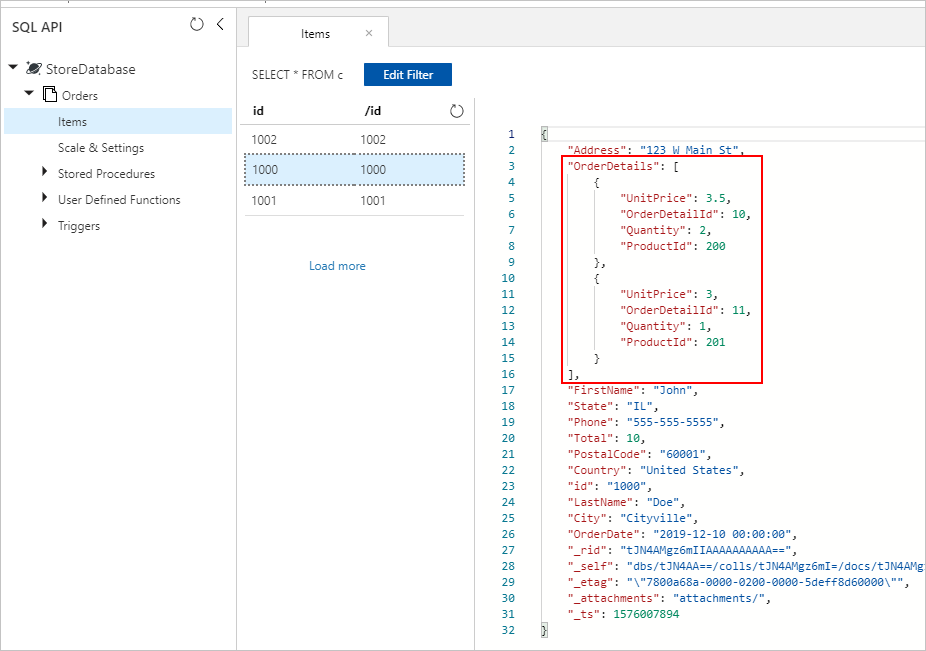
适用于: NoSQL
若要从关系数据库迁移到 Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL,可能需要更改数据模型以进行优化。
一种常见的转换方法是,通过将相关子项嵌入到一个 JSON 文档来反规范化数据。 本文探讨使用 Azure 数据工厂或 Azure Databricks 实现此目的的几个选项。 有关 Azure Cosmos DB 的数据建模的详细信息,请参阅 Azure Cosmos DB 中的数据建模。
示例方案
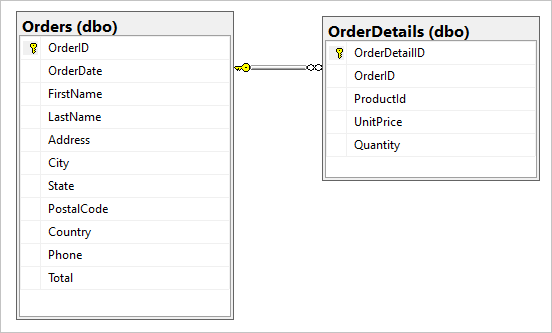
假设 SQL 数据库中包含以下两个表:Orders 和 OrderDetails。
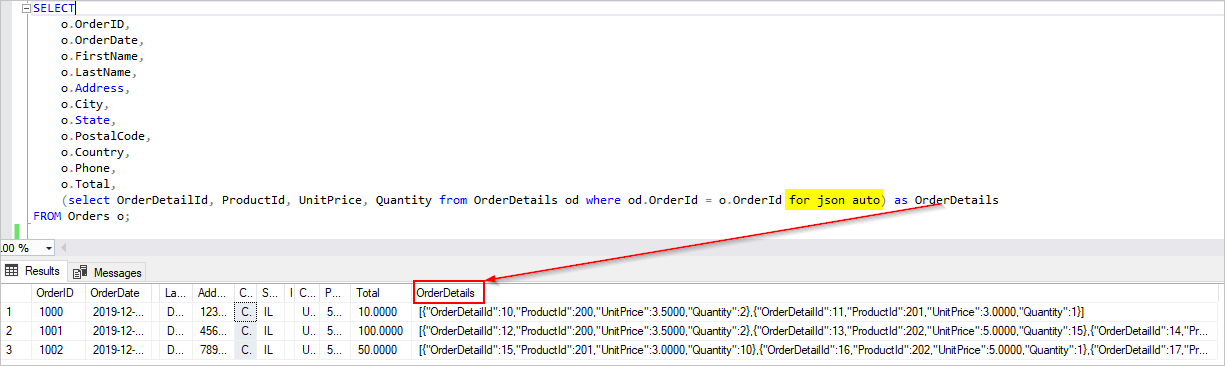
我们希望在迁移期间,将此一对多关系合并到一个 JSON 文档中。 若要创建单个文档,请使用 FOR JSON 创建 T-SQL 查询:
SELECT
o.OrderID,
o.OrderDate,
o.FirstName,
o.LastName,
o.Address,
o.City,
o.State,
o.PostalCode,
o.Country,
o.Phone,
o.Total,
(select OrderDetailId, ProductId, UnitPrice, Quantity from OrderDetails od where od.OrderId = o.OrderId for json auto) as OrderDetails
FROM Orders o;
此查询的结果将包括 Orders 表中的数据:
理想情况下,你希望使用单个 Azure 数据工厂 (ADF) 复制活动来查询用作源的 SQL 数据,并将输出作为适当的 JSON 对象直接写入 Azure Cosmos DB 接收器。 目前,无法在一个复制活动中执行所需的 JSON 转换。 如果我们尝试将上述查询的结果复制到 Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL 容器中,将会看到文档的字符串属性形式的 OrderDetails 字段,而不是预期的 JSON 数组。
可通过以下方式之一解决当前的这种限制:
- 使用包含两个复制活动的 Azure 数据工厂:
- 将 SQL 中的 JSON 格式的数据提取到位于中间 Blob 存储位置的某个文本文件
- 将 JSON 文本文件中的数据加载到 Azure Cosmos DB 中的某个容器。
- 使用 Azure Databricks 从 SQL 中读取数据并将其写入 Azure Cosmos DB - 我们将演示这两个选项。
让我们更详细地了解这些方法:
Azure 数据工厂
尽管我们无法将 OrderDetails 作为 JSON 数组嵌入到目标 Azure Cosmos DB 文档中,但可以使用两个独立的复制活动来解决该问题。
复制活动 #1:SqlJsonToBlobText
对于源数据,我们使用 SQL 查询通过 SQL Server OPENJSON 和 FOR JSON PATH 功能获取结果集,该结果集以单列的形式提供,每行包含一个 JSON 对象(表示订单):
SELECT [value] FROM OPENJSON(
(SELECT
id = o.OrderID,
o.OrderDate,
o.FirstName,
o.LastName,
o.Address,
o.City,
o.State,
o.PostalCode,
o.Country,
o.Phone,
o.Total,
(select OrderDetailId, ProductId, UnitPrice, Quantity from OrderDetails od where od.OrderId = o.OrderId for json auto) as OrderDetails
FROM Orders o FOR JSON PATH)
)
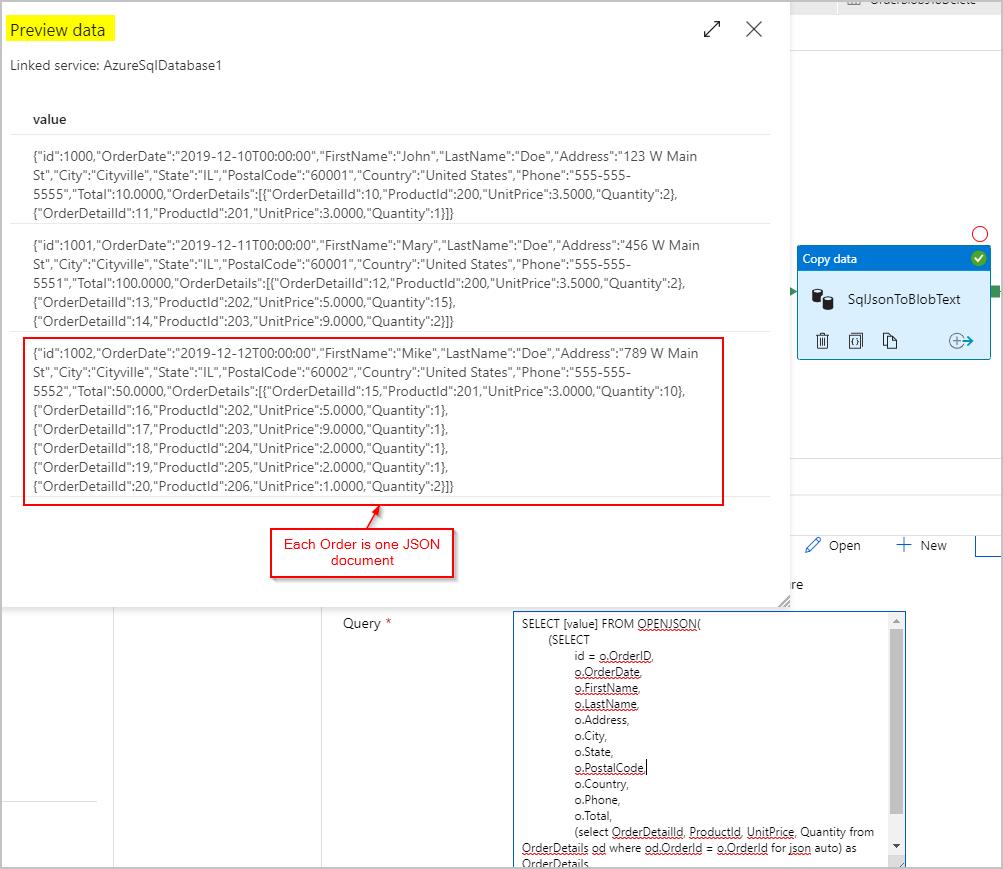
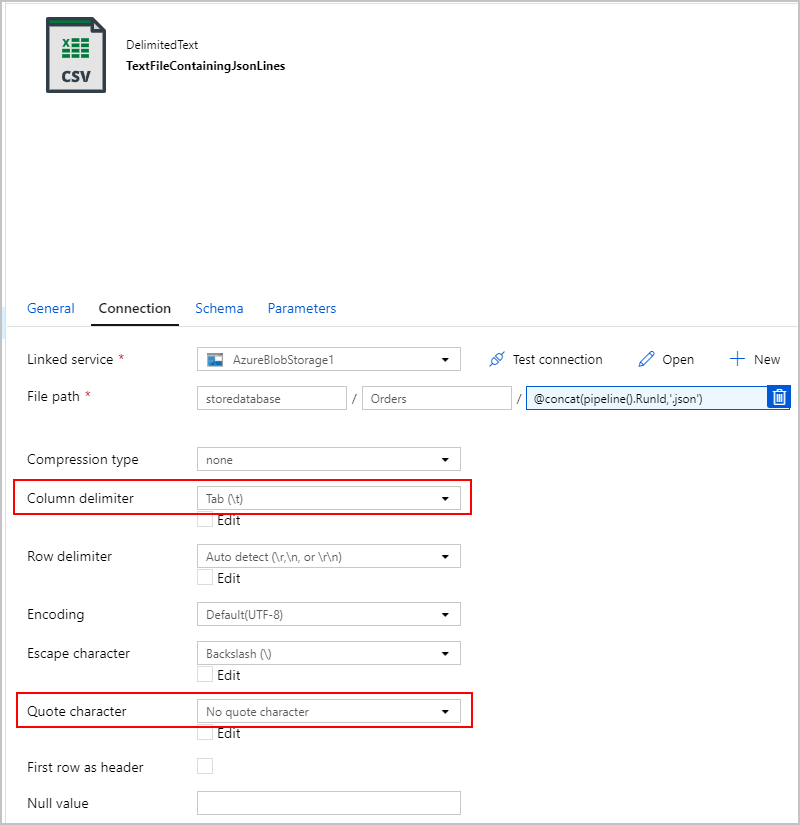
对于 SqlJsonToBlobText 复制活动的接收器,我们选择了“分隔文本”并将其指向 Azure Blob 存储中的特定文件夹。 此接收器包含一个动态生成的唯一文件名(例如 @concat(pipeline().RunId,'.json'))。
我们的文本文件实际上并不是“分隔的”,并且我们不希望使用逗号将其分析成单独的列。 我们还希望保留双引号 (""),并将“列分隔符”设置为制表符 ("\t") 或数据中未出现其他字符,然后将“引号字符”设置为“无引号字符”。
复制活动 #2:BlobJsonToCosmos
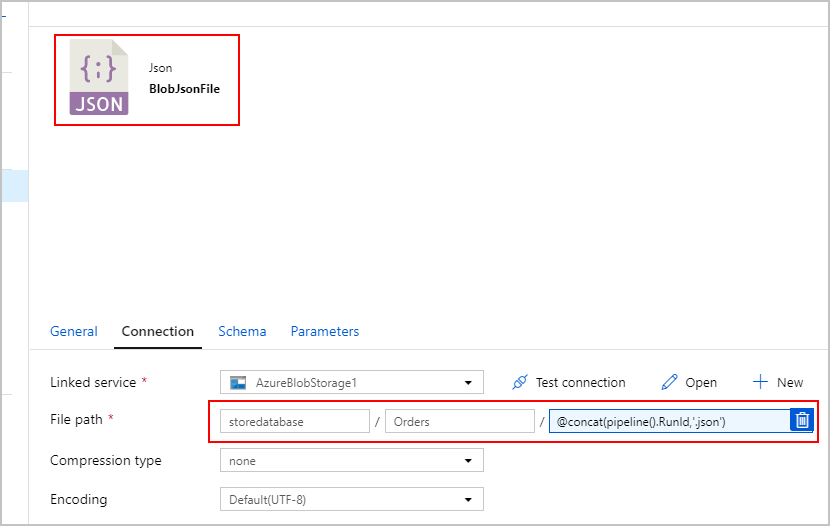
接下来,我们修改 ADF 管道:添加第二个复制活动,用于在 Azure Blob 存储中查找第一个活动创建的文本文件。 第二个复制活动将结果作为“JSON”源进行处理,将文本文件中找到的每个 JSON 行作为一个文档插入到 Azure Cosmos DB 接收器中。
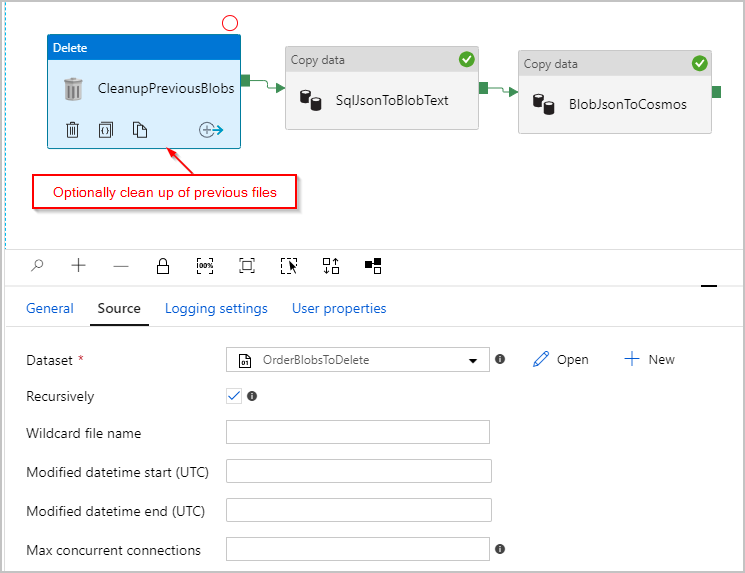
(可选)我们还将一个“删除”活动添加到了管道,以便在每次运行之前删除 /Orders/ 文件夹中剩余的所有旧文件。 现在,我们的 ADF 管道如下所示:
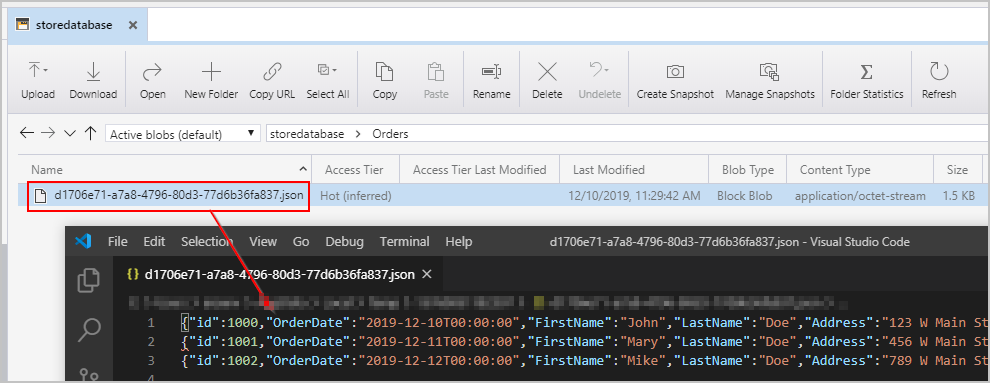
触发上述管道后,会看到中间 Azure Blob 存储位置创建了一个文件,其中的每行包含一个 JSON 对象:
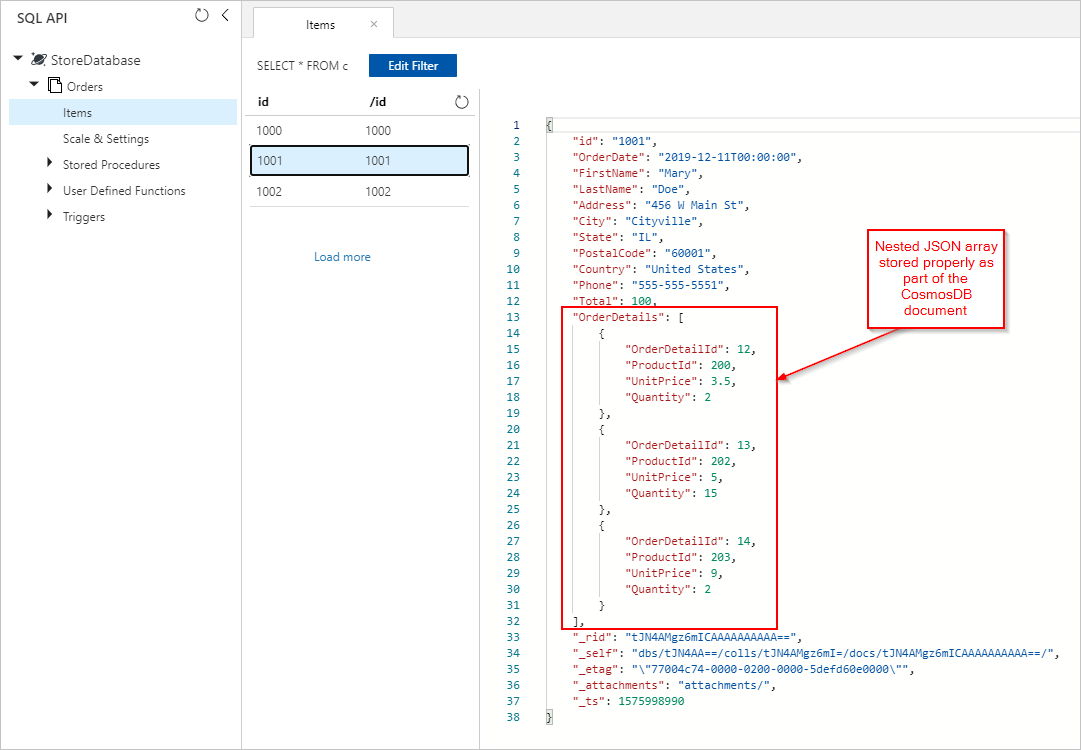
我们还会看到 Orders 文档,其中适当嵌入的 OrderDetails 已插入到 Azure Cosmos DB 集合中:
Azure Databricks
我们还可以在 Azure Databricks 中使用 Spark,将 SQL 数据库源中的数据复制到 Azure Cosmos DB 目标,而无需在 Azure Blob 存储中创建中间文本/JSON 文件。
注意
为简单清晰起见,代码片段显式包含了虚拟数据库密码,但在理想情况下,你应使用 Azure Databricks 机密。
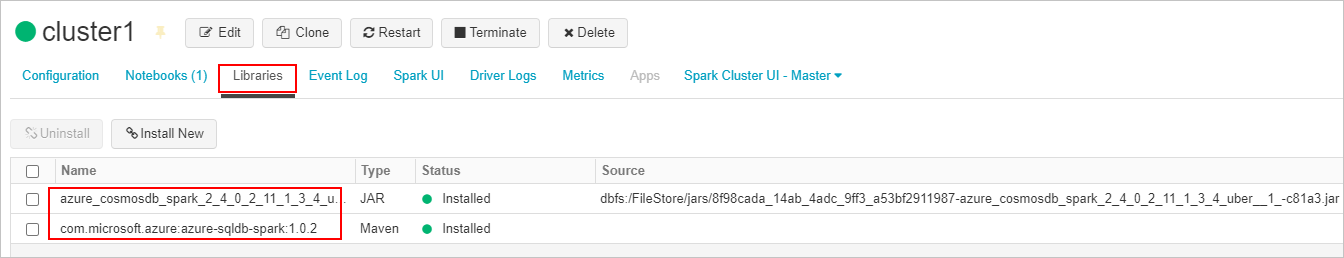
首先,创建所需的 SQL 连接器 并将 Azure Cosmos DB 连接器库并连接到 Azure Databricks 群集。 重启群集以确保加载库。
接下来,我们为 Scala 和 Python 提供了两个示例。
Scala
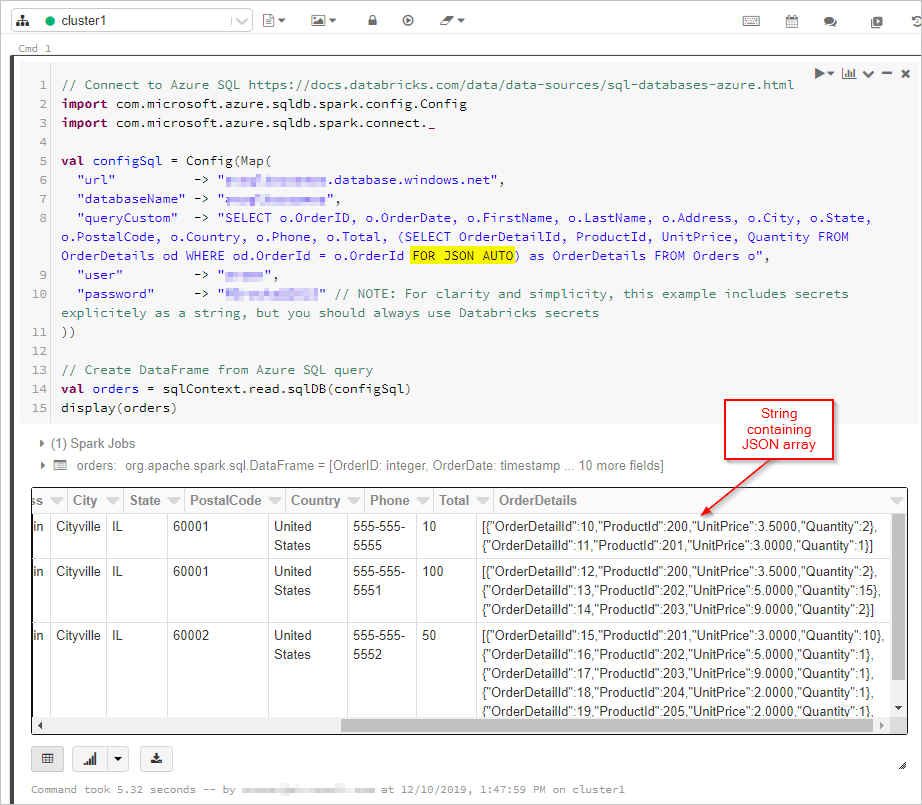
在这里,我们将得到 SQL 查询的结果,并将“FOR JSON”输出到数据帧中:
// Connect to Azure SQL /connectors/sql/
import com.microsoft.azure.sqldb.spark.config.Config
import com.microsoft.azure.sqldb.spark.connect._
val configSql = Config(Map(
"url" -> "xxxx.database.chinacloudapi.cn",
"databaseName" -> "xxxx",
"queryCustom" -> "SELECT o.OrderID, o.OrderDate, o.FirstName, o.LastName, o.Address, o.City, o.State, o.PostalCode, o.Country, o.Phone, o.Total, (SELECT OrderDetailId, ProductId, UnitPrice, Quantity FROM OrderDetails od WHERE od.OrderId = o.OrderId FOR JSON AUTO) as OrderDetails FROM Orders o",
"user" -> "xxxx",
"password" -> "xxxx" // NOTE: For clarity and simplicity, this example includes secrets explicitely as a string, but you should always use Databricks secrets
))
// Create DataFrame from Azure SQL query
val orders = sqlContext.read.sqlDB(configSql)
display(orders)
接下来,我们将连接到 Azure Cosmos DB 数据库和集合:
// Connect to Azure Cosmos DB https://docs.databricks.com/data/data-sources/azure/cosmosdb-connector.html
import org.joda.time._
import org.joda.time.format._
import com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.spark.schema._
import com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.spark.CosmosDBSpark
import com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.spark.config.Config
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._
import org.joda.time._
import org.joda.time.format._
import com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.spark.schema._
import com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.spark.CosmosDBSpark
import com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.spark.config.Config
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._
val configMap = Map(
"Endpoint" -> "https://xxxx.documents.azure.cn:443/",
// NOTE: For clarity and simplicity, this example includes secrets explicitely as a string, but you should always use Databricks secrets
"Masterkey" -> "xxxx",
"Database" -> "StoreDatabase",
"Collection" -> "Orders")
val configAzure Cosmos DB= Config(configMap)
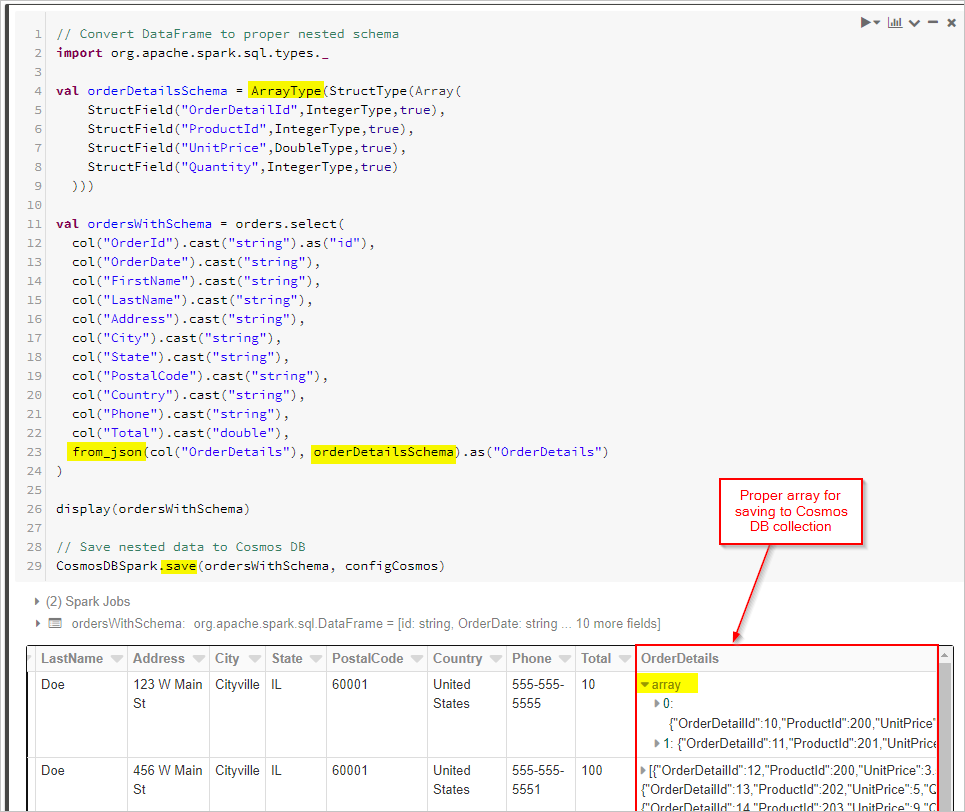
最后,我们定义架构并使用 from_json 应用数据帧,然后将数据帧保存到 Cosmos DB 集合。
// Convert DataFrame to proper nested schema
import org.apache.spark.sql.types._
val orderDetailsSchema = ArrayType(StructType(Array(
StructField("OrderDetailId",IntegerType,true),
StructField("ProductId",IntegerType,true),
StructField("UnitPrice",DoubleType,true),
StructField("Quantity",IntegerType,true)
)))
val ordersWithSchema = orders.select(
col("OrderId").cast("string").as("id"),
col("OrderDate").cast("string"),
col("FirstName").cast("string"),
col("LastName").cast("string"),
col("Address").cast("string"),
col("City").cast("string"),
col("State").cast("string"),
col("PostalCode").cast("string"),
col("Country").cast("string"),
col("Phone").cast("string"),
col("Total").cast("double"),
from_json(col("OrderDetails"), orderDetailsSchema).as("OrderDetails")
)
display(ordersWithSchema)
// Save nested data to Azure Cosmos DB
CosmosDBSpark.save(ordersWithSchema, configCosmos)
Python
作为替代方法,如果源数据库不支持 FOR JSON 或类似操作,则你可能需要在 Spark 中执行 JSON 转换。 或者,可以对大型数据集使用并行操作。 这里提供了一个 PySpark 示例。 首先配置第一个单元中的源数据库和目标数据库连接:
import uuid
import pyspark.sql.functions as F
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
from pyspark.sql.types import StringType,DateType,LongType,IntegerType,TimestampType
#JDBC connect details for SQL Server database
jdbcHostname = "jdbcHostname"
jdbcDatabase = "OrdersDB"
jdbcUsername = "jdbcUsername"
jdbcPassword = "jdbcPassword"
jdbcPort = "1433"
connectionProperties = {
"user" : jdbcUsername,
"password" : jdbcPassword,
"driver" : "com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver"
}
jdbcUrl = "jdbc:sqlserver://{0}:{1};database={2};user={3};password={4}".format(jdbcHostname, jdbcPort, jdbcDatabase, jdbcUsername, jdbcPassword)
#Connect details for Target Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL account
writeConfig = {
"Endpoint": "Endpoint",
"Masterkey": "Masterkey",
"Database": "OrdersDB",
"Collection": "Orders",
"Upsert": "true"
}
然后,我们将查询源数据库(在本案例中为 SQL Server)中的订单及订单明细记录,并将结果放入 Spark 数据帧。 我们还将创建一个列表,其中包含所有订单 ID 和并行操作的线程池:
import json
import ast
import pyspark.sql.functions as F
import uuid
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from functools import reduce
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext
from pyspark.sql.types import *
from pyspark.sql import *
from pyspark.sql.functions import exp
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
from pyspark.sql.functions import lit
from pyspark.sql.functions import array
from pyspark.sql.types import *
from multiprocessing.pool import ThreadPool
#get all orders
orders = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url=jdbcUrl, table="orders", properties=connectionProperties)
#get all order details
orderdetails = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url=jdbcUrl, table="orderdetails", properties=connectionProperties)
#get all OrderId values to pass to map function
orderids = orders.select('OrderId').collect()
#create thread pool big enough to process merge of details to orders in parallel
pool = ThreadPool(10)
然后,创建一个函数用于将 Orders 写入目标 API for NoSQL 集合。 此函数筛选给定订单 ID 的所有订单详细信息,将其转换为 JSON 数组,并将该数组插入 JSON 文档。 然后,该 JSON 文档将按该顺序写入目标 API for NoSQL 容器:
def writeOrder(orderid):
#filter the order on current value passed from map function
order = orders.filter(orders['OrderId'] == orderid[0])
#set id to be a uuid
order = order.withColumn("id", lit(str(uuid.uuid1())))
#add details field to order dataframe
order = order.withColumn("details", lit(''))
#filter order details dataframe to get details we want to merge into the order document
orderdetailsgroup = orderdetails.filter(orderdetails['OrderId'] == orderid[0])
#convert dataframe to pandas
orderpandas = order.toPandas()
#convert the order dataframe to json and remove enclosing brackets
orderjson = orderpandas.to_json(orient='records', force_ascii=False)
orderjson = orderjson[1:-1]
#convert orderjson to a dictionaory so we can set the details element with order details later
orderjsondata = json.loads(orderjson)
#convert orderdetailsgroup dataframe to json, but only if details were returned from the earlier filter
if (orderdetailsgroup.count() !=0):
#convert orderdetailsgroup to pandas dataframe to work better with json
orderdetailsgroup = orderdetailsgroup.toPandas()
#convert orderdetailsgroup to json string
jsonstring = orderdetailsgroup.to_json(orient='records', force_ascii=False)
#convert jsonstring to dictionary to ensure correct encoding and no corrupt records
jsonstring = json.loads(jsonstring)
#set details json element in orderjsondata to jsonstring which contains orderdetailsgroup - this merges order details into the order
orderjsondata['details'] = jsonstring
#convert dictionary to json
orderjsondata = json.dumps(orderjsondata)
#read the json into spark dataframe
df = spark.read.json(sc.parallelize([orderjsondata]))
#write the dataframe (this will be a single order record with merged many-to-one order details) to Azure Cosmos DB db using spark the connector
#https://docs.azure.cn/cosmos-db/spark-connector
df.write.format("com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.spark").mode("append").options(**writeConfig).save()
最后,我们将在线程池上使用映射函数调用要并行执行的 Python writeOrder 函数,并传入先前创建的订单 ID 列表:
#map order details to orders in parallel using the above function
pool.map(writeOrder, orderids)
在这两种方法中,最终都将在 Azure Cosmos DB 集合中的每个 Order 文档中获得正确保存的嵌入 OrderDetails: