Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
This article provides step-by-step instructions to list all server parameters of an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Steps to list all server parameters
Using the Azure portal:
Select your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance.
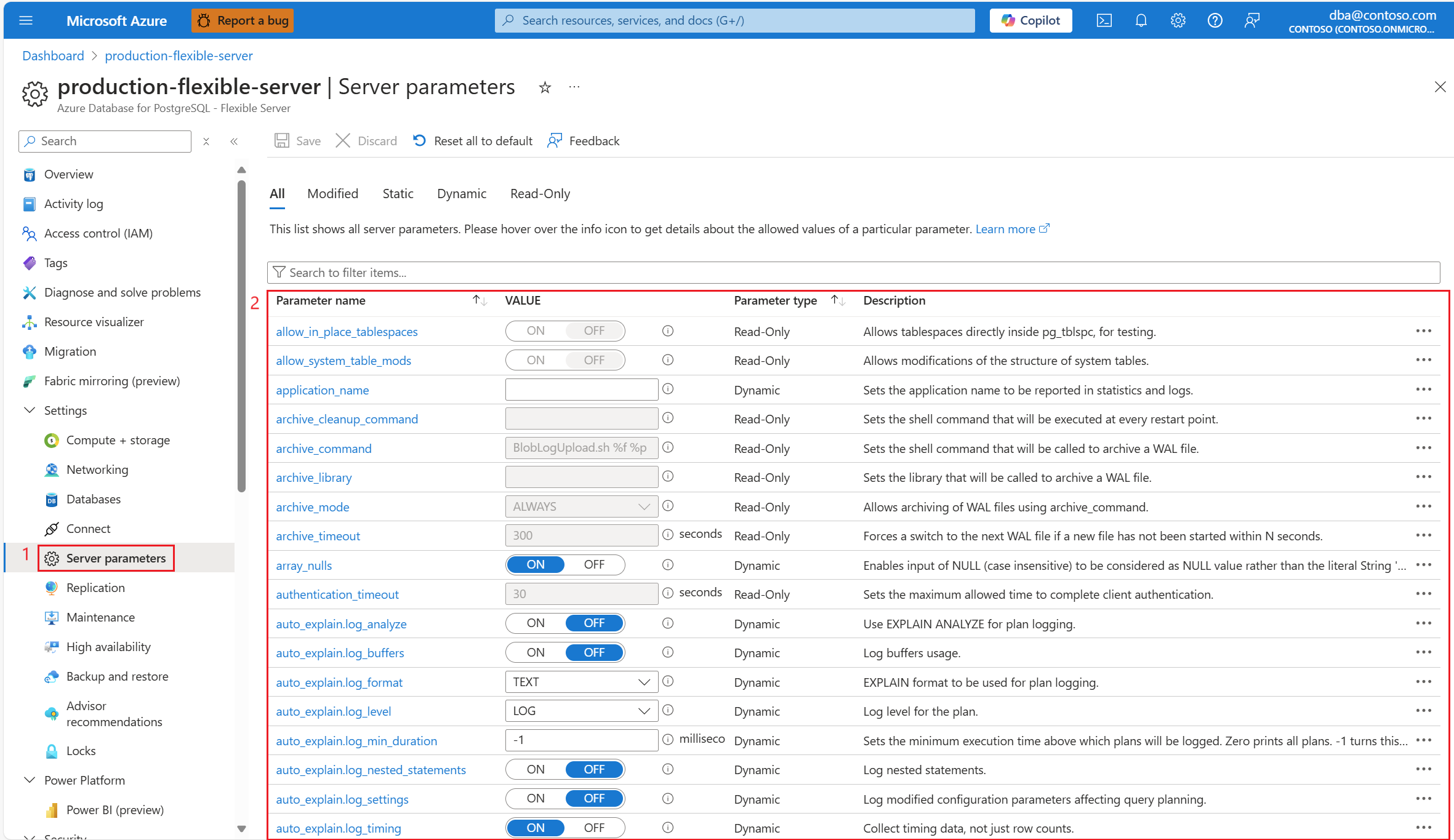
In the resource menu, under Settings, select Server parameters.
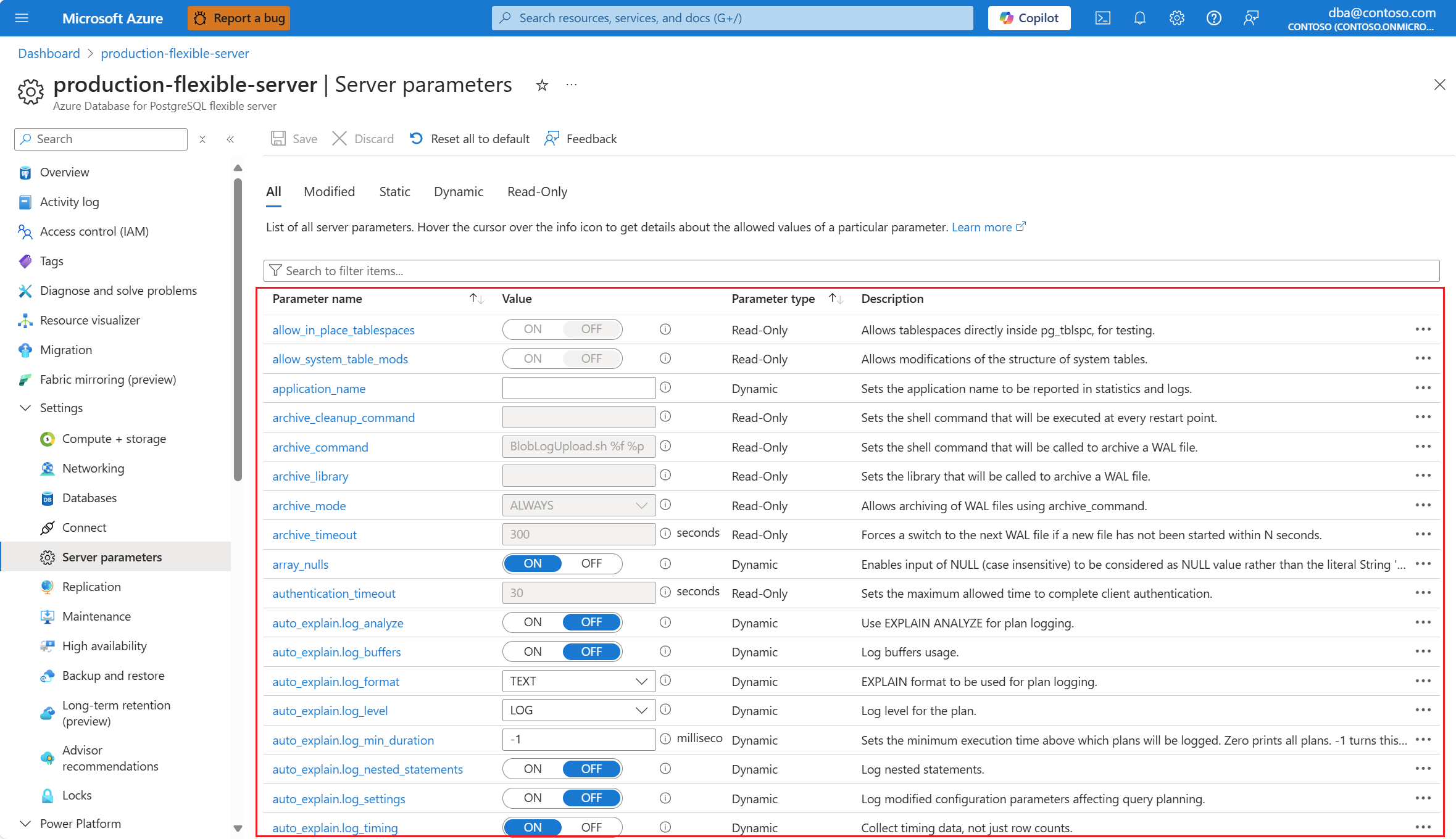
The page shows a list of parameters, their configured values, optional units, whether they're read-only, dynamic, or static, and their descriptions.
Select or hover over the i (information) icon to see which values are allowed for each parameter. Depending on the data type of the parameter, which can be string, enumeration, integer, boolean, numeric, set, the allowed values vary. And it can be regular expression, list of values, range of integers, on/off, range of decimals, list of values, respectively.
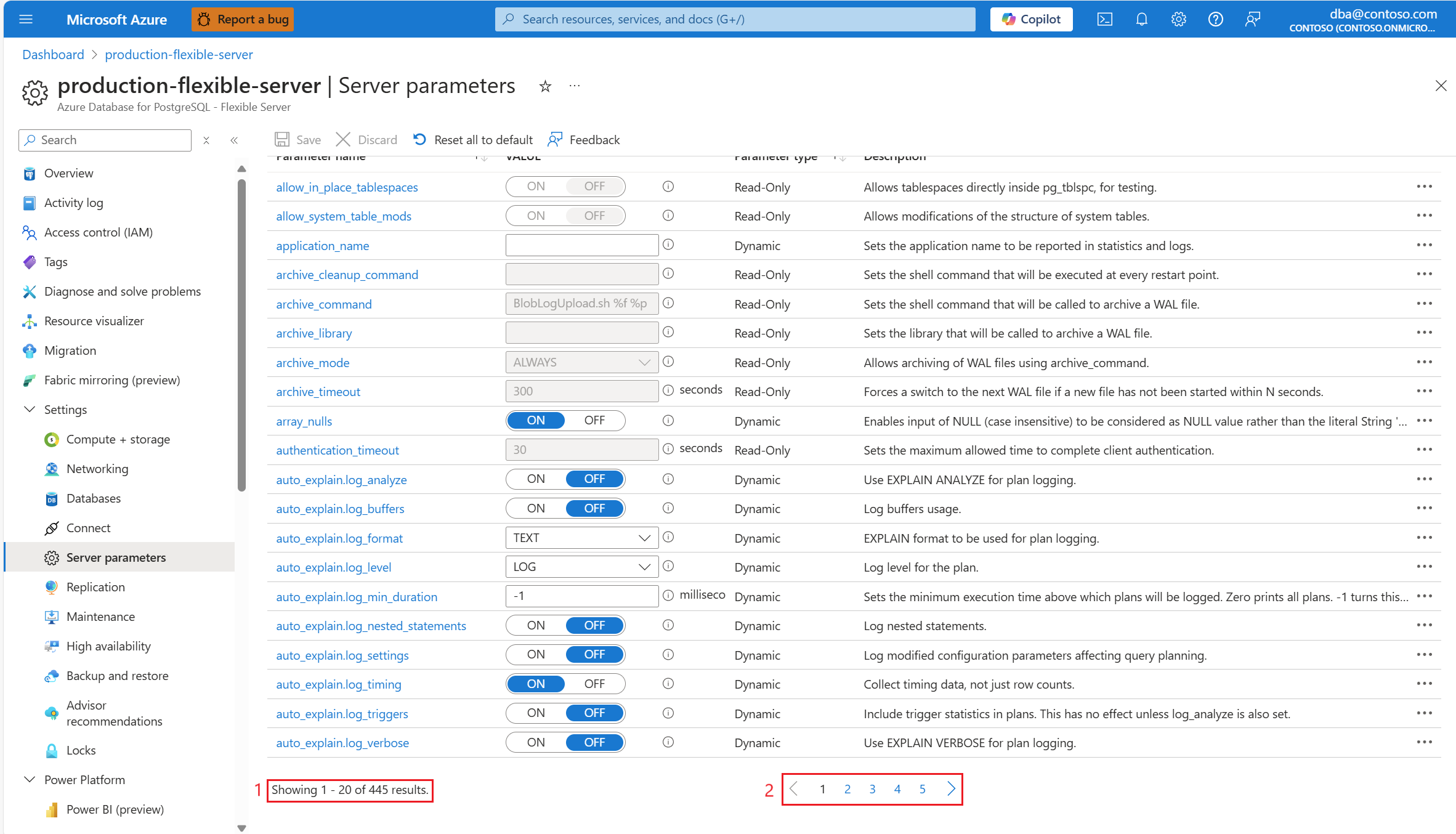
The list of server parameters supported by the instance consists of several hundred items, which are rendered in pages of 20 items each. At the bottom of the page, there's a control to inform you of the position you're at.
There's also a paging control which you can use to navigate through the whole set of pages.
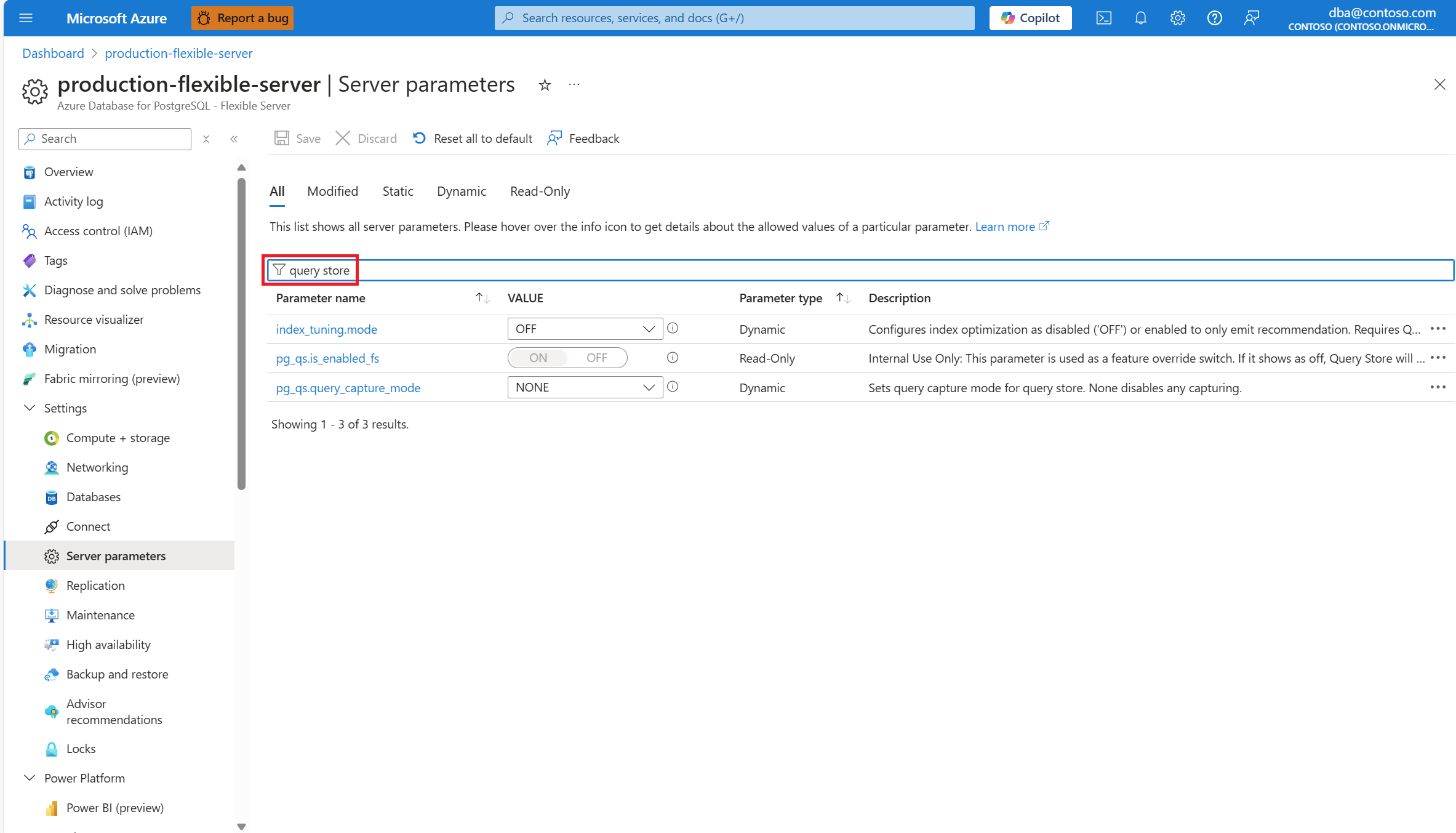
If needed, use the Search to filter items... text box to narrow down the list to those parameters containing the search term in their name or in their description.
The Parameter type column can show any of the following values for each parameter:
| Parameter type | Description |
|---|---|
| Static | Requires a server restart to make the change effective. |
| Dynamic | Can be altered without the need to restart the server instance. However, changes will apply only to new connections established after the modification. |
| Read-only | Isn't user configurable, because of their critical role in maintaining reliability, security, or other operational aspects of the service. |
Related contents
- List server parameters with modified values.
- List read-write static server parameters.
- List read-write dynamic server parameters.
- List read-only server parameters.
- Set the value of one or more server parameters.
- Revert one server parameter to its default.
- Revert all server parameters to their default.