Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
This article outlines how to use the Copy Activity in Azure Data Factory Synapse Analytics pipelines to copy data from and to a MongoDB database. It builds on the copy activity overview article that presents a general overview of copy activity.
Important
The new MongoDB connector provides improved native MongoDB support. If you are using the legacy MongoDB connector in your solution, supported as-is for backward compatibility only, refer to MongoDB connector (legacy) article.
Supported capabilities
This MongoDB connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR |
|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/sink) | ① ② |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For a list of data stores that are supported as sources/sinks, see the Supported data stores table.
Specifically, this MongoDB connector supports versions up to 4.2. If your work requires versions newer than 4.2, consider using MongoDB Atlas with the MongoDB Atlas connector, which provides more comprehensive support and features.
Prerequisites
If your data store is located inside an on-premises network, an Azure virtual network, or Amazon Virtual Private Cloud, you need to configure a self-hosted integration runtime to connect to it.
If your data store is a managed cloud data service, you can use the Azure Integration Runtime. If the access is restricted to IPs that are approved in the firewall rules, you can add Azure Integration Runtime IPs to the allow list.
You can also use the managed virtual network integration runtime feature in Azure Data Factory to access the on-premises network without installing and configuring a self-hosted integration runtime.
For more information about the network security mechanisms and options supported by Data Factory, see Data access strategies.
Getting started
To perform the Copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- The Copy Data tool
- The Azure portal
- The .NET SDK
- The Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- The REST API
- The Azure Resource Manager template
Create a linked service to MongoDB using UI
Use the following steps to create a linked service to MongoDB in the Azure portal UI.
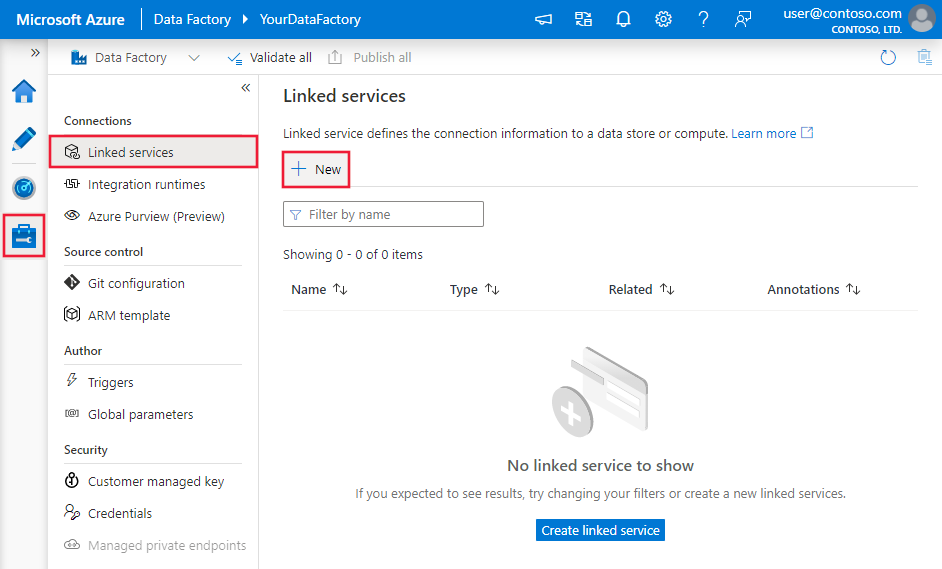
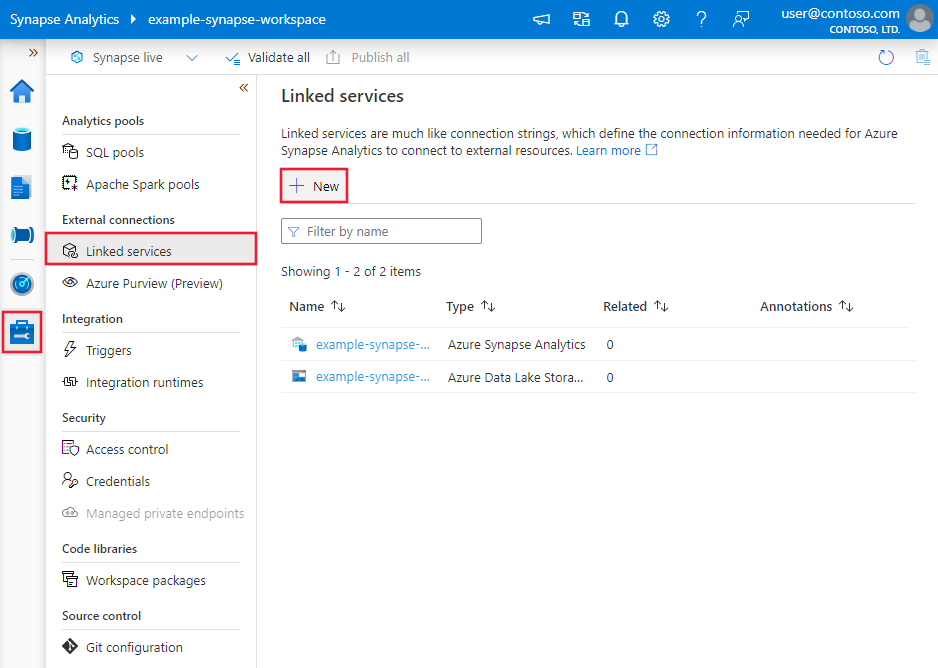
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
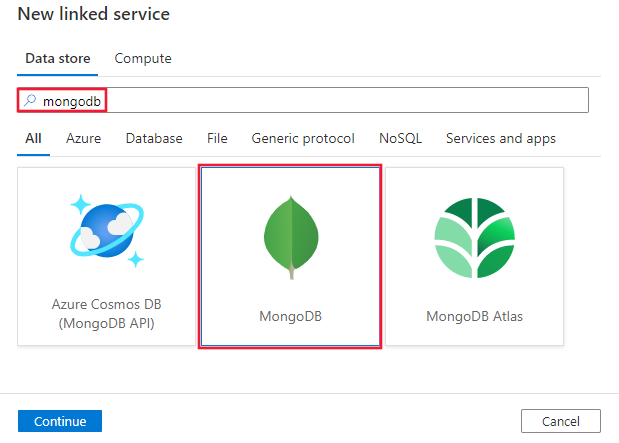
Search for MongoDB and select the MongoDB connector.
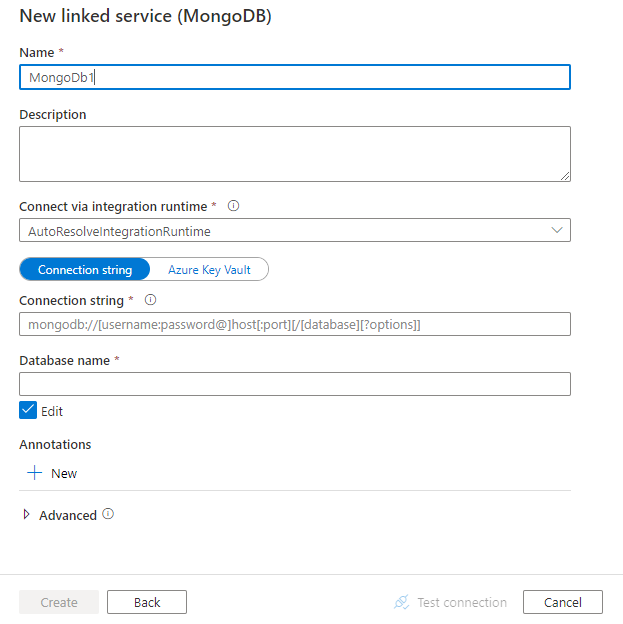
Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that are used to define Data Factory entities specific to MongoDB connector.
Linked service properties
The following properties are supported for MongoDB linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to: MongoDbV2 | Yes |
| connectionString | Specify the MongoDB connection string e.g. mongodb://[username:password@]host[:port][/[database][?options]]. Refer to MongoDB manual on connection string for more details. You can also put a connection string in Azure Key Vault. Refer to Store credentials in Azure Key Vault with more details. |
Yes |
| database | Name of the database that you want to access. | Yes |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to be used to connect to the data store. Learn more from Prerequisites section. If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
Example:
{
"name": "MongoDBLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "MongoDbV2",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "mongodb://[username:password@]host[:port][/[database][?options]]",
"database": "myDatabase"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties that are available for defining datasets, see Datasets and linked services. The following properties are supported for MongoDB dataset:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to: MongoDbV2Collection | Yes |
| collectionName | Name of the collection in MongoDB database. | Yes |
Example:
{
"name": "MongoDbDataset",
"properties": {
"type": "MongoDbV2Collection",
"typeProperties": {
"collectionName": "<Collection name>"
},
"schema": [],
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<MongoDB linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
}
}
}
Copy activity properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties supported by MongoDB source and sink.
MongoDB as source
The following properties are supported in the copy activity source section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to: MongoDbV2Source | Yes |
| filter | Specifies selection filter using query operators. To return all documents in a collection, omit this parameter or pass an empty document ({}). | No |
| cursorMethods.project | Specifies the fields to return in the documents for projection. To return all fields in the matching documents, omit this parameter. | No |
| cursorMethods.sort | Specifies the order in which the query returns matching documents. Refer to cursor.sort(). | No |
| cursorMethods.limit | Specifies the maximum number of documents the server returns. Refer to cursor.limit(). | No |
| cursorMethods.skip | Specifies the number of documents to skip and from where MongoDB begins to return results. Refer to cursor.skip(). | No |
| batchSize | Specifies the number of documents to return in each batch of the response from MongoDB instance. In most cases, modifying the batch size will not affect the user or the application. Azure Cosmos DB limits each batch cannot exceed 40 MB in size, which is the sum of the batchSize number of documents' size, so decrease this value if your document size being large. | No (the default is 100) |
Tip
The service supports consuming BSON document in Strict mode. Make sure your filter query is in Strict mode instead of Shell mode. More description can be found at MongoDB manual.
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromMongoDB",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<MongoDB input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "MongoDbV2Source",
"filter": "{datetimeData: {$gte: ISODate(\"2018-12-11T00:00:00.000Z\"),$lt: ISODate(\"2018-12-12T00:00:00.000Z\")}, _id: ObjectId(\"5acd7c3d0000000000000000\") }",
"cursorMethods": {
"project": "{ _id : 1, name : 1, age: 1, datetimeData: 1 }",
"sort": "{ age : 1 }",
"skip": 3,
"limit": 3
}
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
MongoDB as sink
The following properties are supported in the Copy Activity sink section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the Copy Activity sink must be set to MongoDbV2Sink. | Yes |
| writeBehavior | Describes how to write data to MongoDB. Allowed values: insert and upsert. The behavior of upsert is to replace the document if a document with the same _id already exists; otherwise, insert the document.Note: The service automatically generates an _id for a document if an _id isn't specified either in the original document or by column mapping. This means that you must ensure that, for upsert to work as expected, your document has an ID. |
No (the default is insert) |
| writeBatchSize | The writeBatchSize property controls the size of documents to write in each batch. You can try increasing the value for writeBatchSize to improve performance and decreasing the value if your document size being large. | No (the default is 10,000) |
| writeBatchTimeout | The wait time for the batch insert operation to finish before it times out. The allowed value is timespan. | No (the default is 00:30:00 - 30 minutes) |
Tip
To import JSON documents as-is, refer to Import or export JSON documents section; to copy from tabular-shaped data, refer to Schema mapping.
Example
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyToMongoDB",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Document DB output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "<source type>"
},
"sink": {
"type": "MongoDbV2Sink",
"writeBehavior": "upsert"
}
}
}
]
Import and export JSON documents
You can use this MongoDB connector to easily:
- Copy documents between two MongoDB collections as-is.
- Import JSON documents from various sources to MongoDB, including from Azure Cosmos DB, Azure Blob storage, Azure Data Lake Storage, and other supported file-based stores.
- Export JSON documents from a MongoDB collection to various file-based stores.
To achieve such schema-agnostic copy, skip the "structure" (also called schema) section in dataset and schema mapping in copy activity.
Schema mapping
To copy data from MongoDB to tabular sink or reversed, refer to schema mapping.
Upgrade the MongoDB linked service
Here are steps that help you upgrade your linked service and related queries:
Create a new MongoDB linked service and configure it by referring to Linked service properties.
If you use SQL queries in your pipelines that refer to the old MongoDB linked service, replace them with the equivalent MongoDB queries. See the following table for the replacement examples:
SQL query Equivalent MongoDB query SELECT * FROM usersdb.users.find({})SELECT username, age FROM usersdb.users.find({}, {username: 1, age: 1})SELECT username AS User, age AS Age, statusNumber AS Status, CASE WHEN Status = 0 THEN "Pending" CASE WHEN Status = 1 THEN "Finished" ELSE "Unknown" END AS statusEnum LastUpdatedTime + interval '2' hour AS NewLastUpdatedTime FROM usersdb.users.aggregate([{ $project: { _id: 0, User: "$username", Age: "$age", Status: "$statusNumber", statusEnum: { $switch: { branches: [ { case: { $eq: ["$Status", 0] }, then: "Pending" }, { case: { $eq: ["$Status", 1] }, then: "Finished" } ], default: "Unknown" } }, NewLastUpdatedTime: { $add: ["$LastUpdatedTime", 2 * 60 * 60 * 1000] } } }])SELECT employees.name, departments.name AS department_name FROM employees LEFT JOIN departments ON employees.department_id = departments.id;db.employees.aggregate([ { $lookup: { from: "departments", localField: "department_id", foreignField: "_id", as: "department" } }, { $unwind: "$department" }, { $project: { _id: 0, name: 1, department_name: "$department.name" } } ])
Related content
For a list of data stores supported as sources and sinks by the copy activity, see supported data stores.