Troubleshoot issues with Shared Private Links in Azure AI Search
A shared private link allows Azure AI Search to make secure outbound connections over a private endpoint when accessing customer resources in a virtual network. This article can help you resolve errors that might occur.
Creating a shared private link is a search service control plane operation. You can create a shared private link using either the Azure portal or a Management REST API. During provisioning, the state of the request is "Updating". After the operation completes successfully, status is "Succeeded". A private endpoint to the resource, along with any DNS zones and mappings, is created. This endpoint is used exclusively by your search service instance and is managed through Azure AI Search.
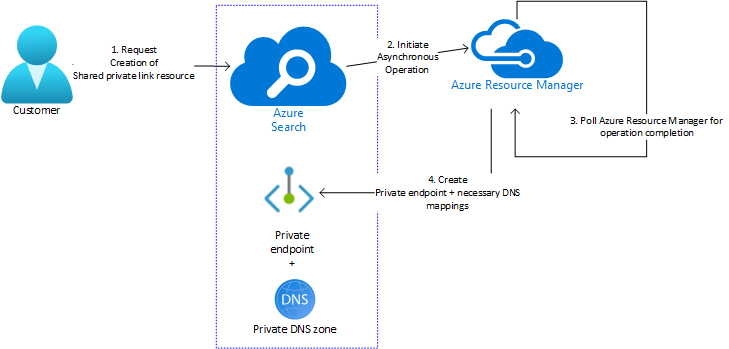
Some common errors that occur during the creation phase are listed below.
Request validation failures
Unsupported SKU: Shared private links are supported on the Basic tier and above. For indexers with skillsets, the minimum tier is Standard 2 (S2).
Invalid name: Naming rules for a shared private link are:
- Length should be between 1 to 60 characters
- Alphanumeric characters
- Names can include underscore
_, period., and hyphen-as long as it's not the first character in the name
Invalid group ID: Group IDs are case-sensitive and must be one of the values from the table below:
Azure resource Group ID First available API version Azure Storage - Blob (or) ADLS Gen 2 blob2020-08-01Azure Storage - Tables table2020-08-01Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL Sql2020-08-01Azure SQL Database sqlServer2020-08-01Azure Database for MySQL (preview) mysqlServer2020-08-01-PreviewAzure Key Vault vault2020-08-01Azure Functions (preview) sites2020-08-01-PreviewResources marked with "(preview)" must be created using a preview version of the Management REST API versions.
privateLinkResourceIdtype validation: Similar togroupId, Azure AI Search validates that the "correct" resource type is specified in theprivateLinkResourceId. The following are valid resource types:Azure resource Resource type First available API version Azure Storage Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts2020-08-01Azure Cosmos DB Microsoft.DocumentDb/databaseAccounts2020-08-01Azure SQL Database Microsoft.Sql/servers2020-08-01Azure Key Vault Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults2020-08-01Azure Database for MySQL (preview) Microsoft.DBforMySQL/servers2020-08-01-PreviewAzure Functions (preview) Microsoft.Web/sites2020-08-01-PreviewIn addition, the specified
groupIdneeds to be valid for the specified resource type. For example,groupId"blob" is valid for type "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts", it can't be used with any other resource type. For a given search management API version, customers can find out the supportedgroupIdand resource type details by utilizing the List supported API.Quota limit enforcement: Search services have quotas imposed on the distinct number of shared private link resources that can be created and the number of various target resource types that are being used (based on
groupId). These are documented in the Shared private link resource limits section of the Azure AI Search service limits page.
Deployment failures
A search service initiates the request to create a shared private link, but Azure Resource Manager performs the actual work. You can check the deployment's status in the Azure portal or by query, and address any errors that might occur.
Shared private link resources that have failed Azure Resource Manager deployment will show up in List and Get API calls, but will have a "Provisioning State" of Failed. Once the reason of the Azure Resource Manager deployment failure has been ascertained, delete the Failed resource and re-create it after applying the appropriate resolution from the following table.
| Deployment failure reason | Description | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| "LinkedAuthorizationFailed" | The error message states that the client has permission to create the shared private link on the search service, but doesn't have permission to perform action 'privateEndpointConnectionApproval/action' on the linked scope. | Re-check the private link ID in the request to make sure there are no errors or omissions in the URI. If Azure AI Search and the Azure PaaS resource are in different subscriptions, and if you're using REST or a command line interface, make sure that the active Azure account is for the Azure PaaS resource. For REST clients, make sure you're not using an expired bearer token, and that the token is valid for the active subscription. |
| Network resource provider not registered on target resource's subscription | A private endpoint (and associated DNS mappings) is created for the target resource (Storage Account, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure SQL) via the Microsoft.Network resource provider (RP). If the subscription that hosts the target resource ("target subscription") isn't registered with Microsoft.Network RP, then the Azure Resource Manager deployment can fail. |
You need to register this RP in their target subscription. You can register the resource provider using the Azure portal, PowerShell, or CLI. |
Invalid groupId for the target resource |
When Azure Cosmos DB accounts are created, you can specify the API type for the database account. While Azure Cosmos DB offers several different API types, Azure AI Search only supports "Sql" as the groupId for shared private link resources. When a shared private link of type "Sql" is created for a privateLinkResourceId pointing to a non-Sql database account, the Azure Resource Manager deployment will fail because of the groupId mismatch. The Azure resource ID of an Azure Cosmos DB account isn't sufficient to determine the API type that is being used. Azure AI Search tries to create the private endpoint, which is then denied by Azure Cosmos DB. |
You should ensure that the privateLinkResourceId of the specified Azure Cosmos DB resource is for a database account of "Sql" API type |
| Target resource not found | Existence of the target resource specified in privateLinkResourceId is checked only during the commencement of the Azure Resource Manager deployment. If the target resource is no longer available, then the deployment will fail. |
You should ensure that the target resource is present in the specified subscription and resource group and isn't moved or deleted. |
| Transient/other errors | The Azure Resource Manager deployment can fail if there's an infrastructure outage or because of other unexpected reasons. This should be rare and usually indicates a transient state. | Retry creating this resource at a later time. If the problem persists, reach out to Azure Support. |
Issues approving the backing private endpoint
A private endpoint is created to the target Azure resource as specified in the shared private link creation request. This is one of the final steps in the asynchronous Azure Resource Manager deployment operation, but Azure AI Search needs to link the private endpoint's private IP address as part of its network configuration. Once this link is done, the provisioningState of the shared private link resource will go to a terminal success state Succeeded. Customers should only approve or deny(or in general modify the configuration of the backing private endpoint) after the state has transitioned to Succeeded. Modifying the private endpoint in any way before this could result in an incomplete deployment operation and can cause the shared private link resource to end up (either immediately, or usually within a few hours) in a Failed state.
Search service network connectivity change stalled in an "Updating" state
Shared private links and private endpoints are used when search service Public Network Access is Disabled. Typically, changing network connectivity should succeed in a few minutes after the request has been accepted. In some circumstances, Azure AI Search may take several hours to complete the connectivity change operation.
If you observe that the connectivity change operation is taking a significant amount of time, wait for a few hours. Connectivity change operations involve operations such as updating DNS records which may take longer than expected.
If Public Network Access is changed, existing shared private links and private endpoints may not work correctly. If existing shared private links and private endpoints stop working during a connectivity change operation, wait a few hours for the operation to complete. If they're still not working, try deleting and recreating them.
Shared private link resource stalled in an "Updating" or "Incomplete" state
Typically, a shared private link resource should go a terminal state (Succeeded or Failed) in a few minutes after the request has been accepted.
In rare circumstances, Azure AI Search can fail to correctly mark the state of the shared private link resource to a terminal state (Succeeded or Failed). This usually occurs due to an unexpected failure. Shared private link resources are automatically transitioned to a Failed state if it has been "stuck" in a non-terminal state for more than a few hours.
If you observe that the shared private link resource hasn't transitioned to a terminal state, wait for a few hours to ensure that it becomes Failed before you can delete it and re-create it. Alternatively, instead of waiting you can try to create another shared private link resource with a different name (keeping all other parameters the same).
Updating a shared private link resource
An existing shared private link resource can be updated using the Create or Update API. Search only allows for narrow updates to the shared private link resource - only the request message can be modified via this API.
It isn't possible to update any of the "core" properties of an existing shared private link resource (such as
privateLinkResourceIdorgroupId) and this will always be unsupported. If any other property besides the request message needs to be changed, we advise customers to delete and re-create the shared private link resource.Attempt to update the request message of a shared private link resource is only possible if it has reached the provisioning state of
Succeeded.
Deleting a shared private link resource
Customers can delete an existing shared private link resource via the Delete API. Similar to the process of creation (or update), this is also an asynchronous operation with four steps:
You request a search service to delete the shared private link resource.
The search service validates that the resource exists and is in a state valid for deletion. If so, it initiates an Azure Resource Manager delete operation to remove the resource.
Search queries for the completion of the operation (which usually takes a few minutes). At this point, the shared private link resource would have a provisioning state of "Deleting".
Once the operation completes successfully, the backing private endpoint and any associated DNS mappings are removed. The resource won't show up as part of List operation and attempting a Get operation on this resource will result in a 404 Not Found.
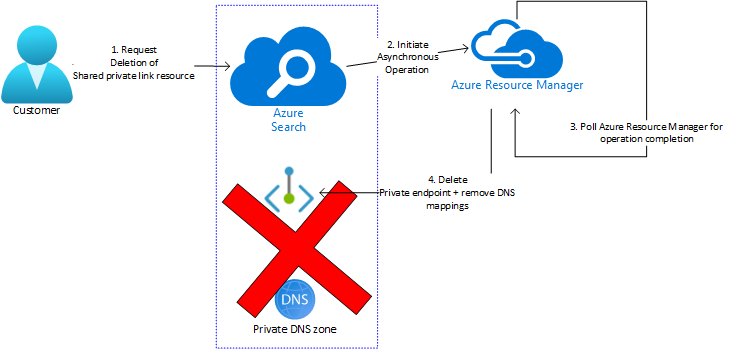
Some common errors that occur during the deletion phase are listed below.
| Failure Type | Description | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Resource is in non-terminal state | A shared private link resource that's not in a terminal state (Succeeded or Failed) can't be deleted. It's possible (rare) for a shared private link resource to be stuck in a non-terminal state for up to 8 hours. |
Wait until the resource has reached a terminal state and retry the delete request. |
| Delete operation failed with error "Conflict" | The Azure Resource Manager operation to delete a shared private link resource reaches out to the resource provider of the target resource specified in privateLinkResourceId ("target RP") before it can remove the private endpoint and DNS mappings. Customers can utilize Azure resource locks to prevent any changes to their resources. When Azure Resource Manager reaches out to the target RP, it requires the target RP to modify the state of the target resource (to remove details about the private endpoint from its metadata). When the target resource has a lock configured on it (or its resource group/subscription), the Azure Resource Manager operation fails with a "Conflict" (and appropriate details). The shared private link resource won't be deleted. |
Customers should remove the lock on the target resource before retrying the deletion operation. Note: This problem can also occur when customers try to delete a search service with shared private link resources that point to "locked" target resources |
| Delete operation failed | The asynchronous Azure Resource Manager delete operation can fail in rare cases. When this operation fails, querying the state of the asynchronous operation will present customers with an error message and appropriate details. | Retry the operation at a later time, or reach out to Azure Support if the problem persists. |
| Resource stuck in "Deleting" state | In rare cases, a shared private link resource might be stuck in "Deleting" state for up to 8 hours, likely due to some catastrophic failure on the search RP. | Wait for 8 hours, after which the resource would transition to Failed state and then reissue the request. |
Next steps
Learn more about shared private link resources and how to use it for secure access to protected content.