Storage options in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
You can create an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance using Azure managed disks, which are block-level storage volumes managed by Azure and used with Azure Virtual Machines. Managed disks are like a physical disk in an on-premises server, but they're virtualized. With managed disks, all you have to do is specify the disk size, the disk type, and provision the disk. Once you provision the disk, Azure handles the rest. Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server supports premium solid-state drives (Premium SSD) and premium solid-state drives version 2 (Premium SSD v2), and the pricing is calculated based on the compute, memory, and storage tier you provision.
Premium SSD
Azure Premium SSD deliver high-performance and low-latency disk support for virtual machines (VMs) with input/output (IO)-intensive workloads. Premium SSD units are suitable for mission-critical production applications.
Premium SSD v2 (preview)
Premium SSD v2 offers higher performance than Premium SSD, while also being less costly, as a general rule. You can individually tweak the performance (capacity, throughput, and input/output operations per second, referred to as IOPS) of Premium SSD v2 at any time. The ability to do these adjustments allow workloads to be cost-efficient, while meeting shifting performance needs. For example, a transaction-intensive database might need to cope with a large amount of IOPS for a couple of exceptionally high-demand days. Or a gaming application might demand higher throughput during peak hours only. Hence, for most general-purpose workloads, Premium SSD v2 can provide the best price for performance.
Note
Premium SSD v2 is currently in preview for Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
Differences between Premium SSD and Premium SSD v2
Unlike Premium SSD, Premium SSD v2 doesn't have dedicated sizes. You can set a Premium SSD v2 disk to any size you prefer, and make granular adjustments as per your workload requirements. Those granular increments can go in steps of 1 GiB. Premium SSD v2 doesn't support host caching, but still provide lower latency than Premium SSD. Premium SSD v2 capacities range from 1 GiB to 64 TiBs.
The following table provides a comparison of different aspect of the types of disk supported by Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server, to help you decide which one suits your needs better.
| Premium SSD v2 | Premium SSD | |
|---|---|---|
| Disk type | SSD | SSD |
| Scenario | Production and performance-sensitive workloads that consistently require low latency and high IOPS and throughput. | Production and performance-sensitive workloads. |
| Max disk size | 65,536 GiB | 32,767 GiB |
| Max throughput | 1,200 MB/s | 900 MB/s |
| Max IOPS | 80,000 | 20,000 |
Premium SSD v2 offers up to 32 TiBs per region per subscription by default, but supports higher capacity by request. To request an increase in capacity, request a quota increase or contact Azure Support.
Premium SSD v2 - IOPS
All Premium SSD v2 disks have a baseline of 3,000 IOPS that is free of charge. After 6 GiB, the maximum IOPS a disk can have increases at a rate of 500 per GiB, up to 80,000 IOPS. So, a disk of 8 GiB can have up to 4,000 IOPS, and a disk of 10 GiB can have up to 5,000 IOPS. To be able to set 80,000 IOPS on a disk, that disk must have at least 160 GiBs. Increasing your IOPS beyond 3,000 increases the price of your disk.
Premium SSD v2 - Throughput
All Premium SSD v2 disks have a baseline throughput of 125 MB/s that is free of charge. After 6 GiB, the maximum throughput that can be set increases by 0.25 MB/s per set IOPS. If a disk has 3,000 IOPS, the maximum throughput it can be set to is 750 MB/s. To raise the throughput for this disk beyond 750 MB/s, its IOPS must be increased. For example, if you increase the IOPS to 4,000, then the maximum throughput that can be set is 1,000. 1,200 MB/s is the maximum throughput supported for disks that have 5,000 IOPS or more. Increasing your throughput beyond 125 MB/s increases the price of your disk.
Note
Premium SSD v2 is currently in preview for Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
Premium SSD v2 - Limitations during preview
High availability, read replicas, geographically redundant backups, data encryption with customer managed keys, or storage autogrowth features aren't supported for Premium SSD v2.
Online migration from Premium SSD (PV1) to Premium SSD v2 (PV2) isn't supported. As an alternative, if you want to migrate across the different storage types, you can perform a point-in-time-restore of your existing server to a new one that is provisioned with a different storage type.
Premium SSD V2 can only be enabled for newly created servers. Enabling Premium SSD V2 on existing servers isn't supported.
The storage that you provision is the amount of storage capacity available to your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. This storage is used for database files, temporary files, transaction logs, and PostgreSQL server logs. The total amount of storage that you provision also defines the I/O capacity available to your server.
| Disk size | Premium SSD IOPS | Premium SSD v2 IOPS |
|---|---|---|
| 32 GiB | Provisioned 120; up to 3,500 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 17179 |
| 64 GiB | Provisioned 240; up to 3,500 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 34359 |
| 128 GiB | Provisioned 500; up to 3,500 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 68719 |
| 256 GiB | Provisioned 1,100; up to 3,500 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
| 512 GiB | Provisioned 2,300; up to 3,500 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale to 80000 |
| 1 TiB | 5,000 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
| 2 TiB | 7,500 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
| 4 TiB | 7,500 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
| 8 TiB | 16,000 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
| 16 TiB | 18,000 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
| 32 TiB | 20,000 | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
| 64 TiB | N/A | First 3000 IOPS free can scale up to 80000 |
The following table provides an overview of premium SSD v2 disk capacities and performance maximums to help you decide which want you should use.
| SSD v2 disk size | Maximum available IOPS | Maximum available throughput (MB/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 GiB-64 TiBs | 3,000-80,000 (Increases by 500 IOPS per GiB) | 125-1,200 (increases by 0.25 MB/s per set IOPS) |
Your virtual machine type also has IOPS limits. Although you can select any storage size, independently from the server type, you might not be able to use all IOPS that the storage provides, especially when you choose a server with a few vCores. To learn more, see compute options in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
Note
Regardless of the type of storage you assign to your instance, storage can only be scaled up, not down.
You can monitor your I/O consumption in the Azure portal, or by using Azure CLI commands. The relevant metrics to monitor are storage limit, storage percentage, storage used, and I/O percentage.
Disk full conditions
When your disk becomes full, the server starts returning errors and prevents any further modifications. Reaching the limit might also cause problems with other operational activities, such as backups and write-ahead log (WAL) archiving.
To avoid this situation, the server is automatically switched to read-only mode when the storage usage reaches 95 percent, or when the available capacity is less than 5 GiB. If you're using Premium SSD storage type, you can use the storage autogrow feature to avoid this issue from occurring.
We recommend that you actively monitor the disk space that's in use, and increase the disk size before you run out of available space in your storage. You can set up an alert to notify you when your server storage is approaching an out-of-disk state. For more information, see how to use the Azure portal to set up alerts on metrics for Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
Storage autogrow (Premium SSD)
Storage autogrow can help ensure that your server always has enough free space available, and doesn't become read-only. When you turn on storage autogrow, disk size increases without affecting the workload. Storage autogrow is only supported for Premium SSD storage tier.
For servers with more than 1 TiB of provisioned storage, the storage autogrow mechanism activates when the available space falls below 10% of the total capacity or 64 GiB, whichever of the two values are smaller. Conversely, for servers with storage under 1 TiB this threshold is adjusted to 20% of the available free space or 64 GiB, depending on which of these values is smaller.
As an illustrative example, let's consider a server with a storage capacity of 2 TiB (which is greater than 1 TiB). In this case, the autogrow limit is set at 64 GiB. This choice is made because 64 GiB is the smaller value when compared to 10% of 2 TiB, which is roughly 204.8 GiB. In contrast, for a server with a storage size of 128 GiB (which is smaller than 1 TiB), the autogrow feature activates when there's only 25.8 GiB of space left. This activation is based on the 20% threshold of the total allocated storage (128 GiB), which is smaller than 64 GiB.
The default behavior increases the disk size to the next premium SSD storage size. This increase is always double in both size and cost, regardless of whether you start the storage scaling operation manually or through storage autogrow. Enabling storage autogrow is valuable when you're managing unpredictable workloads, because it automatically detects low-storage conditions and scales up the storage accordingly.
The process of scaling storage is performed online, without causing any downtime, except when the disk is provisioned at 4,096 GiB. This exception is a limitation of Azure managed disks. If a disk is already 4,096 GiB, the storage scaling activity isn't triggered, even if storage autogrow is turned on. In such cases, you need to scale your storage manually. Please be aware that in this scenario (reaching or crossing the 4096 GiB boundary), manual scaling is an offline operation. We recommend scheduling this task to align with your business needs. All other operations can be performed online.
Note
Regardless of the type of storage you assign to your instance, storage can only be scaled up, not down.
Limitations and considerations of storage autogrowth
Disk scaling operations are typically performed online, except in specific scenarios involving crossing the boundary of 4,096 GiB. These scenarios include reaching or crossing the limit of 4,096 GiB. For instance, scaling from 2,048 GiB to 8,192 GiB triggers an offline operation. In the Azure portal, moving to 4 TB, which is represented as 4,095 GiB, keeps the operation online. However, if you explicitly specify 4 TB as 4,096 GiB, such as in Azure CLI, the scaling operation is completed in offline mode, since it reaches the limit of 4,096 GiB. Oflline scale operation usually takes anywhere between 2 to 10 minutes. With the reduced downtime scaling feature, this duration is reduced to less than 30 seconds. This reduction in downtime during scaling resources improves the overall availability of your database instance.
Host Caching (ReadOnly and Read/Write) is supported on disk sizes less than 4 TiB. Any disk that is provisioned up to 4,095 GiB can take advantage of Host Caching. Host caching isn't supported for disk sizes more than or equal to 4,096 GiB. For example, a P50 premium disk provisioned at 4,095 GiB can take advantage of Host caching and a P50 disk provisioned at 4,096 GiB can't take advantage of Host Caching. Customers moving from lower disk size to 4,096 GiB or higher lose the ability to use disk caching.
This limitation is due to the underlying Azure managed disks, which needs a manual disk scaling operation. You receive an informational message in the portal when you approach this limit.
Storage autogrow isn't triggered when you have high WAL usage.
Note
Storage autogrow depends on online disk scaling, so it never causes downtime.
IOPS scaling
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server supports provisioning of extra IOPS. This feature enables you to provision more IOPS beyond the complimentary IOPS limit. Using this feature, you can increase or decrease the number of IOPS provisioned, to adjust them to your workload requirements at any time.
The compute size selected determines the minimum and maximum IOPS. To learn more about the minimum and maximum IOPS per compute size, see compute size.
Important
The selected compute size determines the minimum and maximum IOPS.
Learn how to scale up or down IOPS.
Price
For the most up-to-date pricing information, see Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server pricing.
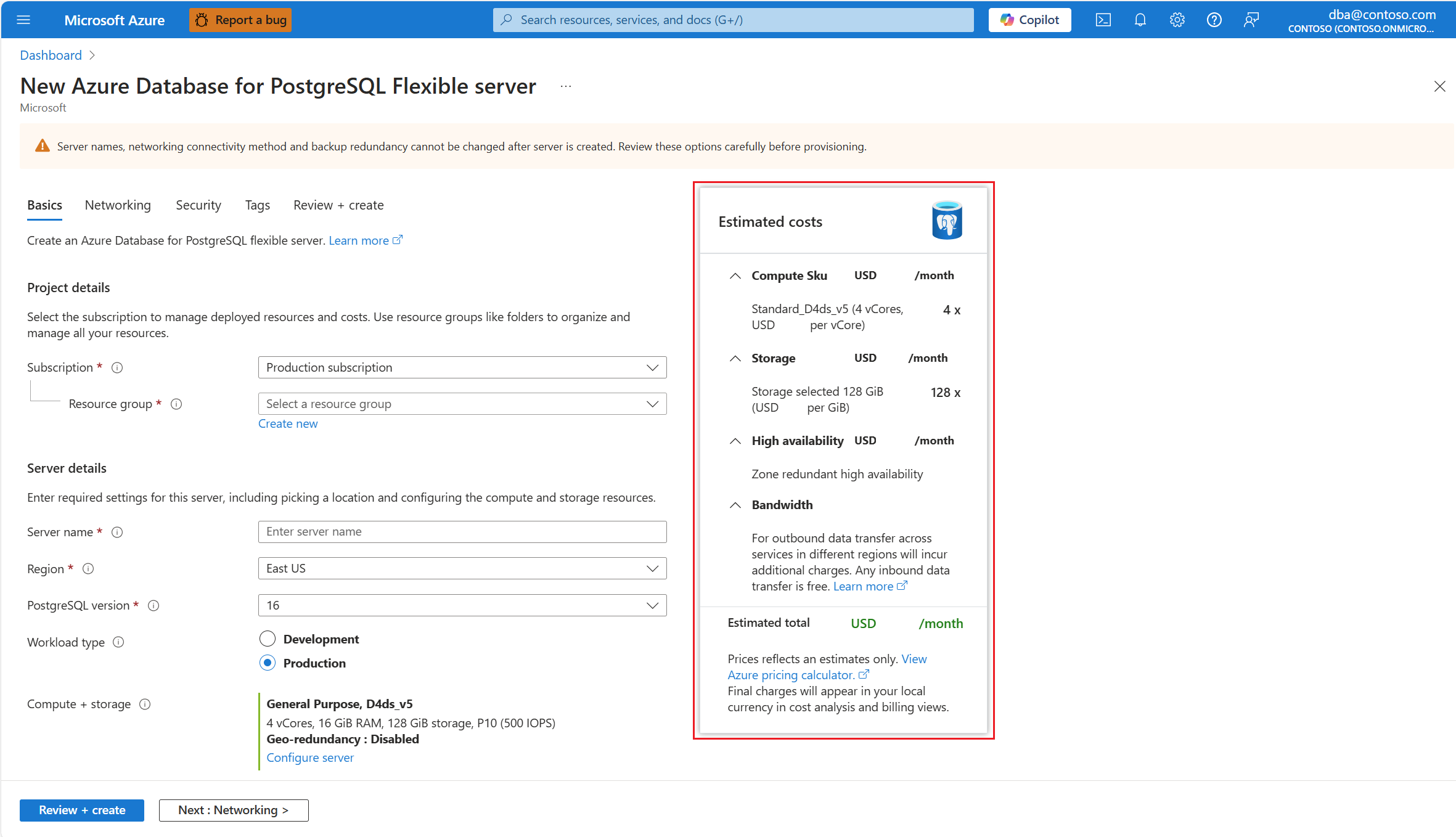
Azure portal also shows you an estimation of the monthly costs of a server configuration, based on the options selected.
That estimation can be seen throughout the server creation experience, in the New Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible server page:
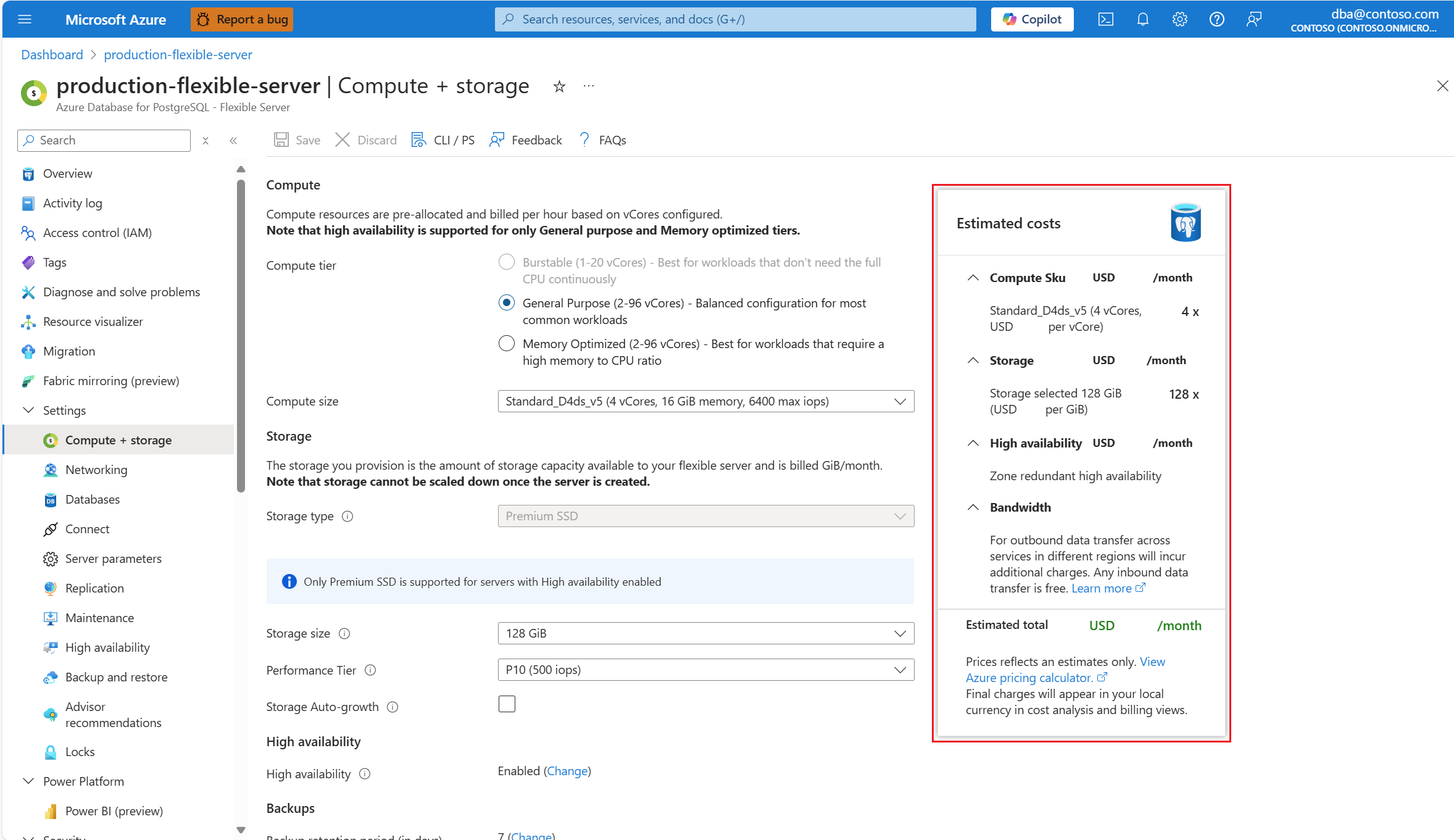
It can also be seen for existing servers if, in the resource menu of an existing instance, under the Settings section, you select Compute + storage:
If you don't have an Azure subscription, you can use the Azure pricing calculator to get an estimated price. In the Azure pricing calculator website, select Databases category, and then select Azure Database for PostgreSQL to add the service to your estimate and then customize the options.