Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
To make third party or locally built code available to your applications, you can install a library onto one of your serverless Apache Spark pools. The packages listed in the requirements.txt file are downloaded from PyPi at the time of pool startup. This requirements file is used every time a Spark instance is created from that Spark pool. Once a library is installed for a Spark pool, it's available for all sessions using the same pool.
In some cases, you may find that a library isn't appearing in your Apache Spark pool. This case often occurs when there's an error in the provided requirements.txt or specified libraries. When an error occurs in the library installation process, the Apache Spark pool will revert back to libraries specified in the Synapse base runtime.
The goal of this document is to provide common issues and to help you debug library installation errors.
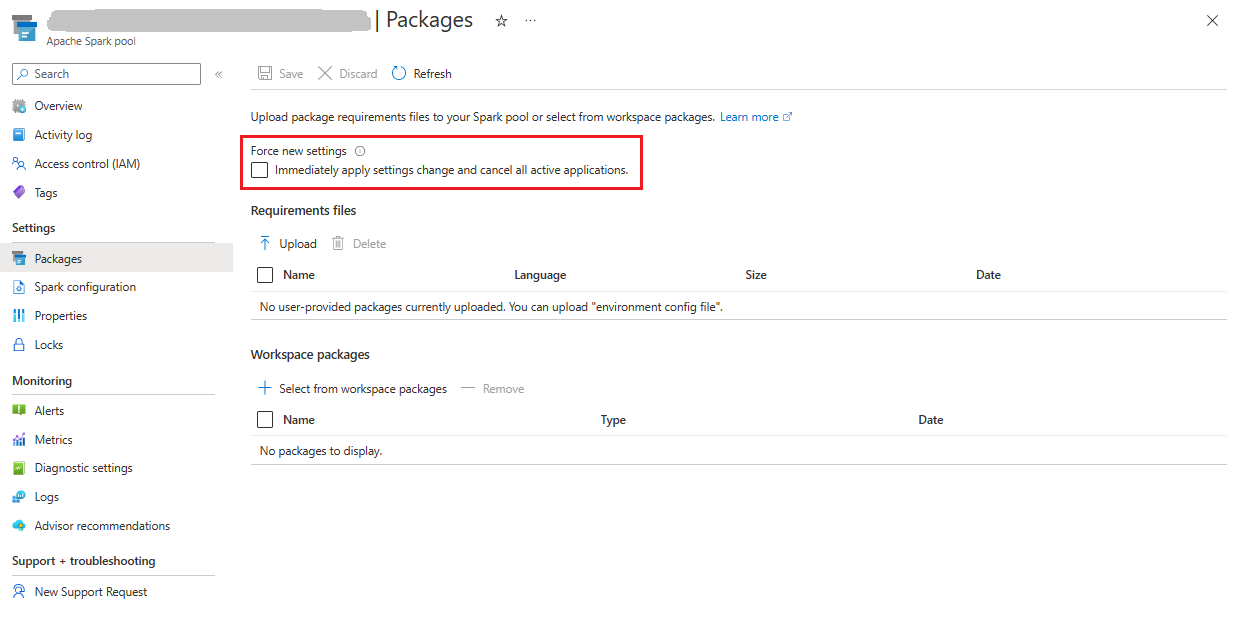
Force update your Apache Spark pool
When you update the libraries in your Apache Spark pool, these changes will be picked up once the pool has restarted. If you have active jobs, these jobs will continue to run on the original version of the spark pool.
You can force the changes to apply by selecting the option to Force new settings. This setting will end the all current sessions for the selected Spark pool. Once the sessions are ended, you'll have to wait for the pool to restart.
Track installation progress
A system reserved Spark job is started each time a pool is updated with a new set of libraries. This Spark job helps monitor the status of the library installation. If the installation fails because of library conflicts or other issues, the Spark pool will revert to its previous or default state.
In addition, users can also inspect the installation logs to identify dependency conflicts or see which libraries were installed during the pool update.
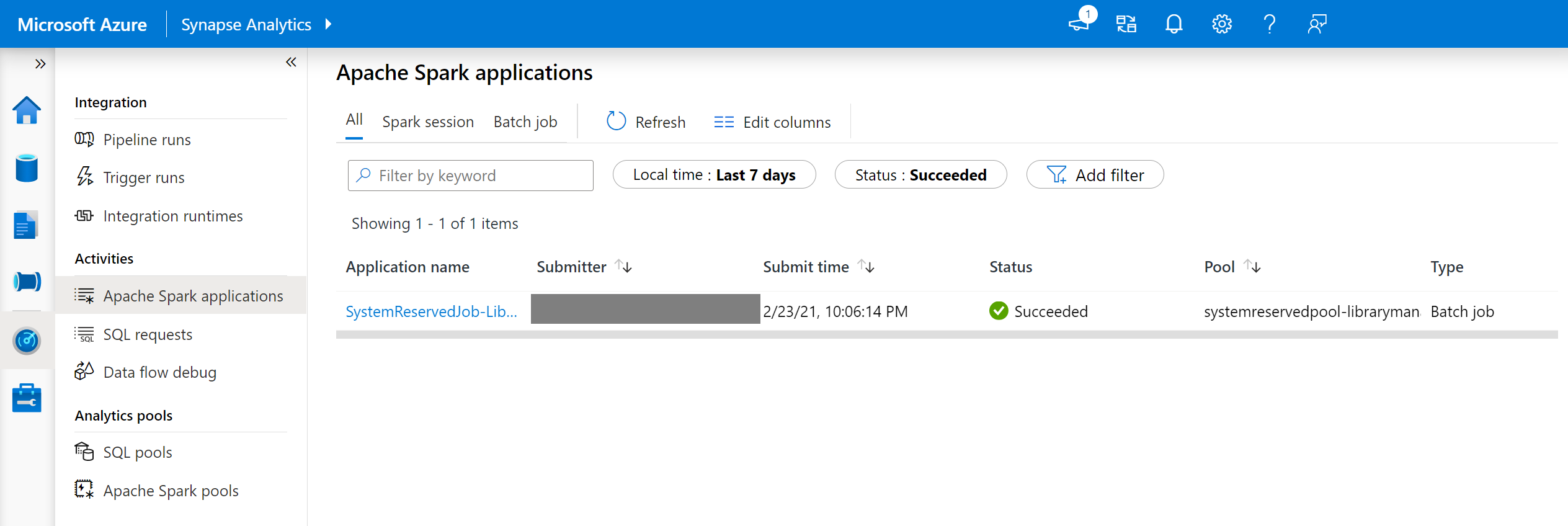
To view these logs:
- Navigate to the Spark applications list in the Monitor tab.
- Select the system Spark application job that corresponds to your pool update. These system jobs run under the SystemReservedJob-LibraryManagement title.
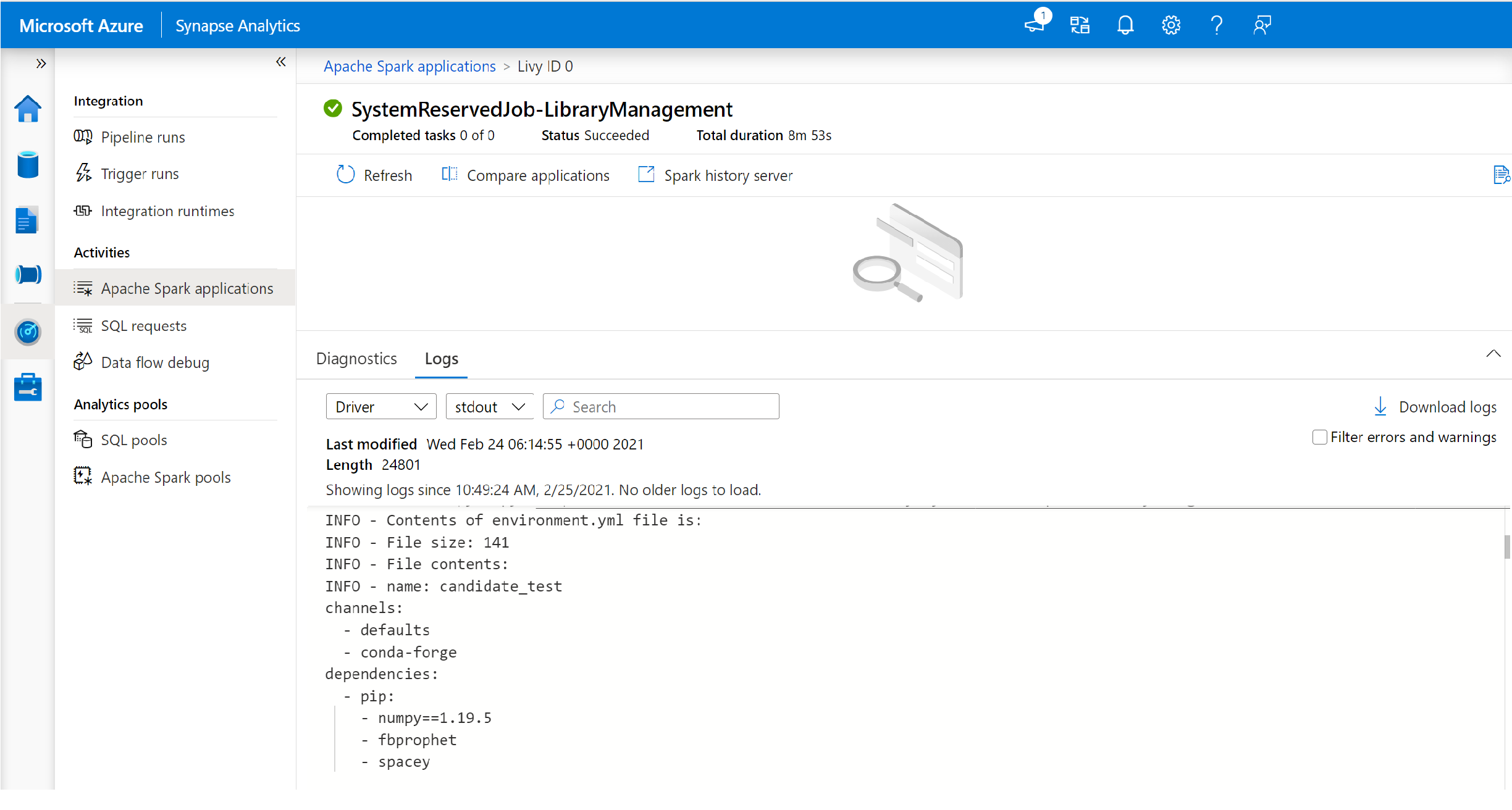
- Switch to view the driver and stdout logs.
- Within the results, you'll see the logs related to the installation of your packages.
Track installation failures
In certain cases, users can also inspect the full installation logs available in the Spark History Server to identify complicated dependency conflicts. The logs available through the Spark UI could be truncated and accessing the full installation logs through the Spark History Server would be useful in complex library installation scenarios.
To view the full installation logs:
- Navigate to the Spark applications list in the Monitor tab.
- Select the system Spark application job that corresponds to the failed pool update. These system jobs run under the SystemReservedJob-LibraryManagement title.
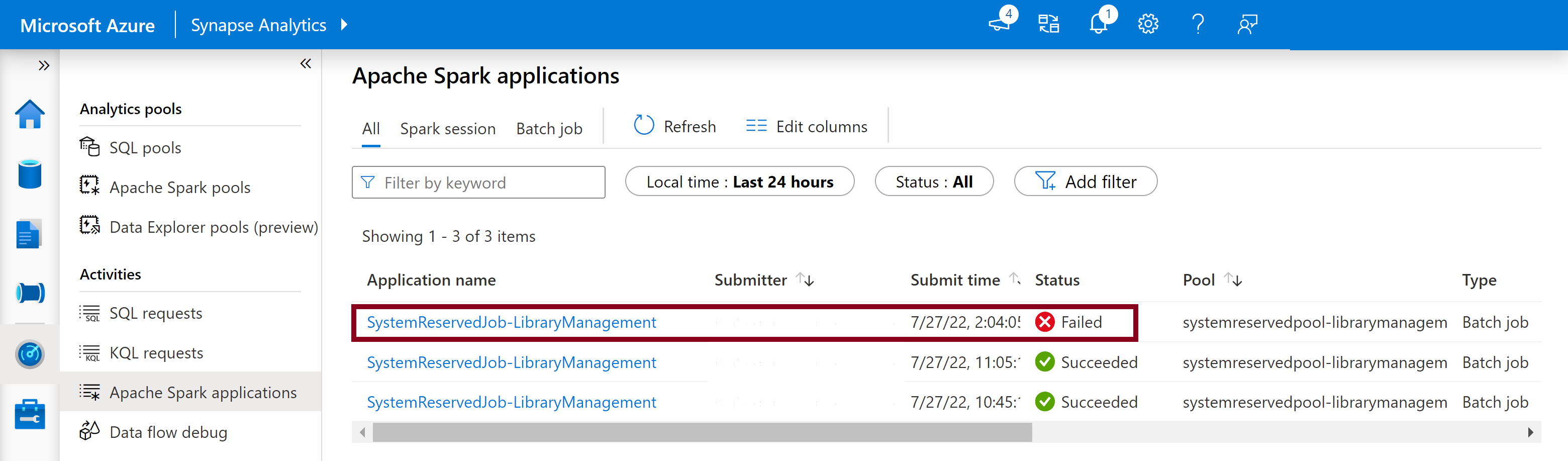
- Select the highlighted Spark history server option which would open the Spark history server details page in a new tab.
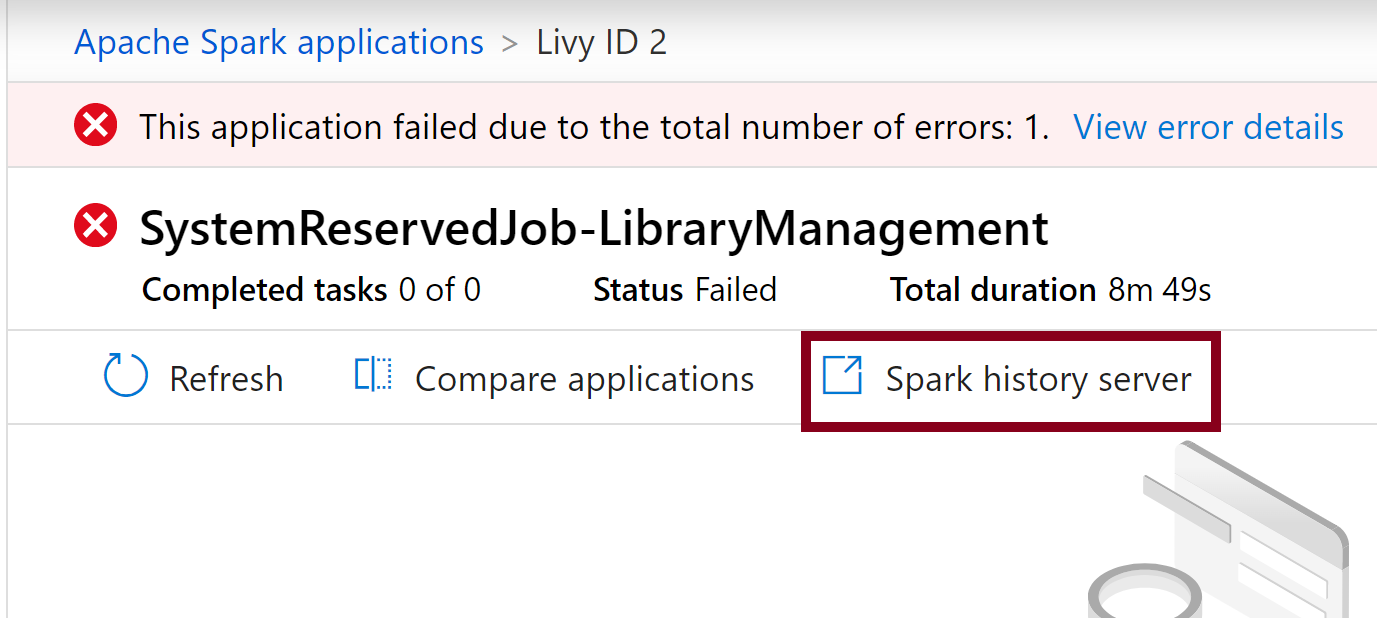
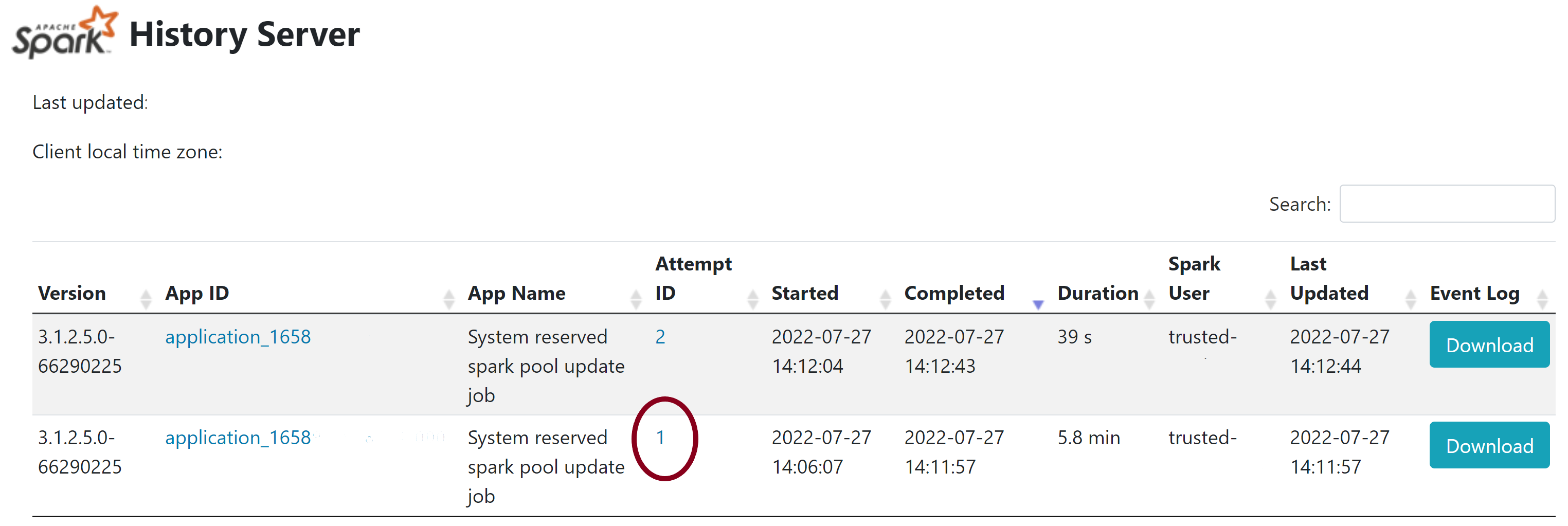
- In this page, you will see 2 attempts, select Attempt 1 as shown below.
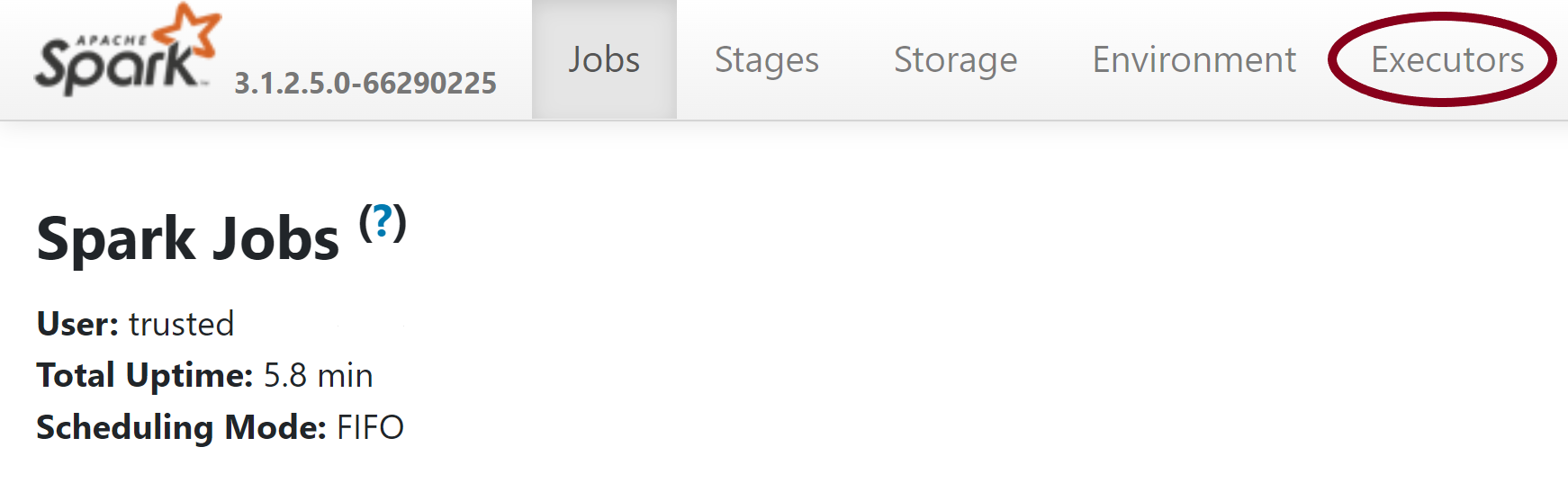
- On the top navigation bar in the Spark history server page, switch to the Executors tab.
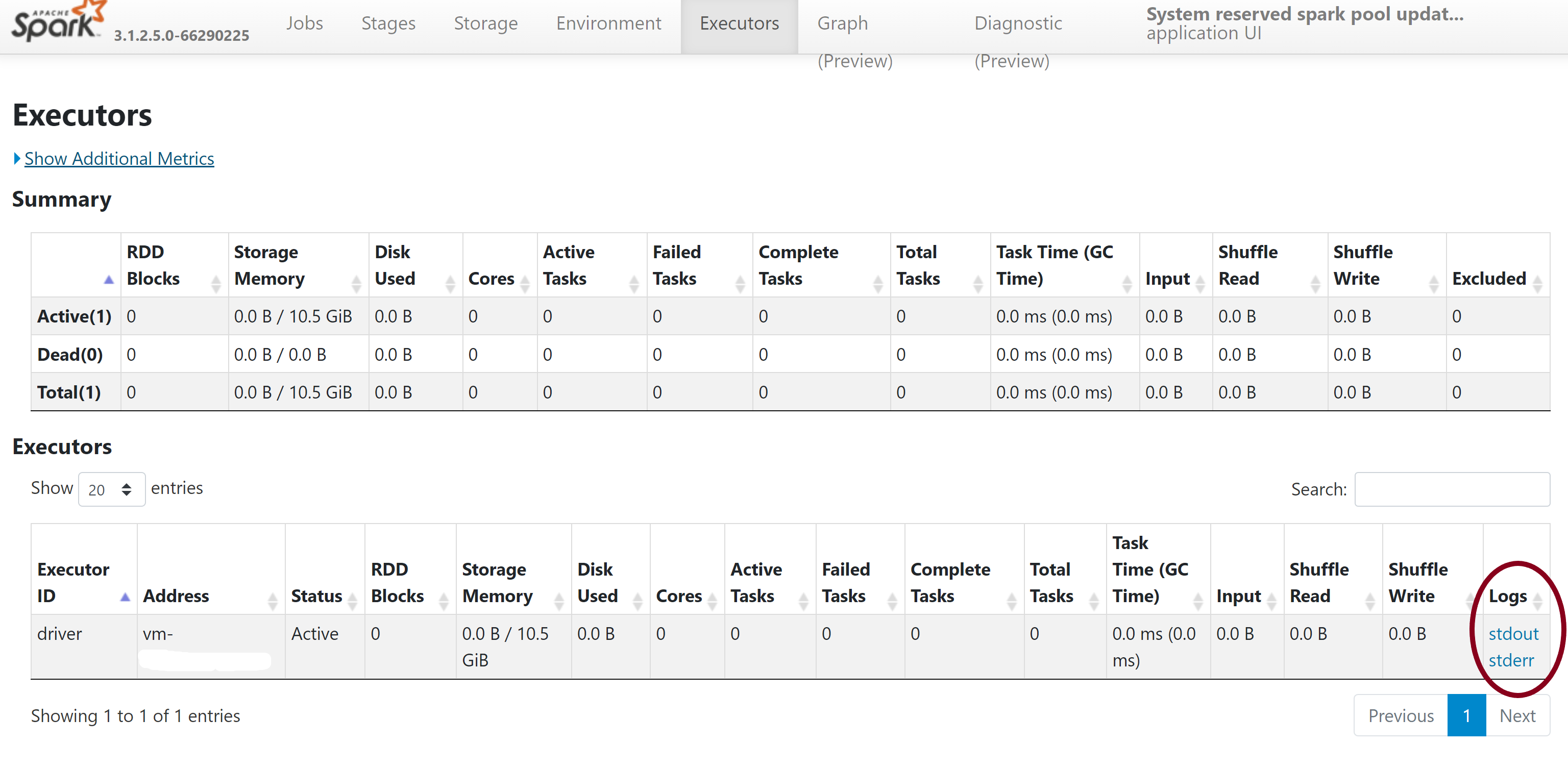
- Download the stdout and stderr log files to access the full library management output and error logs.
Validate your permissions
To install and update libraries, you must have the Storage Blob Data Contributor or Storage Blob Data Owner permissions on the primary Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 Storage account that is linked to the Azure Synapse Analytics workspace.
To validate that you have these permissions, you can run the following code:
from pyspark.sql.types import StructType,StructField, StringType, IntegerType
data2 = [("James","Smith","Joe","4355","M",3000),
("Michael","Rose","Edward","40288","F",4000)
]
schema = StructType([ \
StructField("firstname",StringType(),True), \
StructField("middlename",StringType(),True), \
StructField("lastname",StringType(),True), \
StructField("id", StringType(), True), \
StructField("gender", StringType(), True), \
StructField("salary", IntegerType(), True) \
])
df = spark.createDataFrame(data=data2,schema=schema)
df.write.csv("abfss://<<ENTER NAME OF FILE SYSTEM>>@<<ENTER NAME OF PRIMARY STORAGE ACCOUNT>>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/validate_permissions.csv")
If you receive an error, you are likely missing the required permissions. To learn how to obtain the required permissions, visit this document: Assign Storage Blob Data Contributor or Storage Blob Data Owner permissions.
In addition, if you are running a Pipeline, then the Workspace MSI must have Storage Blob Data Owner or Storage Blob Data Contributor permissions as well. To learn how to grant your workspace identity this permission, visit: Grant permissions to workspace managed identity.
Check the environment configuration file
An environment configuration file can be used to upgrade the Conda environment. This acceptable file formats for Python pool management are listed as Environment Specifications.
It is important to note the following restrictions:
- The contents of the requirements file must not include extra blank lines or characters.
- The Synapse Runtime includes a set of libraries that are pre-installed onto every serverless Apache Spark pool. Packages that come pre-installed onto the base runtime cannot be removed or uninstalled.
- Altering the PySpark, Python, Scala/Java, .NET, or Spark version is not supported.
- Python session-scoped libraries only accepts files with a YML extension.
Validate wheel files
The Synapse serverless Apache Spark pools are based off the Linux distribution. When downloading and installing Wheel files directly from PyPI, be sure to select the version that is built on Linux and runs on the same Python version as the Spark pool.
Important
Custom packages can be added or modified between sessions. However, you'll need to wait for the pool and session to restart to see the updated package.
Check for dependency conflicts
In general, Python dependency resolution can be tricky to manage. To help debug dependency conflicts locally, you can create your own virtual environment based off the Synapse Runtime and validate your changes.
To recreate the environment and validate your updates:
Download the template to locally recreate the Synapse runtime. There may be slight differences between the template and the actual Synapse environment.
Create a virtual environment using the following instructions. This environment allows you to create an isolated Python installation with the specified list of libraries.
conda myenv create -f environment.yml conda activate myenvUse
pip install -r <provide your req.txt file>to update the virtual environment with your specified packages. If the installation results in an error, then there may be a conflict between what is pre-installed in the Synapse base runtime and what is specified in the provided requirements file. These dependency conflicts must be resolved in order to get the updated libraries on your serverless Apache Spark pool.
Important
Issues may arise when using pip and conda together. When combining pip and conda, it's best to follow these recommended best practices.
Next steps
- View the default libraries: Apache Spark version support