Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article provides a conceptual overview of fleets, member clusters, and hub clusters in Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager (Fleet).
What are fleets?
A fleet resource acts as a grouping entity for multiple AKS clusters. You can use them to manage multiple AKS clusters as a single entity, orchestrate updates across multiple clusters, propagate Kubernetes resources across multiple clusters, and provide a single pane of glass for managing multiple clusters. You can create a fleet with or without a hub cluster.
A fleet consists of the following components:
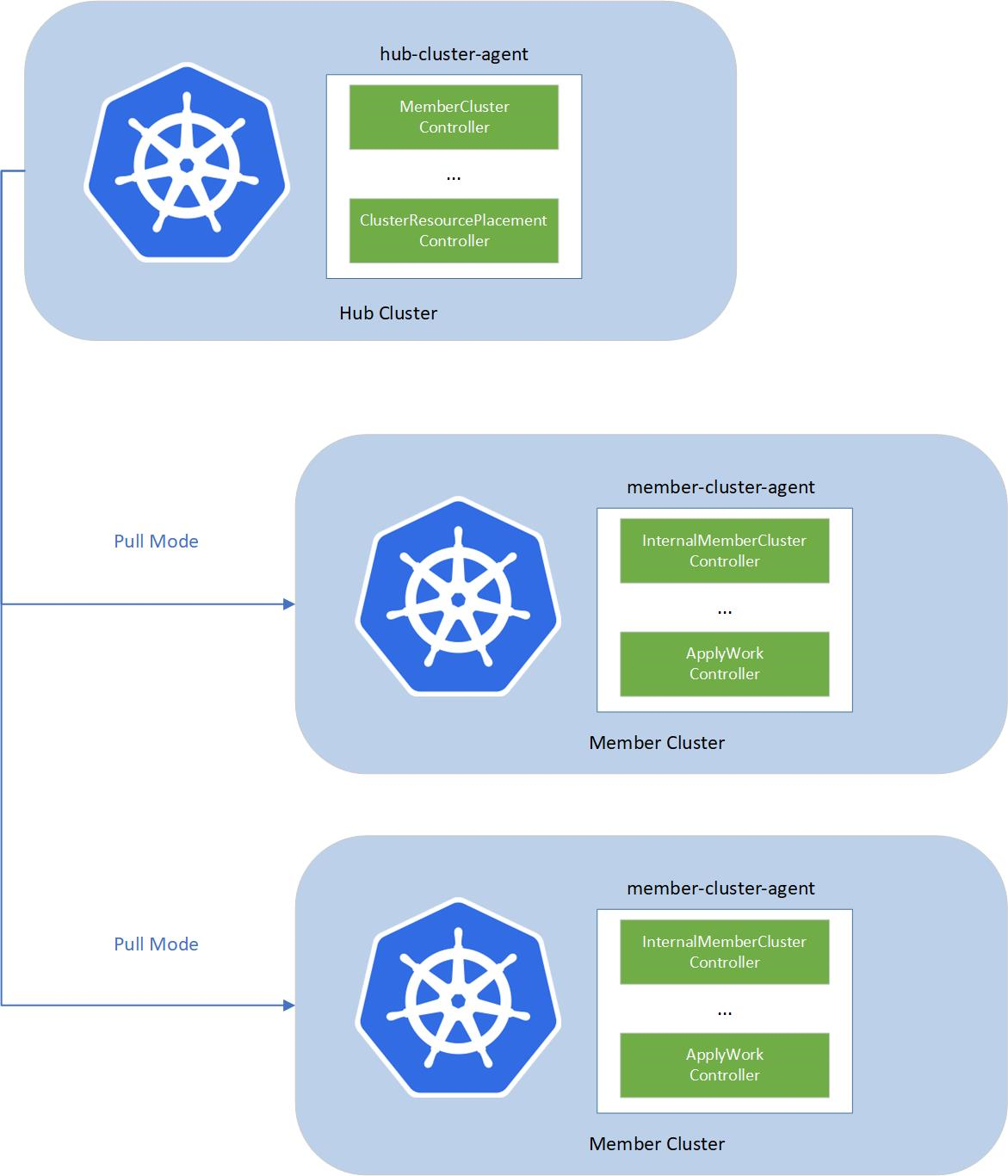
- fleet-hub-agent: A Kubernetes controller that creates and reconciles all the fleet-related custom resources (CRs) in the hub cluster.
- fleet-member-agent: A Kubernetes controller that creates and reconciles all the fleet-related CRs in the member clusters. This controller pulls the latest CRs from the hub cluster and consistently reconciles the member clusters to match the desired state.
What are hub clusters?
In Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager, hub clusters play a crucial role in managing multiple member clusters, but they are optional.
The hub cluster facilitates the orchestration of updates and resource management across member clusters. However, you can create a fleet without a hub cluster. This flexibility allows you to manage clusters as a single entity without the need for a dedicated hub. This would be more suitable for simpler setups or specific use cases.
What are member clusters?
The MemberCluster represents a cluster-scoped API established within the hub cluster, serving as a representation of a cluster within the fleet. This API offers a dependable, uniform, and automated approach for multi-cluster applications to identify registered clusters within a fleet. It also facilitates applications in querying a list of clusters managed by the fleet or in observing cluster statuses for subsequent actions.
You can join Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) clusters to a fleet as member clusters. Member clusters must reside in the same Microsoft Entra tenant as the fleet, but they can be in different regions, different resource groups, and/or different subscriptions.
Taints
Member clusters support the specification of taints, which apply to the MemberCluster resource. Each taint object consists of the following fields:
key: The key of the taint.value: The value of the taint.effect: The effect of the taint, such asNoSchedule.
Once a MemberCluster is tainted, it lets the scheduler know that the cluster shouldn't receive resources as part of the resource propagation from the hub cluster. The NoSchedule effect is a signal to the scheduler to avoid scheduling resources from a ClusterResourcePlacement to the MemberCluster.
For more information, see the open-source Fleet documentation.