Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Data flows are available both in Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Pipelines. This article applies to mapping data flows. If you are new to transformations, please refer to the introductory article Transform data using a mapping data flow.
Use the Parse transformation to parse text columns in your data that are strings in document form. The current supported types of embedded documents that can be parsed are JSON, XML, and delimited text.
Configuration
In the parse transformation configuration panel, you first pick the type of data contained in the columns that you wish to parse inline. The parse transformation also contains the following configuration settings.
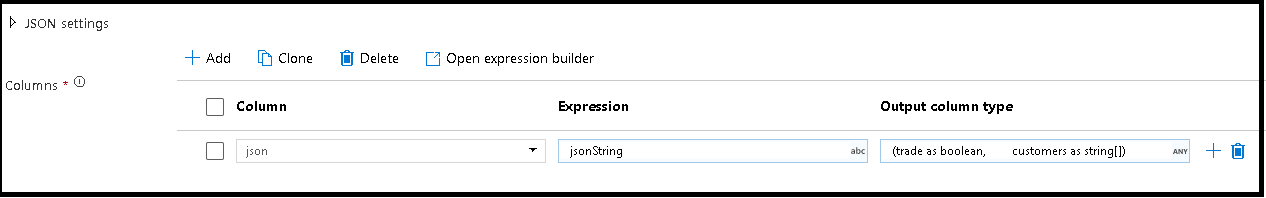
Column
Similar to derived columns and aggregates, the Column property is where you either modify an existing column by selecting it from the drop-down picker. Or you can type in the name of a new column here. ADF stores the parsed source data in this column. In most cases, you want to define a new column that parses the incoming embedded document string field.
Expression
Use the expression builder to set the source for your parsing. Setting the source can be as simple as just selecting the source column with the self-contained data that you wish to parse, or you can create complex expressions to parse.
Example expressions
Source string data:
chrome|steel|plastic- Expression:
(desc1 as string, desc2 as string, desc3 as string)
- Expression:
Source JSON data:
{"ts":1409318650332,"userId":"309","sessionId":1879,"page":"NextSong","auth":"Logged In","method":"PUT","status":200,"level":"free","itemInSession":2,"registration":1384448}- Expression:
(level as string, registration as long)
- Expression:
Source Nested JSON data:
{"car" : {"model" : "camaro", "year" : 1989}, "color" : "white", "transmission" : "v8"}- Expression:
(car as (model as string, year as integer), color as string, transmission as string)
- Expression:
Source XML data:
<Customers><Customer>122</Customer><CompanyName>Great Lakes Food Market</CompanyName></Customers>- Expression:
(Customers as (Customer as integer, CompanyName as string))
- Expression:
Source XML with Attribute data:
<cars><car model="camaro"><year>1989</year></car></cars>- Expression:
(cars as (car as ({@model} as string, year as integer)))
- Expression:
Expressions with reserved characters:
{ "best-score": { "section 1": 1234 } }- The above expression doesn't work since the '-' character in
best-scoreis interpreted as a subtraction operation. Use a variable with bracket notation in these cases to tell the JSON engine to interpret the text literally:var bestScore = data["best-score"]; { bestScore : { "section 1": 1234 } }
- The above expression doesn't work since the '-' character in
Note: If you run into errors extracting attributes (specifically, @model) from a complex type, a workaround is to convert the complex type to a string, remove the @ symbol (specifically, replace(toString(your_xml_string_parsed_column_name.cars.car),'@','') ), and then use the parse JSON transformation activity.
Output column type
Here's where you configure the target output schema from the parsing that is written into a single column. The easiest way to set a schema for your output from parsing is to select the 'Detect Type' button on the top right of the expression builder. ADF attempts to autodetect the schema from the string field, which you're parsing and set it for you in the output expression.
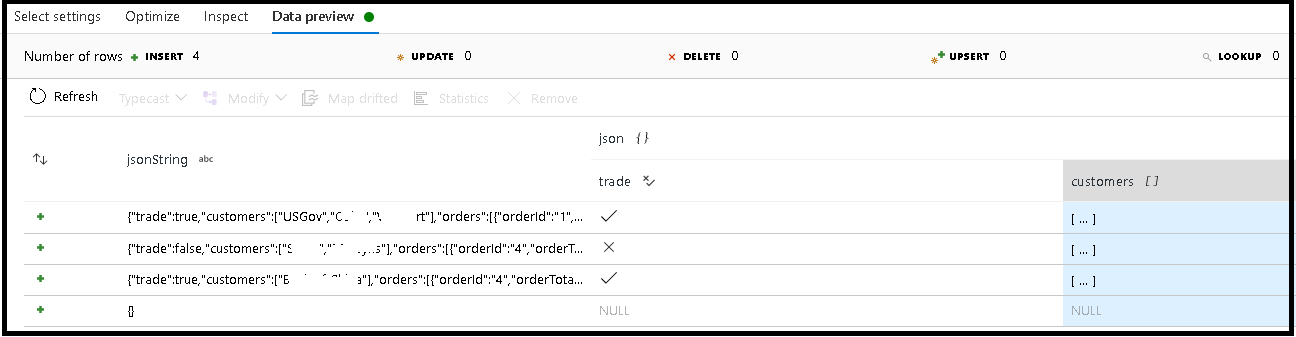
In this example, we defined parsing of the incoming field "jsonString", which is plain text, but formatted as a JSON structure. We're going to store the parsed results as JSON in a new column called "json" with this schema:
(trade as boolean, customers as string[])
Refer to the inspect tab and data preview to verify your output is mapped properly.
Use the Derived Column activity to extract hierarchical data (that is, your_complex_column_name.car.model in the expression field)
Examples
source(output(
name as string,
location as string,
satellites as string[],
goods as (trade as boolean, customers as string[], orders as (orderId as string, orderTotal as double, shipped as (orderItems as (itemName as string, itemQty as string)[]))[])
),
allowSchemaDrift: true,
validateSchema: false,
ignoreNoFilesFound: false,
documentForm: 'documentPerLine') ~> JsonSource
source(output(
movieId as string,
title as string,
genres as string
),
allowSchemaDrift: true,
validateSchema: false,
ignoreNoFilesFound: false) ~> CsvSource
JsonSource derive(jsonString = toString(goods)) ~> StringifyJson
StringifyJson parse(json = jsonString ? (trade as boolean,
customers as string[]),
format: 'json',
documentForm: 'arrayOfDocuments') ~> ParseJson
CsvSource derive(csvString = 'Id|name|year\n\'1\'|\'test1\'|\'1999\'') ~> CsvString
CsvString parse(csv = csvString ? (id as integer,
name as string,
year as string),
format: 'delimited',
columnNamesAsHeader: true,
columnDelimiter: '|',
nullValue: '',
documentForm: 'documentPerLine') ~> ParseCsv
ParseJson select(mapColumn(
jsonString,
json
),
skipDuplicateMapInputs: true,
skipDuplicateMapOutputs: true) ~> KeepStringAndParsedJson
ParseCsv select(mapColumn(
csvString,
csv
),
skipDuplicateMapInputs: true,
skipDuplicateMapOutputs: true) ~> KeepStringAndParsedCsv
Data flow script
Syntax
Examples
parse(json = jsonString ? (trade as boolean,
customers as string[]),
format: 'json|XML|delimited',
documentForm: 'singleDocument') ~> ParseJson
parse(csv = csvString ? (id as integer,
name as string,
year as string),
format: 'delimited',
columnNamesAsHeader: true,
columnDelimiter: '|',
nullValue: '',
documentForm: 'documentPerLine') ~> ParseCsv
Related content
- Use the Flatten transformation to pivot rows to columns.
- Use the Derived column transformation to transform rows.