Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
The Time Series Insights service will be retired on 7 July 2024. Consider migrating existing environments to alternative solutions as soon as possible.
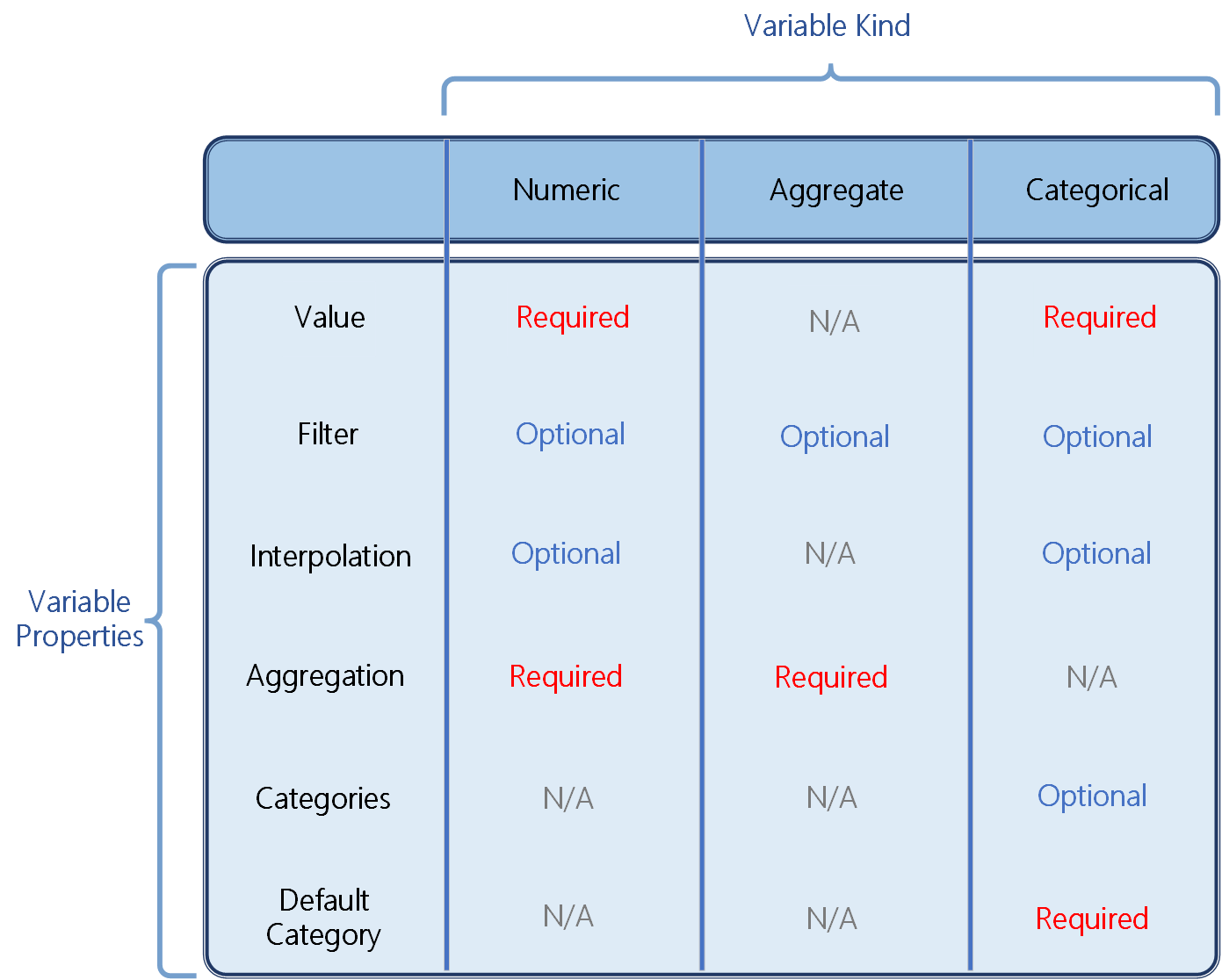
This article describes the Time Series Model variables that specify formula and computation rules on events.
Each variable can be one of three kinds: numeric, categorical, and aggregate.
- Numeric kinds work with continuous numeric values.
- Categorical kinds work with a defined set of discrete values.
- Aggregate kinds combine multiple variables of a single kind (either all numeric or all categorical).
The following table displays which properties are relevant for each variable kind.
Numeric variables
| Variable property | Description |
|---|---|
| Variable filter | Filters are optional conditional clauses to restrict the number of rows being considered for computation. |
| Variable value | Telemetry values used for computation coming from the device or sensors or transformed by using Time Series Expressions. Numeric kind variables must be either Double or Long to match the data type of the incoming data. |
| Variable interpolation | Interpolation specifies how to reconstruct a signal by using existing data. Step and Linear interpolation options are available for numeric variables. |
| Variable aggregation | Perform computations through the supported aggregation functions for Numeric variable kinds. |
Variables conform to the following JSON example:
"Interpolated Speed": {
"kind": "numeric",
"value": {
"tsx": "$event['Speed-Sensor'].Double"
},
"filter": null,
"interpolation": {
"kind": "step",
"boundary": {
"span": "P1D"
}
},
"aggregation": {
"tsx": "right($value)"
}
}
Categorical variables
| Variable property | Description |
|---|---|
| Variable filter | Filters are optional conditional clauses to restrict the number of rows being considered for computation. |
| Variable value | Telemetry values used for computation coming from the device or sensors. Categorical kind variables must be either Long or String to match the data type of the incoming data. |
| Variable interpolation | Interpolation specifies how to reconstruct a signal by using existing data. The Step interpolation option is available for categorical variables. |
| Variable categories | Categories create a mapping between the values coming from the device or sensors to a label. |
| Variable default category | The default category is for all values that aren't being mapped in the "categories" property. |
Variables conform to the following JSON example:
"Status": {
"kind": "categorical",
"value": {
"tsx": "$event.Status.Long"
},
"interpolation": {
"kind": "step",
"boundary": {
"span" : "PT1M"
}
},
"categories": [
{
"values": [0, 1, 2, 3],
"label": "Good"
},
{
"values": [4],
"label": "Bad"
}
],
"defaultCategory": {
"label": "Not Applicable"
}
}
Aggregate variables
| Variable property | Description |
|---|---|
| Variable filter | Filters are optional conditional clauses to restrict the number of rows being considered for computation. |
| Variable aggregation | Perform computations through the supported aggregation functions for Aggregate variable kinds. |
Variables conform to the following JSON example:
"Speed Range": {
"kind": "aggregate",
"filter": null,
"aggregation": {
"tsx": "max($event.Speed.Double) - min($event.Speed.Double)"
}
}
Variables are stored in the type definition of a time series model and can be provided inline via APIs to override or complement the stored definition.
Next steps
Learn more about Time Series Model.
Read more about how to define variables inline using Query APIs.