing
dataframe1$width <- dataframe1$width / scale - bias
dataframe2$width <- dataframe2$width / scale - bias
# Return datasets as a Named List
return(list(dataset1=dataframe1, dataset2=dataframe2))
}
读取 .zip 文件作为输入
此示例演示如何使用 .zip 文件中的数据集作为“执行 R 脚本”组件的输入。
- 创建 CSV 格式的数据文件,并将其命名为“mydatafile.csv”。
- 创建一个 .zip 文件,并将该 CSV 文件添加到此存档。
- 将压缩文件上载到 Azure 机器学习工作区。
- 将生成的数据集连接到“执行 R 组件”组件的 ScriptBundle 输入。
- 使用以下代码从压缩文件中读取 CSV 数据。
azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){
print("R script run.")
mydataset<-read.csv("./Script Bundle/mydatafile.csv",encoding="UTF-8");
# Return datasets as a Named List
return(list(dataset1=mydataset, dataset2=dataframe2))
}
复制行
此示例演示如何复制数据集中的正面记录来平衡示例:
azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){
data.set <- dataframe1[dataframe1[,1]==-1,]
# positions of the positive samples
pos <- dataframe1[dataframe1[,1]==1,]
# replicate the positive samples to balance the sample
for (i in 1:20) data.set <- rbind(data.set,pos)
row.names(data.set) <- NULL
# Return datasets as a Named List
return(list(dataset1=data.set, dataset2=dataframe2))
}
在“执行 R 脚本”组件之间传递 R 对象
可以使用内部序列化机制在“执行 R 脚本”组件的实例之间传递 R 对象。 此示例假定您要在两个“执行 R 脚本”组件之间移动命名为 A 的 R 对象。
将第一个“执行 R 脚本”组件添加到管道中。 然后在“R 脚本”文本框中输入以下代码以创建序列化对象
A作为组件输出数据表中的列:azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){ print("R script run.") # some codes generated A serialized <- as.integer(serialize(A,NULL)) data.set <- data.frame(serialized,stringsAsFactors=FALSE) return(list(dataset1=data.set, dataset2=dataframe2)) }此时会完成显式转换到整数类型,因为序列化函数输出 R
Raw格式的数据,而设计器不支持该格式。添加“执行 R 脚本”组件的第二个实例,并将其连接到前一个组件的输出端口。
在“R 脚本”文本框中键入以下代码,从输入数据表中提取对象
A。azureml_main <- function(dataframe1, dataframe2){ print("R script run.") A <- unserialize(as.raw(dataframe1$serialized)) # Return datasets as a Named List return(list(dataset1=dataframe1, dataset2=dataframe2)) }
预安装的 R 包
以下预安装的 R 包当前可用:
| 程序包 | 版本 |
|---|---|
| askpass | 1.1 |
| assertthat | 0.2.1 |
| backports | 1.1.4 |
| base | 3.5.1 |
| base64enc | 0.1-3 |
| BH | 1.69.0-1 |
| bindr | 0.1.1 |
| bindrcpp | 0.2.2 |
| bitops | 1.0-6 |
| 启动 | 1.3-22 |
| broom | 0.5.2 |
| callr | 3.2.0 |
| caret | 6.0-84 |
| caTools | 1.17.1.2 |
| cellranger | 1.1.0 |
| class | 7.3-15 |
| cli | 1.1.0 |
| clipr | 0.6.0 |
| cluster | 2.0.7-1 |
| codetools | 0.2-16 |
| colorspace | 1.4-1 |
| compiler | 3.5.1 |
| crayon | 1.3.4 |
| curl | 3.3 |
| data.table | 1.12.2 |
| datasets | 3.5.1 |
| DBI | 1.0.0 |
| dbplyr | 1.4.1 |
| digest | 0.6.19 |
| dplyr | 0.7.6 |
| e1071 | 1.7-2 |
| 评估 | 0.14 |
| fansi | 0.4.0 |
| forcats | 0.3.0 |
| foreach | 1.4.4 |
| foreign | 0.8-71 |
| fs | 1.3.1 |
| gdata | 2.18.0 |
| generics | 0.0.2 |
| ggplot2 | 3.2.0 |
| glmnet | 2.0-18 |
| glue | 1.3.1 |
| gower | 0.2.1 |
| gplots | 3.0.1.1 |
| graphics | 3.5.1 |
| grDevices | 3.5.1 |
| grid | 3.5.1 |
| gtable | 0.3.0 |
| gtools | 3.8.1 |
| haven | 2.1.0 |
| highr | 0.8 |
| hms | 0.4.2 |
| htmltools | 0.3.6 |
| httr | 1.4.0 |
| ipred | 0.9-9 |
| iterators | 1.0.10 |
| jsonlite | 1.6 |
| KernSmooth | 2.23-15 |
| knitr | 1.23 |
| labeling | 0.3 |
| lattice | 0.20-38 |
| lava | 1.6.5 |
| lazyeval | 0.2.2 |
| lubridate | 1.7.4 |
| magrittr | 1.5 |
| markdown | 1 |
| MASS | 7.3-51.4 |
| 矩阵 | 1.2-17 |
| 方法 | 3.5.1 |
| mgcv | 1.8-28 |
| mime | 0.7 |
| ModelMetrics | 1.2.2 |
| modelr | 0.1.4 |
| munsell | 0.5.0 |
| nlme | 3.1-140 |
| nnet | 7.3-12 |
| numDeriv | 2016.8-1.1 |
| openssl | 1.4 |
| parallel | 3.5.1 |
| pillar | 1.4.1 |
| pkgconfig | 2.0.2 |
| plogr | 0.2.0 |
| plyr | 1.8.4 |
| prettyunits | 1.0.2 |
| processx | 3.3.1 |
| prodlim | 2018.04.18 |
| 进度 | 1.2.2 |
| ps | 1.3.0 |
| purrr | 0.3.2 |
| quadprog | 1.5-7 |
| quantmod | 0.4-15 |
| R6 | 2.4.0 |
| randomForest | 4.6-14 |
| RColorBrewer | 1.1-2 |
| Rcpp | 1.0.1 |
| RcppRoll | 0.3.0 |
| readr | 1.3.1 |
| readxl | 1.3.1 |
| recipes | 0.1.5 |
| rematch | 1.0.1 |
| reprex | 0.3.0 |
| reshape2 | 1.4.3 |
| reticulate | 1.12 |
| rlang | 0.4.0 |
| rmarkdown | 1.13 |
| ROCR | 1.0-7 |
| rpart | 4.1-15 |
| rstudioapi | 0.1 |
| rvest | 0.3.4 |
| scales | 1.0.0 |
| selectr | 0.4-1 |
| spatial | 7.3-11 |
| splines | 3.5.1 |
| SQUAREM | 2017.10-1 |
| stats | 3.5.1 |
| stats4 | 3.5.1 |
| stringi | 1.4.3 |
| stringr | 1.3.1 |
| survival | 2.44-1.1 |
| sys | 3.2 |
| tcltk | 3.5.1 |
| tibble | 2.1.3 |
| tidyr | 0.8.3 |
| tidyselect | 0.2.5 |
| tidyverse | 1.2.1 |
| timeDate | 3043.102 |
| tinytex | 0.13 |
| 工具 | 3.5.1 |
| tseries | 0.10-47 |
| TTR | 0.23-4 |
| utf8 | 1.1.4 |
| utils | 3.5.1 |
| vctrs | 0.1.0 |
| viridisLite | 0.3.0 |
| whisker | 0.3-2 |
| withr | 2.1.2 |
| xfun | 0.8 |
| xml2 | 1.2.0 |
| xts | 0.11-2 |
| yaml | 2.2.0 |
| zeallot | 0.1.0 |
| 动物园 | 1.8-6 |
后续步骤
请参阅 Azure 机器学习可用的组件集。