重要
LUIS 将于 2025 年 10 月 1 日停用,从 2023 年 4 月 1 日开始,你将无法创建新的 LUIS 资源。 建议将 LUIS 应用程序迁移到对话语言理解,以便从持续的产品支持和多语言功能中受益。
通过此快速入门,使用 C#、Python 或 JavaScript 创建并查询带有 LUIS SDK 客户端库的 Azure LUIS 人工智能 (AI) 应用。 还可以使用 cURL 来发送使用 REST API 的请求。
通过语言理解 (LUIS),你可在用户的自然语言对话文本中应用自然语言处理 (NLP),以预测整体含义并提炼出相关的详细信息。
- 使用“创作”客户端库和 REST API,可以创建、编辑、训练和发布 LUIS 应用。
- 使用“预测运行时”客户端库和 REST API,可以查询已发布的应用。
使用适用于 .NET 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库执行以下操作:
- 创建应用
- 使用示例言语添加意向(机器学习实体)
- 训练和发布应用
- 查询预测运行时
参考文档 | 创作和预测库源代码 | 创作和预测 NuGet | C# 示例
先决条件
- .NET Core 和 .NET Core CLI 的当前版本。
- Azure 订阅 - 创建试用订阅
- 有了 Azure 订阅后,在 Azure 门户中创建语言理解创作资源,以获取创作密钥和终结点。 等待其部署并单击“转到资源”按钮。
- 需要从创建的资源获取密钥和终结点,以便将应用程序连接到语言理解创作。 你稍后会在快速入门中将密钥和终结点粘贴到下方的代码中。 可以使用免费定价层 (
F0) 来试用该服务。
- 需要从创建的资源获取密钥和终结点,以便将应用程序连接到语言理解创作。 你稍后会在快速入门中将密钥和终结点粘贴到下方的代码中。 可以使用免费定价层 (
设置
新建 C# 应用程序
在首选编辑器或 IDE 中创建新的 .NET Core 应用程序。
在控制台窗口(例如 CMD、PowerShell 或 Bash)中,使用 dotnet
new命令创建名为language-understanding-quickstart的新控制台应用。 此命令将创建包含单个源文件的简单“Hello World”C# 项目:Program.cs。dotnet new console -n language-understanding-quickstart将目录更改为新创建的应用文件夹。
cd language-understanding-quickstart可使用以下代码生成应用程序:
dotnet build生成输出不应包含警告或错误。
... Build succeeded. 0 Warning(s) 0 Error(s) ...
安装 NuGet 库
在应用程序目录中,使用以下命令安装适用于 .NET 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Language.LUIS.Authoring --version 3.2.0-preview.3
dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Language.LUIS.Runtime --version 3.1.0-preview.1
创作对象模型
语言理解 (LUIS) 创作客户端是对 Azure 进行身份验证的 LUISAuthoringClient 对象,其中包含创作密钥。
创作的代码示例
创建客户端后,可以使用此客户端访问如下所述的功能:
- 应用 - 创建、删除、发布
- 示例言语 - 添加、按 ID 删除
- 特征 - 管理短语列表
- 模型 - 管理意向和实体
- 模式 - 管理模式
- 训练 - 训练应用和轮询训练状态
- 版本 - 使用克隆、导出和删除操作进行管理
预测对象模型
语言理解 (LUIS) 预测运行时客户端是对 Azure 进行身份验证的 LUISRuntimeClient 对象,其中包含资源密钥。
预测运行时的代码示例
创建客户端后,可以使用此客户端访问如下所述的功能:
代码示例
以下代码片段演示如何使用适用于 Python 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库来执行以下操作:
添加依赖项
在首选的编辑器或 IDE 中,从项目目录打开 Program.cs 文件。 将现有 using 代码替换为以下 using 指令:
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Language.LUIS.Authoring;
using Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Language.LUIS.Authoring.Models;
using Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Language.LUIS.Runtime;
using Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Language.LUIS.Runtime.Models;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
添加样板代码
更改
Main方法的签名以允许异步调用:public static async Task Main()将其余代码添加到
Program类的Main方法中(除非另有指定)。
为应用创建变量
创建两组变量:第一组为你更改的变量,第二组保留在代码示例中显示的状态。
重要
完成后,请记住将密钥从代码中删除,并且永远不要公开发布该密钥。 对于生产来说,请使用安全的方式存储和访问凭据,例如 Azure Key Vault。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Azure AI 服务安全性一文。
- 创建用于保存创作密钥和资源名称的变量。
var key = "PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_AUTHORING_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE";
var authoringEndpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_AUTHORING_ENDPOINT_HERE";
var predictionEndpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_PREDICTION_ENDPOINT_HERE";
- 创建用于保存终结点、应用名称、版本和意向名称的变量。
var appName = "Contoso Pizza Company";
var versionId = "0.1";
var intentName = "OrderPizzaIntent";
验证客户端
使用密钥创建 ApiKeyServiceClientCredentials 对象,并在终结点中使用该对象创建一个 LUISAuthoringClient 对象。
var credentials = new Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Language.LUIS.Authoring.ApiKeyServiceClientCredentials(key);
var client = new LUISAuthoringClient(credentials) { Endpoint = authoringEndpoint };
创建 LUIS 应用
LUIS 应用包含自然语言处理 (NLP) 模型,包括意向、实体和示例言语。
创建 ApplicationCreateObject。 名称和语言区域性是必需的属性。 调用 Apps.AddAsync 方法。 响应为应用 ID。
var newApp = new ApplicationCreateObject
{
Culture = "en-us",
Name = appName,
InitialVersionId = versionId
};
var appId = await client.Apps.AddAsync(newApp);
为应用创建意向
LUIS 应用模型中的主要对象是意向。 意向与用户言语意向的分组相符。 用户可以提问,或者做出表述,指出希望机器人(或其他客户端应用程序)提供特定的有针对性响应。 意向的示例包括预订航班、询问目的地城市的天气,以及询问客户服务的联系信息。
使用唯一意向的名称创建 ModelCreateObject,然后将应用 ID、版本 ID 和 ModelCreateObject 传递给 Model.AddIntentAsync 方法。 响应为意向 ID。
intentName 值硬编码为 OrderPizzaIntent,作为intentName中变量的一部分。
await client.Model.AddIntentAsync(appId, versionId, new ModelCreateObject()
{
Name = intentName
});
为应用创建实体
尽管实体不是必需的,但在大多数应用中都可以看到实体。 实体从用户言语中提取信息,只有使用这些信息才能实现用户的意向。 有多种类型的预生成实体和自定义实体,每种实体具有自身的数据转换对象 (DTO) 模型。 在应用中添加的常见预生成实体包括 number、datetimeV2、geographyV2 和 ordinal。
必须知道,实体不会使用意向进行标记。 它们可以并且通常应用到多个意向。 只会为特定的单个意向标记示例用户言语。
实体的创建方法属于 Model 类的一部分。 每个实体类型有自身的数据转换对象 (DTO) 模型,该模型通常在 model 命名空间中包含单词 model。
实体创建代码会创建机器学习实体,其中包含子实体以及应用于 Quantity 子实体的功能。
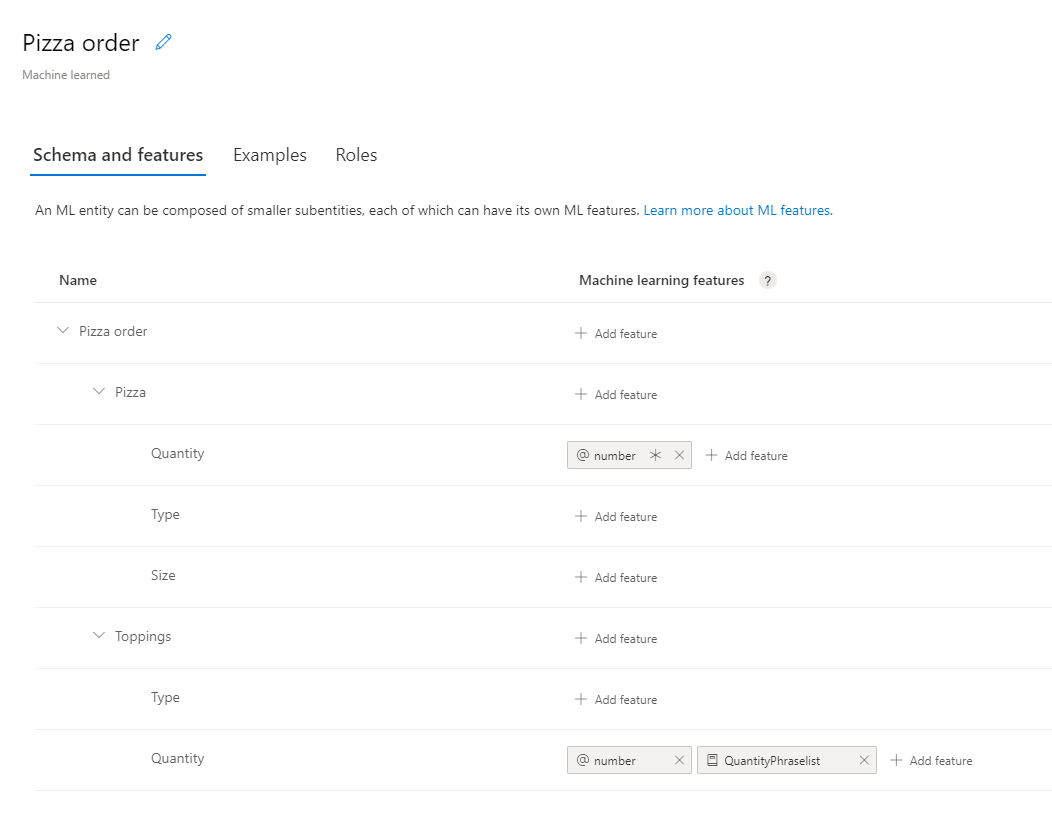
// Add Prebuilt entity
await client.Model.AddPrebuiltAsync(appId, versionId, new[] { "number" });
// </AuthoringCreatePrebuiltEntity>
// Define ml entity with children and grandchildren
var mlEntityDefinition = new EntityModelCreateObject
{
Name = "Pizza order",
Children = new[]
{
new ChildEntityModelCreateObject
{
Name = "Pizza",
Children = new[]
{
new ChildEntityModelCreateObject { Name = "Quantity" },
new ChildEntityModelCreateObject { Name = "Type" },
new ChildEntityModelCreateObject { Name = "Size" }
}
},
new ChildEntityModelCreateObject
{
Name = "Toppings",
Children = new[]
{
new ChildEntityModelCreateObject { Name = "Type" },
new ChildEntityModelCreateObject { Name = "Quantity" }
}
}
}
};
// Add ML entity
var mlEntityId = await client.Model.AddEntityAsync(appId, versionId, mlEntityDefinition); ;
// Add phraselist feature
var phraselistId = await client.Features.AddPhraseListAsync(appId, versionId, new PhraselistCreateObject
{
EnabledForAllModels = false,
IsExchangeable = true,
Name = "QuantityPhraselist",
Phrases = "few,more,extra"
});
// Get entity and subentities
var model = await client.Model.GetEntityAsync(appId, versionId, mlEntityId);
var toppingQuantityId = GetModelGrandchild(model, "Toppings", "Quantity");
var pizzaQuantityId = GetModelGrandchild(model, "Pizza", "Quantity");
// add model as feature to subentity model
await client.Features.AddEntityFeatureAsync(appId, versionId, pizzaQuantityId, new ModelFeatureInformation { ModelName = "number", IsRequired = true });
await client.Features.AddEntityFeatureAsync(appId, versionId, toppingQuantityId, new ModelFeatureInformation { ModelName = "number"});
// add phrase list as feature to subentity model
await client.Features.AddEntityFeatureAsync(appId, versionId, toppingQuantityId, new ModelFeatureInformation { FeatureName = "QuantityPhraselist" });
对该类使用以下方法,查找 Quantity 子实体的 ID,以便将功能分配给该子实体。
static Guid GetModelGrandchild(NDepthEntityExtractor model, string childName, string grandchildName)
{
return model.Children.
Single(c => c.Name == childName).
Children.
Single(c => c.Name == grandchildName).Id;
}
将示例言语添加到意向
为了确定言语的意向并提取实体,应用需要言语示例。 这些示例需要针对特定的单个意向,并且应该标记所有自定义实体。 无需标记预生成实体。
通过创建 ExampleLabelObject 对象的列表来添加示例言语(每个示例言语对应于一个对象)。 每个示例应使用实体名称和实体值的名称/值对字典来标记所有实体。 实体值应与示例言语文本中显示的值完全相同。
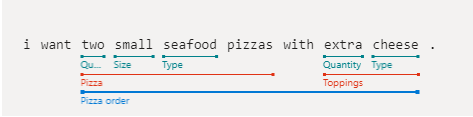
结合应用 ID、版本 ID 和示例调用 Examples.AddAsync。
// Define labeled example
var labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity = new ExampleLabelObject
{
Text = "I want two small seafood pizzas with extra cheese.",
IntentName = intentName,
EntityLabels = new[]
{
new EntityLabelObject
{
StartCharIndex = 7,
EndCharIndex = 48,
EntityName = "Pizza order",
Children = new[]
{
new EntityLabelObject
{
StartCharIndex = 7,
EndCharIndex = 30,
EntityName = "Pizza",
Children = new[]
{
new EntityLabelObject { StartCharIndex = 7, EndCharIndex = 9, EntityName = "Quantity" },
new EntityLabelObject { StartCharIndex = 11, EndCharIndex = 15, EntityName = "Size" },
new EntityLabelObject { StartCharIndex = 17, EndCharIndex = 23, EntityName = "Type" }
}
},
new EntityLabelObject
{
StartCharIndex = 37,
EndCharIndex = 48,
EntityName = "Toppings",
Children = new[]
{
new EntityLabelObject { StartCharIndex = 37, EndCharIndex = 41, EntityName = "Quantity" },
new EntityLabelObject { StartCharIndex = 43, EndCharIndex = 48, EntityName = "Type" }
}
}
}
},
}
};
// Add an example for the entity.
// Enable nested children to allow using multiple models with the same name.
// The quantity subentity and the phraselist could have the same exact name if this is set to True
await client.Examples.AddAsync(appId, versionId, labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity, enableNestedChildren: true);
训练应用
创建模型后,需要为此模型版本训练 LUIS 应用。 训练后的模型可在容器中使用,或者将其发布到过渡槽或生产槽。
Train.TrainVersionAsync 方法需要应用 ID 和版本 ID。
极小的模型(如本快速入门中所示的模型)很快就能完成训练。 对于生产级应用程序,应用的训练应该包括轮询调用 GetStatusAsync 方法以确定训练何时或者是否成功。 响应是一个 ModelTrainingInfo 对象列表,其中分别列出了每个对象的状态。 所有对象必须成功,才能将训练视为完成。
await client.Train.TrainVersionAsync(appId, versionId);
while (true)
{
var status = await client.Train.GetStatusAsync(appId, versionId);
if (status.All(m => m.Details.Status == "Success"))
{
// Assumes that we never fail, and that eventually we'll always succeed.
break;
}
}
将应用发布到生产槽
使用 PublishAsync 方法发布 LUIS 应用。 这会将当前已训练的版本发布到终结点上的指定槽。 客户端应用程序使用此终结点发送用户言语,以预测意向和提取实体。
await client.Apps.PublishAsync(appId, new ApplicationPublishObject { VersionId = versionId, IsStaging=false});
对预测运行时客户端进行身份验证
将 ApiKeyServiceClientCredentials 对象和密钥一起使用,并在终结点中使用该对象创建一个 LUISRuntimeClient 对象。
注意
此快速入门使用创作密钥作为运行时凭据的一部分。 允许创作密钥通过几个查询来查询运行时。 对于暂存和生产级别的代码,请将创作密钥替换为预测运行时密钥。
var runtimeClient = new LUISRuntimeClient(credentials) { Endpoint = predictionEndpoint };
从运行时获取预测
添加以下代码以创建对预测运行时的请求。
用户言语是 PredictionRequest 对象的一部分。
GetSlotPredictionAsync 方法需要多个参数,如应用 ID、槽名称、用于满足请求的预测请求对象。 其他选项(如详细、显示所有意向和日志)都是可选的。
// Production == slot name
var request = new PredictionRequest { Query = "I want two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa" };
var prediction = await runtimeClient.Prediction.GetSlotPredictionAsync(appId, "Production", request);
Console.Write(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(prediction, Formatting.Indented));
预测响应是一个 JSON 对象,其中包括意向和找到的所有实体。
{
"query": "I want two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa",
"prediction": {
"topIntent": "OrderPizzaIntent",
"intents": {
"OrderPizzaIntent": {
"score": 0.753606856
},
"None": {
"score": 0.119097039
}
},
"entities": {
"Pizza order": [
{
"Pizza": [
{
"Quantity": [
2
],
"Type": [
"pepperoni"
],
"Size": [
"small"
],
"$instance": {
"Quantity": [
{
"type": "builtin.number",
"text": "two",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 3,
"score": 0.968156934,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Type": [
{
"type": "Type",
"text": "pepperoni",
"startIndex": 17,
"length": 9,
"score": 0.9345611,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Size": [
{
"type": "Size",
"text": "small",
"startIndex": 11,
"length": 5,
"score": 0.9592077,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"Toppings": [
{
"Type": [
"salsa"
],
"Quantity": [
"more"
],
"$instance": {
"Type": [
{
"type": "Type",
"text": "salsa",
"startIndex": 44,
"length": 5,
"score": 0.7292897,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Quantity": [
{
"type": "Quantity",
"text": "more",
"startIndex": 39,
"length": 4,
"score": 0.9320932,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"$instance": {
"Pizza": [
{
"type": "Pizza",
"text": "two small pepperoni pizzas",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 26,
"score": 0.812199831,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Toppings": [
{
"type": "Toppings",
"text": "more salsa",
"startIndex": 39,
"length": 10,
"score": 0.7250252,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"$instance": {
"Pizza order": [
{
"type": "Pizza order",
"text": "two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 42,
"score": 0.769223332,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
}
}
运行应用程序
从应用程序目录使用 dotnet run 命令运行应用程序。
dotnet run
使用适用于 Node.js 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库来执行以下操作:
- 创建应用
- 使用示例言语添加意向(机器学习实体)
- 训练和发布应用
- 查询预测运行时
先决条件
- Node.js
- Azure 订阅 - 创建试用订阅
- 有了 Azure 订阅后,在 Azure 门户中创建语言理解创作资源,以获取创作密钥和终结点。 等待其部署并单击“转到资源”按钮。
- 需要从创建的资源获取密钥和终结点,以便将应用程序连接到语言理解创作。 你稍后会在快速入门中将密钥和终结点粘贴到下方的代码中。 可以使用免费定价层 (
F0) 来试用该服务。
- 需要从创建的资源获取密钥和终结点,以便将应用程序连接到语言理解创作。 你稍后会在快速入门中将密钥和终结点粘贴到下方的代码中。 可以使用免费定价层 (
设置
创建新的 JavaScript 应用程序
在控制台窗口中,为应用程序创建一个新目录,并将其移动到该目录中。
mkdir quickstart-sdk && cd quickstart-sdk通过创建
package.json文件,将该目录初始化为 JavaScript 应用程序。npm init -y为 JavaScript 代码创建名为
index.js的文件。touch index.js
安装 NPM 库
在应用程序目录中,使用以下命令安装依赖项,每次执行一行:
npm install @azure/ms-rest-js
npm install @azure/cognitiveservices-luis-authoring
npm install @azure/cognitiveservices-luis-runtime
package.json 应如下所示:
{
"name": "quickstart-sdk",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"@azure/cognitiveservices-luis-authoring": "^4.0.0-preview.3",
"@azure/cognitiveservices-luis-runtime": "^5.0.0",
"@azure/ms-rest-js": "^2.0.8"
}
}
创作对象模型
语言理解 (LUIS) 创作客户端是对 Azure 进行身份验证的 LUISAuthoringClient 对象,其中包含创作密钥。
创作的代码示例
创建客户端后,可以使用此客户端访问如下所述的功能:
- 应用 - 添加、删除、发布
- 示例言语 - 按批添加、按 ID 删除
- 特征 - 管理短语列表
- 模型 - 管理意向和实体
- 模式 - 管理模式
- 训练 - 训练应用和轮询训练状态
- 版本 - 使用克隆、导出和删除操作进行管理
预测对象模型
语言理解 (LUIS) 创作客户端是对 Azure 进行身份验证的 LUISAuthoringClient 对象,其中包含创作密钥。
预测运行时的代码示例
创建客户端后,可以使用此客户端访问如下所述的功能:
代码示例
以下代码片段演示如何使用适用于 Python 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库来执行以下操作:
添加依赖项
在首选编辑器或 IDE 中打开 index.js 文件,并添加以下依赖项。
const msRest = require("@azure/ms-rest-js");
const LUIS_Authoring = require("@azure/cognitiveservices-luis-authoring");
const LUIS_Prediction = require("@azure/cognitiveservices-luis-runtime");
添加样板代码
添加
quickstart方法及其调用。 此方法保存大部分剩余代码。 在文件末尾调用此方法。const quickstart = async () => { // add calls here } quickstart() .then(result => console.log("Done")) .catch(err => { console.log(`Error: ${err}`) })在 quickstart 方法中添加剩余代码(除非另有指定)。
为应用创建变量
创建两组变量:第一组为你更改的变量,第二组保留在代码示例中显示的状态。
重要
完成后,请记住将密钥从代码中删除,并且永远不要公开发布该密钥。 对于生产来说,请使用安全的方式存储和访问凭据,例如 Azure Key Vault。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Azure AI 服务安全性一文。
- 创建用于保存创作密钥和资源名称的变量。
const authoringKey = 'PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_AUTHORING_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE';
const authoringEndpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_AUTHORING_ENDPOINT_HERE";
const predictionEndpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_PREDICTION_ENDPOINT_HERE";
- 创建用于保存终结点、应用名称、版本和意向名称的变量。
const appName = "Contoso Pizza Company";
const versionId = "0.1";
const intentName = "OrderPizzaIntent";
验证客户端
使用密钥创建 CognitiveServicesCredentials 对象,并在终结点中使用该对象创建一个 LUISAuthoringClient 对象。
const luisAuthoringCredentials = new msRest.ApiKeyCredentials({
inHeader: { "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key": authoringKey }
});
const client = new LUIS_Authoring.LUISAuthoringClient(
luisAuthoringCredentials,
authoringEndpoint
);
创建 LUIS 应用
LUIS 应用包含自然语言处理 (NLP) 模型,包括意向、实体和示例言语。
创建 AppsOperation 对象的 add 方法,用于创建应用。 名称和语言区域性是必需的属性。
const create_app_payload = {
name: appName,
initialVersionId: versionId,
culture: "en-us"
};
const createAppResult = await client.apps.add(
create_app_payload
);
const appId = createAppResult.body
为应用创建意向
LUIS 应用模型中的主要对象是意向。 意向与用户言语意向的分组相符。 用户可以提问,或者做出表述,指出希望机器人(或其他客户端应用程序)提供特定的有针对性响应。 意向的示例包括预订航班、询问目的地城市的天气,以及询问客户服务的联系信息。
将 model.add_intent 方法与唯一意向的名称配合使用,然后传递应用 ID、版本 ID 和新的意向名称。
intentName 值硬编码为 OrderPizzaIntent,作为intentName中变量的一部分。
await client.model.addIntent(
appId,
versionId,
{ name: intentName }
);
为应用创建实体
尽管实体不是必需的,但在大多数应用中都可以看到实体。 实体从用户言语中提取信息,只有使用这些信息才能实现用户的意向。 有多种类型的预生成实体和自定义实体,每种实体具有自身的数据转换对象 (DTO) 模型。 在应用中添加的常见预生成实体包括 number、datetimeV2、geographyV2 和 ordinal。
必须知道,实体不会使用意向进行标记。 它们可以并且通常应用到多个意向。 只会为特定的单个意向标记示例用户言语。
实体的创建方法属于 Model 类的一部分。 每个实体类型有自身的数据转换对象 (DTO) 模型。
实体创建代码会创建机器学习实体,其中包含子实体以及应用于 Quantity 子实体的功能。

// Add Prebuilt entity
await client.model.addPrebuilt(appId, versionId, ["number"]);
// Define ml entity with children and grandchildren
const mlEntityDefinition = {
name: "Pizza order",
children: [
{
name: "Pizza",
children: [
{ name: "Quantity" },
{ name: "Type" },
{ name: "Size" }
]
},
{
name: "Toppings",
children: [
{ name: "Type" },
{ name: "Quantity" }
]
}
]
};
// Add ML entity
const response = await client.model.addEntity(appId, versionId, mlEntityDefinition);
const mlEntityId = response.body;
// Add phraselist feature
const phraselistResponse = await client.features.addPhraseList(appId, versionId, {
enabledForAllModels: false,
isExchangeable: true,
name: "QuantityPhraselist",
phrases: "few,more,extra"
});
const phraseListId = phraselistResponse.body;
// Get entity and subentities
const model = await client.model.getEntity(appId, versionId, mlEntityId);
const toppingQuantityId = getModelGrandchild(model, "Toppings", "Quantity");
const pizzaQuantityId = getModelGrandchild(model, "Pizza", "Quantity");
// add model as feature to subentity model
await client.features.addEntityFeature(appId, versionId, pizzaQuantityId, { modelName: "number", isRequired: true });
await client.features.addEntityFeature(appId, versionId, toppingQuantityId, { modelName: "number" });
// <AuthoringAddModelAsFeature>
// add phrase list as feature to subentity model
await client.features.addEntityFeature(appId, versionId, toppingQuantityId, { featureName: "QuantityPhraselist" });
将以下方法置于 quickstart 方法之上,查找 Quantity 子实体的 ID,以便将功能分配给该子实体。
const getModelGrandchild = (model, childName, grandchildName) => {
return model.children.find(c => c.name == childName).children.find(c => c.name == grandchildName).id
}
将示例言语添加到意向
为了确定言语的意向并提取实体,应用需要言语示例。 这些示例需要针对特定的单个意向,并且应该标记所有自定义实体。 无需标记预生成实体。
通过创建 ExampleLabelObject 对象的列表来添加示例言语(每个示例言语对应于一个对象)。 每个示例应使用实体名称和实体值的名称/值对字典来标记所有实体。 实体值应与示例言语文本中显示的值完全相同。

结合应用 ID、版本 ID 和示例调用 examples.add。
// Define labeled example
const labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity =
{
text: "I want two small seafood pizzas with extra cheese.",
intentName: intentName,
entityLabels: [
{
startCharIndex: 7,
endCharIndex: 48,
entityName: "Pizza order",
children: [
{
startCharIndex: 7,
endCharIndex: 30,
entityName: "Pizza",
children: [
{
startCharIndex: 7,
endCharIndex: 9,
entityName: "Quantity"
},
{
startCharIndex: 11,
endCharIndex: 15,
entityName: "Size"
},
{
startCharIndex: 17,
endCharIndex: 23,
entityName: "Type"
}]
},
{
startCharIndex: 37,
endCharIndex: 48,
entityName: "Toppings",
children: [
{
startCharIndex: 37,
endCharIndex: 41,
entityName: "Quantity"
},
{
startCharIndex: 43,
endCharIndex: 48,
entityName: "Type"
}]
}
]
}
]
};
console.log("Labeled Example Utterance:", JSON.stringify(labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity, null, 4 ));
// Add an example for the entity.
// Enable nested children to allow using multiple models with the same name.
// The quantity subentity and the phraselist could have the same exact name if this is set to True
await client.examples.add(appId, versionId, labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity, { enableNestedChildren: true });
训练应用
创建模型后,需要为此模型版本训练 LUIS 应用。 训练后的模型可在容器中使用,或者将其发布到过渡槽或生产槽。
train.trainVersion 方法需要应用 ID 和版本 ID。
极小的模型(如本快速入门中所示的模型)很快就能完成训练。 对于生产级应用程序,应用的训练应该包括轮询调用 get_status 方法以确定训练何时成功或者是否成功。 响应是一个 ModelTrainingInfo 对象列表,其中分别列出了每个对象的状态。 所有对象必须成功,才能将训练视为完成。
await client.train.trainVersion(appId, versionId);
while (true) {
const status = await client.train.getStatus(appId, versionId);
if (status.every(m => m.details.status == "Success")) {
// Assumes that we never fail, and that eventually we'll always succeed.
break;
}
}
将应用发布到生产槽
使用 app.publish 方法发布 LUIS 应用。 这会将当前已训练的版本发布到终结点上的指定槽。 客户端应用程序使用此终结点发送用户言语,以预测意向和提取实体。
await client.apps.publish(appId, { versionId: versionId, isStaging: false });
对预测运行时客户端进行身份验证
将 msRest.ApiKeyCredentials 对象与密钥一起使用,并在终结点中使用该对象创建一个 LUIS.LUISRuntimeClient 对象。
注意
此快速入门使用创作密钥作为运行时凭据的一部分。 允许创作密钥通过几个查询来查询运行时。 对于暂存和生产级别的代码,请将创作密钥替换为预测运行时密钥。
const luisPredictionClient = new LUIS_Prediction.LUISRuntimeClient(
luisAuthoringCredentials,
predictionEndpoint
);
从运行时获取预测
添加以下代码以创建对预测运行时的请求。 用户言语是 predictionRequest 对象的一部分。
luisRuntimeClient.prediction.getSlotPrediction 方法需要多个参数,如应用 ID、槽名称、用于满足请求的预测请求对象。 其他选项(如详细、显示所有意向和日志)都是可选的。
// Production == slot name
const request = { query: "I want two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa" };
const response = await luisPredictionClient.prediction.getSlotPrediction(appId, "Production", request);
console.log(JSON.stringify(response.prediction, null, 4 ));
预测响应是一个 JSON 对象,其中包括意向和找到的所有实体。
{
"query": "I want two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa",
"prediction": {
"topIntent": "OrderPizzaIntent",
"intents": {
"OrderPizzaIntent": {
"score": 0.753606856
},
"None": {
"score": 0.119097039
}
},
"entities": {
"Pizza order": [
{
"Pizza": [
{
"Quantity": [
2
],
"Type": [
"pepperoni"
],
"Size": [
"small"
],
"$instance": {
"Quantity": [
{
"type": "builtin.number",
"text": "two",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 3,
"score": 0.968156934,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Type": [
{
"type": "Type",
"text": "pepperoni",
"startIndex": 17,
"length": 9,
"score": 0.9345611,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Size": [
{
"type": "Size",
"text": "small",
"startIndex": 11,
"length": 5,
"score": 0.9592077,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"Toppings": [
{
"Type": [
"salsa"
],
"Quantity": [
"more"
],
"$instance": {
"Type": [
{
"type": "Type",
"text": "salsa",
"startIndex": 44,
"length": 5,
"score": 0.7292897,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Quantity": [
{
"type": "Quantity",
"text": "more",
"startIndex": 39,
"length": 4,
"score": 0.9320932,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"$instance": {
"Pizza": [
{
"type": "Pizza",
"text": "two small pepperoni pizzas",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 26,
"score": 0.812199831,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Toppings": [
{
"type": "Toppings",
"text": "more salsa",
"startIndex": 39,
"length": 10,
"score": 0.7250252,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"$instance": {
"Pizza order": [
{
"type": "Pizza order",
"text": "two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 42,
"score": 0.769223332,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
}
}
运行应用程序
在快速入门文件中使用 node index.js 命令运行应用程序。
node index.js
使用适用于 Python 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库来执行以下操作:
- 创建应用
- 使用示例言语添加意向(机器学习实体)
- 训练和发布应用
- 查询预测运行时
参考文档 | 创作和预测库源代码 | 包 (Pypi) | 示例
先决条件
- 最新版本的 Python 3.x。
- Azure 订阅 - 创建试用订阅
- 有了 Azure 订阅后,在 Azure 门户中创建语言理解创作资源,以获取创作密钥和终结点。 等待其部署并单击“转到资源”按钮。
- 需要从创建的资源获取密钥和终结点,以便将应用程序连接到语言理解创作。 你稍后会在快速入门中将密钥和终结点粘贴到下方的代码中。 可以使用免费定价层 (
F0) 来试用该服务。
- 需要从创建的资源获取密钥和终结点,以便将应用程序连接到语言理解创作。 你稍后会在快速入门中将密钥和终结点粘贴到下方的代码中。 可以使用免费定价层 (
设置
创建新的 Python 应用程序
在控制台窗口中,为应用程序创建一个新目录,并将其移动到该目录中。
mkdir quickstart-sdk && cd quickstart-sdk为 Python 代码创建名为
authoring_and_predict.py的文件。touch authoring_and_predict.py
使用 Pip 安装客户端库
在应用程序目录中,使用以下命令安装适用于 python 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库:
pip install azure-cognitiveservices-language-luis
创作对象模型
语言理解 (LUIS) 创作客户端是对 Azure 进行身份验证的 LUISAuthoringClient 对象,其中包含创作密钥。
创作的代码示例
创建客户端后,可以使用此客户端访问如下所述的功能:
- 应用 - 创建、删除、发布
- 示例言语 - 按批添加、按 ID 删除
- 特征 - 管理短语列表
- 模型 - 管理意向和实体
- 模式 - 管理模式
- 训练 - 训练应用和轮询训练状态
- 版本 - 使用克隆、导出和删除操作进行管理
预测对象模型
语言理解 (LUIS) 预测运行时客户端是对 Azure 进行身份验证的 LUISRuntimeClient 对象,其中包含资源密钥。
预测运行时的代码示例
创建客户端后,可以使用此客户端访问如下所述的功能:
代码示例
以下代码片段演示如何使用适用于 Python 的语言理解 (LUIS) 客户端库来执行以下操作:
添加依赖项
将客户端库添加到 python 文件中。
from azure.cognitiveservices.language.luis.authoring import LUISAuthoringClient
from azure.cognitiveservices.language.luis.authoring.models import ApplicationCreateObject
from azure.cognitiveservices.language.luis.runtime import LUISRuntimeClient
from msrest.authentication import CognitiveServicesCredentials
from functools import reduce
import json, time, uuid
添加样板代码
添加
quickstart方法及其调用。 此方法保存大部分剩余代码。 在文件末尾调用此方法。def quickstart(): # add calls here, remember to indent properly quickstart()在 quickstart 方法中添加剩余代码(除非另有指定)。
为应用创建变量
创建两组变量:第一组为你更改的变量,第二组保留在代码示例中显示的状态。
重要
完成后,请记住将密钥从代码中删除,并且永远不要公开发布该密钥。 对于生产来说,请使用安全的方式存储和访问凭据,例如 Azure Key Vault。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Azure AI 服务安全性一文。
- 创建用于保存创作密钥和资源名称的变量。
authoringKey = 'PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_AUTHORING_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE'
authoringEndpoint = 'PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_AUTHORING_ENDPOINT_HERE'
predictionKey = 'PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_PREDICTION_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE'
predictionEndpoint = 'PASTE_YOUR_LUIS_PREDICTION_ENDPOINT_HERE'
- 创建用于保存终结点、应用名称、版本和意向名称的变量。
# We use a UUID to avoid name collisions.
appName = "Contoso Pizza Company " + str(uuid.uuid4())
versionId = "0.1"
intentName = "OrderPizzaIntent"
验证客户端
使用密钥创建 CognitiveServicesCredentials 对象,并在终结点中使用该对象创建一个 LUISAuthoringClient 对象。
client = LUISAuthoringClient(authoringEndpoint, CognitiveServicesCredentials(authoringKey))
创建 LUIS 应用
LUIS 应用包含自然语言处理 (NLP) 模型,包括意向、实体和示例言语。
创建 AppsOperation 对象的 add 方法,用于创建应用。 名称和语言区域性是必需的属性。
# define app basics
appDefinition = ApplicationCreateObject (name=appName, initial_version_id=versionId, culture='en-us')
# create app
app_id = client.apps.add(appDefinition)
# get app id - necessary for all other changes
print("Created LUIS app with ID {}".format(app_id))
为应用创建意向
LUIS 应用模型中的主要对象是意向。 意向与用户言语意向的分组相符。 用户可以提问,或者做出表述,指出希望机器人(或其他客户端应用程序)提供特定的有针对性响应。 意向的示例包括预订航班、询问目的地城市的天气,以及询问客户服务的联系信息。
将 model.add_intent 方法与唯一意向的名称配合使用,然后传递应用 ID、版本 ID 和新的意向名称。
intentName 值硬编码为 OrderPizzaIntent,作为intentName中变量的一部分。
client.model.add_intent(app_id, versionId, intentName)
为应用创建实体
尽管实体不是必需的,但在大多数应用中都可以看到实体。 实体从用户言语中提取信息,只有使用这些信息才能实现用户的意向。 有多种类型的预生成实体和自定义实体,每种实体具有自身的数据转换对象 (DTO) 模型。 在应用中添加的常见预生成实体包括 number、datetimeV2、geographyV2 和 ordinal。
必须知道,实体不会使用意向进行标记。 它们可以并且通常应用到多个意向。 只会为特定的单个意向标记示例用户言语。
实体的创建方法属于 ModelOperations 类的一部分。 每个实体类型有自身的数据转换对象 (DTO) 模型。
实体创建代码会创建机器学习实体,其中包含子实体以及应用于 Quantity 子实体的功能。

# Add Prebuilt entity
client.model.add_prebuilt(app_id, versionId, prebuilt_extractor_names=["number"])
# define machine-learned entity
mlEntityDefinition = [
{
"name": "Pizza",
"children": [
{ "name": "Quantity" },
{ "name": "Type" },
{ "name": "Size" }
]
},
{
"name": "Toppings",
"children": [
{ "name": "Type" },
{ "name": "Quantity" }
]
}]
# add entity to app
modelId = client.model.add_entity(app_id, versionId, name="Pizza order", children=mlEntityDefinition)
# define phraselist - add phrases as significant vocabulary to app
phraseList = {
"enabledForAllModels": False,
"isExchangeable": True,
"name": "QuantityPhraselist",
"phrases": "few,more,extra"
}
# add phrase list to app
phraseListId = client.features.add_phrase_list(app_id, versionId, phraseList)
# Get entity and subentities
modelObject = client.model.get_entity(app_id, versionId, modelId)
toppingQuantityId = get_grandchild_id(modelObject, "Toppings", "Quantity")
pizzaQuantityId = get_grandchild_id(modelObject, "Pizza", "Quantity")
# add model as feature to subentity model
prebuiltFeatureRequiredDefinition = { "model_name": "number", "is_required": True }
client.features.add_entity_feature(app_id, versionId, pizzaQuantityId, prebuiltFeatureRequiredDefinition)
# add model as feature to subentity model
prebuiltFeatureNotRequiredDefinition = { "model_name": "number" }
client.features.add_entity_feature(app_id, versionId, toppingQuantityId, prebuiltFeatureNotRequiredDefinition)
# add phrase list as feature to subentity model
phraseListFeatureDefinition = { "feature_name": "QuantityPhraselist", "model_name": None }
client.features.add_entity_feature(app_id, versionId, toppingQuantityId, phraseListFeatureDefinition)
将以下方法置于 quickstart 方法之上,查找 Quantity 子实体的 ID,以便将功能分配给该子实体。
def get_grandchild_id(model, childName, grandChildName):
theseChildren = next(filter((lambda child: child.name == childName), model.children))
theseGrandchildren = next(filter((lambda child: child.name == grandChildName), theseChildren.children))
grandChildId = theseGrandchildren.id
return grandChildId
将示例言语添加到意向
为了确定言语的意向并提取实体,应用需要言语示例。 这些示例需要针对特定的单个意向,并且应该标记所有自定义实体。 无需标记预生成实体。
通过创建 ExampleLabelObject 对象的列表来添加示例言语(每个示例言语对应于一个对象)。 每个示例应使用实体名称和实体值的名称/值对字典来标记所有实体。 实体值应与示例言语文本中显示的值完全相同。

结合应用 ID、版本 ID 和示例调用 examples.add。
# Define labeled example
labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity = {
"text": "I want two small seafood pizzas with extra cheese.",
"intentName": intentName,
"entityLabels": [
{
"startCharIndex": 7,
"endCharIndex": 48,
"entityName": "Pizza order",
"children": [
{
"startCharIndex": 7,
"endCharIndex": 30,
"entityName": "Pizza",
"children": [
{
"startCharIndex": 7,
"endCharIndex": 9,
"entityName": "Quantity"
},
{
"startCharIndex": 11,
"endCharIndex": 15,
"entityName": "Size"
},
{
"startCharIndex": 17,
"endCharIndex": 23,
"entityName": "Type"
}]
},
{
"startCharIndex": 37,
"endCharIndex": 48,
"entityName": "Toppings",
"children": [
{
"startCharIndex": 37,
"endCharIndex": 41,
"entityName": "Quantity"
},
{
"startCharIndex": 43,
"endCharIndex": 48,
"entityName": "Type"
}]
}
]
}
]
}
print("Labeled Example Utterance:", labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity)
# Add an example for the entity.
# Enable nested children to allow using multiple models with the same name.
# The quantity subentity and the phraselist could have the same exact name if this is set to True
client.examples.add(app_id, versionId, labeledExampleUtteranceWithMLEntity, { "enableNestedChildren": True })
训练应用
创建模型后,需要为此模型版本训练 LUIS 应用。 训练后的模型可在容器中使用,或者将其发布到过渡槽或生产槽。
train.train_version 方法需要应用 ID 和版本 ID。
极小的模型(如本快速入门中所示的模型)很快就能完成训练。 对于生产级应用程序,应用的训练应该包括轮询调用 get_status 方法以确定训练何时成功或者是否成功。 响应是一个 ModelTrainingInfo 对象列表,其中分别列出了每个对象的状态。 所有对象必须成功,才能将训练视为完成。
client.train.train_version(app_id, versionId)
waiting = True
while waiting:
info = client.train.get_status(app_id, versionId)
# get_status returns a list of training statuses, one for each model. Loop through them and make sure all are done.
waiting = any(map(lambda x: 'Queued' == x.details.status or 'InProgress' == x.details.status, info))
if waiting:
print ("Waiting 10 seconds for training to complete...")
time.sleep(10)
else:
print ("trained")
waiting = False
将应用发布到生产槽
使用 app.publish 方法发布 LUIS 应用。 这会将当前已训练的版本发布到终结点上的指定槽。 客户端应用程序使用此终结点发送用户言语,以预测意向和提取实体。
# Mark the app as public so we can query it using any prediction endpoint.
# Note: For production scenarios, you should instead assign the app to your own LUIS prediction endpoint. See:
# https://docs.azure.cn/cognitive-services/luis/luis-how-to-azure-subscription#assign-a-resource-to-an-app
client.apps.update_settings(app_id, is_public=True)
responseEndpointInfo = client.apps.publish(app_id, versionId, is_staging=False)
对预测运行时客户端进行身份验证
将凭据对象与密钥一起使用,并在终结点中使用该对象创建一个 LUISRuntimeClientConfiguration 对象。
注意
此快速入门使用创作密钥作为运行时凭据的一部分。 允许创作密钥通过几个查询来查询运行时。 对于暂存和生产级别的代码,请将创作密钥替换为预测运行时密钥。
runtimeCredentials = CognitiveServicesCredentials(predictionKey)
clientRuntime = LUISRuntimeClient(endpoint=predictionEndpoint, credentials=runtimeCredentials)
从运行时获取预测
添加以下代码以创建对预测运行时的请求。
用户言语是 prediction_request 对象的一部分。
get_slot_prediction 方法需要多个参数,如应用 ID、槽名称,以及用于履行请求的预测请求对象。 其他选项(如详细、显示所有意向和日志)都是可选的。 该请求返回 PredictionResponse 对象。
# Production == slot name
predictionRequest = { "query" : "I want two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa" }
predictionResponse = clientRuntime.prediction.get_slot_prediction(app_id, "Production", predictionRequest)
print("Top intent: {}".format(predictionResponse.prediction.top_intent))
print("Sentiment: {}".format (predictionResponse.prediction.sentiment))
print("Intents: ")
for intent in predictionResponse.prediction.intents:
print("\t{}".format (json.dumps (intent)))
print("Entities: {}".format (predictionResponse.prediction.entities))
预测响应是一个 JSON 对象,其中包括意向和找到的所有实体。
{
"query": "I want two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa",
"prediction": {
"topIntent": "OrderPizzaIntent",
"intents": {
"OrderPizzaIntent": {
"score": 0.753606856
},
"None": {
"score": 0.119097039
}
},
"entities": {
"Pizza order": [
{
"Pizza": [
{
"Quantity": [
2
],
"Type": [
"pepperoni"
],
"Size": [
"small"
],
"$instance": {
"Quantity": [
{
"type": "builtin.number",
"text": "two",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 3,
"score": 0.968156934,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Type": [
{
"type": "Type",
"text": "pepperoni",
"startIndex": 17,
"length": 9,
"score": 0.9345611,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Size": [
{
"type": "Size",
"text": "small",
"startIndex": 11,
"length": 5,
"score": 0.9592077,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"Toppings": [
{
"Type": [
"salsa"
],
"Quantity": [
"more"
],
"$instance": {
"Type": [
{
"type": "Type",
"text": "salsa",
"startIndex": 44,
"length": 5,
"score": 0.7292897,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Quantity": [
{
"type": "Quantity",
"text": "more",
"startIndex": 39,
"length": 4,
"score": 0.9320932,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"$instance": {
"Pizza": [
{
"type": "Pizza",
"text": "two small pepperoni pizzas",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 26,
"score": 0.812199831,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
],
"Toppings": [
{
"type": "Toppings",
"text": "more salsa",
"startIndex": 39,
"length": 10,
"score": 0.7250252,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
],
"$instance": {
"Pizza order": [
{
"type": "Pizza order",
"text": "two small pepperoni pizzas with more salsa",
"startIndex": 7,
"length": 42,
"score": 0.769223332,
"modelTypeId": 1,
"modelType": "Entity Extractor",
"recognitionSources": [
"model"
]
}
]
}
}
}
}
运行应用程序
在快速入门文件中使用 python 命令运行应用程序。
python authoring_and_predict.py
在本快速入门中,将按顺序执行三次 REST 调用。
- 首先,需使用 REST 批处理添加标签调用来上传一批示例语句,这些示例语句将用于训练 Pizza 应用模型。
- 接下来,开始使用 REST 训练应用程序版本调用来开启 Pizza 应用的训练会话。
- 最后,要使用 REST 获取版本训练状态调用获取 Pizza 应用训练会话的状态。
先决条件
免费的 LUIS 帐户。
文本编辑器,如 Visual Studio Code。
命令行程序 cURL。 在 macOS、大多数 Linux 分发版和 Windows 10 版本 1803 及更高版本上已安装该 cURL 程序。
若需要安装 cURL,可在 cURL 下载页中下载 cURL。
创建 Pizza 应用
创建披萨应用。
- 选择 pizza-app-for-luis-v6.json,打开
pizza-app-for-luis.json文件的 GitHub 页面。 - 右键单击或长按“原始”按钮,然后选择“将链接另存为”,将 保存到计算机。
- 登录到 LUIS 门户。
- 选择我的应用。
- 在“我的应用”页面上,选择“+ 新建用于对话的应用” 。
- 选择“导入为 JSON”。
- 在“导入新应用”对话框中,选择“选择文件”按钮 。
- 选择下载的
pizza-app-for-luis.json文件,然后选择“打开”。 - 在“导入新应用”对话框的“名称”字段中,输入 Pizza 应用的名称,然后选择“完成”按钮 。
随即导入应用。
如果看到一个对话框“如何创建有效的 LUIS 应用”,关闭该对话框。
训练并发布 Pizza 应用
Pizza 应用中应会显示“意向”页面,其中显示了一个意向列表。
在 LUIS 网站的右上方,选择“训练”按钮。
当“训练”按钮处于禁用状态时,即表示训练完成。
若要在聊天机器人或其他客户端应用程序中接收 LUIS 预测,需要将应用发布到预测终结点。
在右上方的导航栏中选择“发布”。
选择“生产”槽,然后选择“完成” 。
在通知中选择“访问终结点 URL”,以转到“Azure 资源”页 。 只有你拥有与应用关联的预测资源时,才能看到 URL。 还可以单击“管理”来找到“Azure 资源”页 。
向披萨应用添加创作资源
- 选择“管理”。
- 选择“Azure 资源”。
- 选择“创作资源”。
- 选择“更改创作资源”。
如果你有创作资源,请输入你的创作资源的租户名称、订阅名称以及 LUIS 资源名称。
如果你没有创作资源:
- 选择“新建资源”。
- 输入租户名称、资源名称、订阅名称和 Azure 资源组名称。
现在 Pizza 应用可以使用了。
记录 Pizza 应用的访问值
若要使用新的披萨应用,你需要该披萨应用的应用 ID、授权密钥和授权终结点。 若要获取预测,需要单独的预测终结点和预测密钥。
若要查找这些值:
- 在“意向”页面,选择“管理” 。
- 在“应用程序设置”页面,记录“应用 ID” 。
- 选择“Azure 资源”。
- 选择“创作资源”。
- 从“创作资源”和“预测资源”选项卡,记录“主键” 。 此值是你的创作密钥。
- 记录“终结点 URL”。 此值是你的创作终结点。
创建 JSON 文件来训练 Pizza 应用
若要创建包含三个示例言语的 JSON 文件,请将以下 JSON 数据保存到名为 ExampleUtterances.JSON 的文件中:
[
{
"text": "order a pizza",
"intentName": "ModifyOrder",
"entityLabels": [
{
"entityName": "Order",
"startCharIndex": 6,
"endCharIndex": 12
}
]
},
{
"text": "order a large pepperoni pizza",
"intentName": "ModifyOrder",
"entityLabels": [
{
"entityName": "Order",
"startCharIndex": 6,
"endCharIndex": 28
},
{
"entityName": "FullPizzaWithModifiers",
"startCharIndex": 6,
"endCharIndex": 28
},
{
"entityName": "PizzaType",
"startCharIndex": 14,
"endCharIndex": 28
},
{
"entityName": "Size",
"startCharIndex": 8,
"endCharIndex": 12
}
]
},
{
"text": "I want two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust",
"intentName": "ModifyOrder",
"entityLabels": [
{
"entityName": "Order",
"startCharIndex": 7,
"endCharIndex": 46
},
{
"entityName": "FullPizzaWithModifiers",
"startCharIndex": 7,
"endCharIndex": 46
},
{
"entityName": "PizzaType",
"startCharIndex": 17,
"endCharIndex": 32
},
{
"entityName": "Size",
"startCharIndex": 11,
"endCharIndex": 15
},
{
"entityName": "Quantity",
"startCharIndex": 7,
"endCharIndex": 9
},
{
"entityName": "Crust",
"startCharIndex": 37,
"endCharIndex": 46
}
]
}
]`
示例言语 JSON 遵循特定格式。
text 字段包含示例话语的文本。 intentName 字段必须对应于 LUIS 应用中的现有意向名称。 entityLabels 字段是必填的。 如果不想标记任何实体,请提供一个空数组。
如果 entityLabels 数组不为空,则 startCharIndex 和 endCharIndex 需要标记 entityName 字段中引用的实体。 该索引从零开始。 如果标签的起始或结尾位于文本中的空白处,则添加话语的 API 调用将失败。
添加示例话语
若要上传这批示例言语,请将以下命令复制到文本编辑器中:
curl "***YOUR-AUTHORING-ENDPOINT***/luis/authoring/v3.0-preview/apps/***YOUR-APP-ID***/versions/***YOUR-APP-VERSION***/examples?verbose=true&show-all-intents=true" ^ --request POST ^ --header "Content-Type:application/json" ^ --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: ***YOUR-AUTHORING-KEY***" ^ --data "@ExampleUtterances.JSON"将以
***YOUR-开头的值替换为你自己的值。信息 目的 ***YOUR-AUTHORING-ENDPOINT***创作 URL 终结点。 例如,"https://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-RESOURCE-NAME.api.cognitive.azure.cn/"。 在创建资源时设置资源名称。 ***YOUR-APP-ID***LUIS 应用 ID。 ***YOUR-APP-VERSION***LUIS 应用版本。 对于 Pizza 应用,版本号为“0.1”(不含引号)。 ***YOUR-AUTHORING-KEY***32 字符创作密钥。 分配的密钥和资源可以在 LUIS 门户的“Azure 资源”页上的“管理”部分中看到。 应用 ID 可以在“应用程序设置”页的同一“管理”部分中找到。
重要
完成后,请记住将密钥从代码中删除,并且永远不要公开发布该密钥。 对于生产来说,请使用安全的方式存储和访问凭据,例如 Azure Key Vault。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Azure AI 服务安全性一文。
启动命令提示符 (Windows) 或终端(macOS 和 Linux),并将目录更改为保存
ExampleUtterances.JSON文件的目录。从编辑器中复制 cURL 命令,并将其粘贴到命令提示符 (Windows) 或终端(macOS 和 Linux)中。 按 Enter 执行该命令。
应会看到以下响应:
[{"value":{"ExampleId":1255129706,"UtteranceText":"order a pizza"},"hasError":false},{"value":{"ExampleId":1255129707,"UtteranceText":"order a large pepperoni pizza"},"hasError":false},{"value":{"ExampleId":1255129708,"UtteranceText":"i want two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust"},"hasError":false}]下面是为提高可读性而进行了格式设置的输出:
[ { "value": { "ExampleId": 1255129706, "UtteranceText": "order a pizza" }, "hasError": false }, { "value": { "ExampleId": 1255129707, "UtteranceText": "order a large pepperoni pizza" }, "hasError": false }, { "value": { "ExampleId": 1255129708, "UtteranceText": "i want two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust" }, "hasError": false } ]
训练 Pizza 应用模型
若要开启 Pizza 应用的训练会话,请将以下命令复制到文本编辑器中:
curl "***YOUR-AUTHORING-ENDPOINT***/luis/authoring/v3.0-preview/apps/***YOUR-APP-ID***/versions/***YOUR-APP-VERSION***/train?verbose=true&show-all-intents=true" ^ --data "" ^ --request POST ^ --header "Content-Type:application/json" ^ --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: ***YOUR-AUTHORING-KEY***"与之前所做的操作一样,将以
***YOUR-开头的值替换为你自己的值。从编辑器中复制 cURL 命令,并将其粘贴到命令提示符 (Windows) 或终端(macOS 和 Linux)中。 按 Enter 执行该命令。
应会看到以下响应:
{"statusId":2,"status":"UpToDate"}下面是为提高可读性而进行了格式设置的输出:
{ "statusId": 2, "status": "UpToDate" }
获取训练状态
若要获取训练会话的训练状态,请将以下命令复制到文本编辑器中:
curl "***YOUR-AUTHORING-ENDPOINT***/luis/authoring/v3.0-preview/apps/***YOUR-APP-ID***/versions/***YOUR-APP-VERSION***/train?verbose=true&show-all-intents=true" ^ --request GET ^ --header "Content-Type:application/json" ^ --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: ***YOUR-AUTHORING-KEY***"与之前所做的操作一样,将以
***YOUR-开头的值替换为你自己的值。从编辑器中复制 cURL 命令,并将其粘贴到命令提示符 (Windows) 或终端(macOS 和 Linux)中。 按 Enter 执行该命令。
应会看到以下响应:
[{"modelId":"8eb7ad8f-5db5-4c28-819b-ca3905fffd80","details":{"statusId":2,"status":"UpToDate","exampleCount":171}},{"modelId":"6f53bc92-ae54-44ce-bc4e-010d1f8cfda0","details":{"statusId":2,"status":"UpToDate","exampleCount":171}},{"modelId":"6cb17888-ad6e-464c-82c0-d37fd1f2c4f8","details":{"statusId":2,"status":"UpToDate","exampleCount":171}},{"modelId":"a16fc4fd-1949-4e77-9de3-30369f16c3a5","details":{"statusId":2,"status":"UpToDate","exampleCount":171}},{"modelId":"6bacdb75-1889-4f93-8971-8c8995ff8960","details":{"statusId":2,"status":"UpToDate","exampleCount":171}},{"modelId":"be963f4c-4898-48d7-9eba-3c6af0867b9d","details":{"statusId":2,"status":"UpToDate","exampleCount":171}}]下面是为提高可读性而进行了格式设置的输出:
[ { "modelId": "8eb7ad8f-5db5-4c28-819b-ca3905fffd80", "details": { "statusId": 2, "status": "UpToDate", "exampleCount": 171 } }, { "modelId": "6f53bc92-ae54-44ce-bc4e-010d1f8cfda0", "details": { "statusId": 2, "status": "UpToDate", "exampleCount": 171 } }, { "modelId": "6cb17888-ad6e-464c-82c0-d37fd1f2c4f8", "details": { "statusId": 2, "status": "UpToDate", "exampleCount": 171 } }, { "modelId": "a16fc4fd-1949-4e77-9de3-30369f16c3a5", "details": { "statusId": 2, "status": "UpToDate", "exampleCount": 171 } }, { "modelId": "6bacdb75-1889-4f93-8971-8c8995ff8960", "details": { "statusId": 2, "status": "UpToDate", "exampleCount": 171 } }, { "modelId": "be963f4c-4898-48d7-9eba-3c6af0867b9d", "details": { "statusId": 2, "status": "UpToDate", "exampleCount": 171 } } ]
从预测终结点获取意向
使用 cURL 查询预测终结点并获取预测结果。
注意
此命令使用预测终结点。
请将以下命令复制到自己的文本编辑器中:
curl "https://***YOUR-PREDICTION-ENDPOINT***/luis/prediction/v3.0/apps/***YOUR-APP-ID***/slots/production/predict" ^ --request GET ^ --get ^ --data "subscription-key=***YOUR-PREDICTION-KEY***" ^ --data "verbose=true" ^ --data "show-all-intents=true" ^ --data-urlencode "query=I want two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust please"将以
***YOUR-开头的值替换为你自己的值。信息 目的 ***YOUR-PREDICTION-ENDPOINT***预测 URL 终结点。 位于 LUIS 门户中,你的应用的“Azure 资源”页。
例如,https://api.cognitive.azure.cn/。***YOUR-APP-ID***你的应用程序 ID。 位于 LUIS 门户中,你的应用的“应用程序设置”页。 ***YOUR-PREDICTION-KEY***32 字符预测密钥。 位于 LUIS 门户中,你的应用的“Azure 资源”页。 将文本复制到控制台窗口并按 Enter 执行该命令:
查看以 JSON 形式返回的预测响应:
{"query":"I want two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust please","prediction":{"topIntent":"ModifyOrder","intents":{"ModifyOrder":{"score":1.0},"None":{"score":8.55E-09},"Greetings":{"score":1.82222226E-09},"CancelOrder":{"score":1.47272727E-09},"Confirmation":{"score":9.8125E-10}},"entities":{"Order":[{"FullPizzaWithModifiers":[{"PizzaType":["pepperoni pizzas"],"Size":[["Large"]],"Quantity":[2],"Crust":[["Thin"]],"$instance":{"PizzaType":[{"type":"PizzaType","text":"pepperoni pizzas","startIndex":17,"length":16,"score":0.9978157,"modelTypeId":1,"modelType":"Entity Extractor","recognitionSources":["model"]}],"Size":[{"type":"SizeList","text":"large","startIndex":11,"length":5,"score":0.9984481,"modelTypeId":1,"modelType":"Entity Extractor","recognitionSources":["model"]}],"Quantity":[{"type":"builtin.number","text":"two","startIndex":7,"length":3,"score":0.999770939,"modelTypeId":1,"modelType":"Entity Extractor","recognitionSources":["model"]}],"Crust":[{"type":"CrustList","text":"thin crust","startIndex":37,"length":10,"score":0.933985531,"modelTypeId":1,"modelType":"Entity Extractor","recognitionSources":["model"]}]}}],"$instance":{"FullPizzaWithModifiers":[{"type":"FullPizzaWithModifiers","text":"two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust","startIndex":7,"length":40,"score":0.90681237,"modelTypeId":1,"modelType":"Entity Extractor","recognitionSources":["model"]}]}}],"ToppingList":[["Pepperoni"]],"$instance":{"Order":[{"type":"Order","text":"two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust","startIndex":7,"length":40,"score":0.9047088,"modelTypeId":1,"modelType":"Entity Extractor","recognitionSources":["model"]}],"ToppingList":[{"type":"ToppingList","text":"pepperoni","startIndex":17,"length":9,"modelTypeId":5,"modelType":"List Entity Extractor","recognitionSources":["model"]}]}}}}已通过格式化提高可读性的 JSON 响应:
{ "query": "I want two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust please", "prediction": { "topIntent": "ModifyOrder", "intents": { "ModifyOrder": { "score": 1.0 }, "None": { "score": 8.55e-9 }, "Greetings": { "score": 1.82222226e-9 }, "CancelOrder": { "score": 1.47272727e-9 }, "Confirmation": { "score": 9.8125e-10 } }, "entities": { "Order": [ { "FullPizzaWithModifiers": [ { "PizzaType": [ "pepperoni pizzas" ], "Size": [ [ "Large" ] ], "Quantity": [ 2 ], "Crust": [ [ "Thin" ] ], "$instance": { "PizzaType": [ { "type": "PizzaType", "text": "pepperoni pizzas", "startIndex": 17, "length": 16, "score": 0.9978157, "modelTypeId": 1, "modelType": "Entity Extractor", "recognitionSources": [ "model" ] } ], "Size": [ { "type": "SizeList", "text": "large", "startIndex": 11, "length": 5, "score": 0.9984481, "modelTypeId": 1, "modelType": "Entity Extractor", "recognitionSources": [ "model" ] } ], "Quantity": [ { "type": "builtin.number", "text": "two", "startIndex": 7, "length": 3, "score": 0.999770939, "modelTypeId": 1, "modelType": "Entity Extractor", "recognitionSources": [ "model" ] } ], "Crust": [ { "type": "CrustList", "text": "thin crust", "startIndex": 37, "length": 10, "score": 0.933985531, "modelTypeId": 1, "modelType": "Entity Extractor", "recognitionSources": [ "model" ] } ] } } ], "$instance": { "FullPizzaWithModifiers": [ { "type": "FullPizzaWithModifiers", "text": "two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust", "startIndex": 7, "length": 40, "score": 0.90681237, "modelTypeId": 1, "modelType": "Entity Extractor", "recognitionSources": [ "model" ] } ] } } ], "ToppingList": [ [ "Pepperoni" ] ], "$instance": { "Order": [ { "type": "Order", "text": "two large pepperoni pizzas on thin crust", "startIndex": 7, "length": 40, "score": 0.9047088, "modelTypeId": 1, "modelType": "Entity Extractor", "recognitionSources": [ "model" ] } ], "ToppingList": [ { "type": "ToppingList", "text": "pepperoni", "startIndex": 17, "length": 9, "modelTypeId": 5, "modelType": "List Entity Extractor", "recognitionSources": [ "model" ] } ] } } } }
清理资源
可从 LUIS 门户删除应用并从 Azure 门户删除 Azure 资源。
如果使用 REST API,请在完成快速入门后从文件系统中删除 ExampleUtterances.JSON 文件。
疑难解答
- 对客户端库进行身份验证 - 身份验证错误通常表明使用了错误的密钥和终结点。 为了方便起见,此快速入门使用预测运行时的创作密钥和终结点,但只有在不超出每月配额的情况下才有效。 如果无法使用创作密钥和终结点,则需要在访问预测运行时 SDK 客户端库时使用预测运行时密钥和终结点。
- 创建实体 - 如果在创建本教程中使用的嵌套式机器学习实体时遇到错误,请确保已复制代码且未更改代码以创建其他实体。
- 创建示例言语 - 如果在创建本教程中使用的标记示例言语时遇到错误,请确保已复制代码且未更改代码以创建其他标记示例。
- 训练 - 如果收到一条训练错误,则通常表示该应用为空(没有带示例言语的意图),或表示该应用的意图或实体格式错误。
- 杂项错误 - 由于代码使用文本和 JSON 对象调用客户端库,所以请确保你没有更改代码。
其他错误 - 如果遇到以上列表中未涵盖的错误,请在此页面底部提供反馈,告知我们。 包括所安装的客户端库的编程语言和版本。