Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
To lift & shift your on-premises SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) workloads to the cloud, you can provision Azure-SSIS Integration Runtime (IR) in Azure Data Factory (ADF). For more information, see Provision an Azure-SSIS IR. An Azure-SSIS IR supports:
- Running packages deployed into SSIS catalog (SSISDB) hosted by Azure SQL Database server/Managed Instance (Project Deployment Model)
- Running packages deployed into file system, Azure Files, or SQL Server database (MSDB) hosted by Azure SQL Managed Instance (Package Deployment Model)
When you use Package Deployment Model, you can choose whether you want to provision your Azure-SSIS IR with package stores. They provide a package management layer on top of file system, Azure Files, or MSDB hosted by Azure SQL Managed Instance. Azure-SSIS IR package store allows you to import/export/delete/run packages and monitor/stop running packages via SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) similar to the legacy SSIS package store.
Connect to Azure-SSIS IR
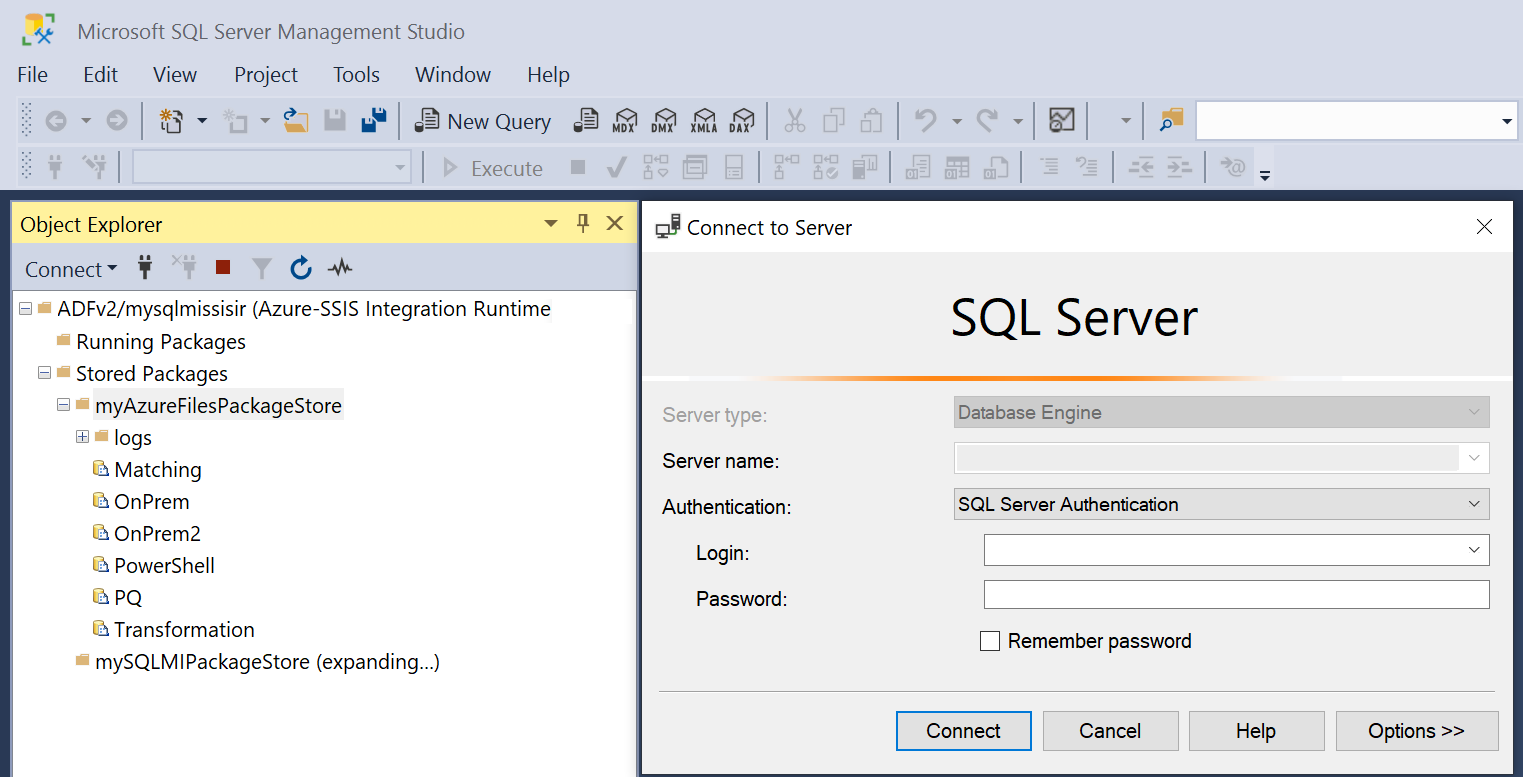
Once your Azure-SSIS IR is provisioned, you can connect to it to browse its package stores on SSMS.
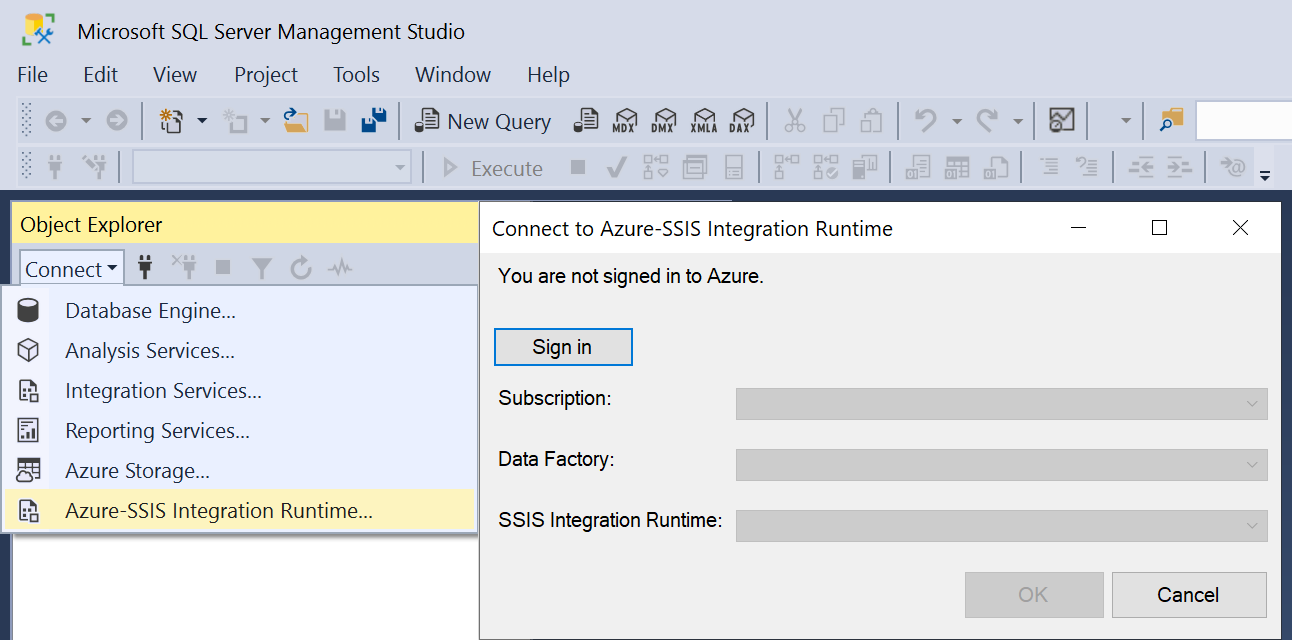
On the Object Explorer window of SSMS, select Azure-SSIS Integration Runtime in the Connect drop-down menu. Next, sign in to Azure and select the relevant subscription, ADF, and Azure-SSIS IR that you've provisioned with package stores. Your Azure-SSIS IR will appear with Running Packages and Stored Packages nodes underneath. Expand the Stored Packages node to see your package stores underneath. Expand your package stores to see folders and packages underneath. You might be asked to enter the access credentials for your package stores, if SSMS fails to connect to them automatically. For example, if you expand a package store on top of MSDB, you might be asked to connect to your Azure SQL Managed Instance first.
Manage folders and packages
After you connect to your Azure-SSIS IR on SSMS, you can right-click on any package stores, folders, or packages to pop up a menu and select New Folder, Import Package, Export Package, Delete, or Refresh.
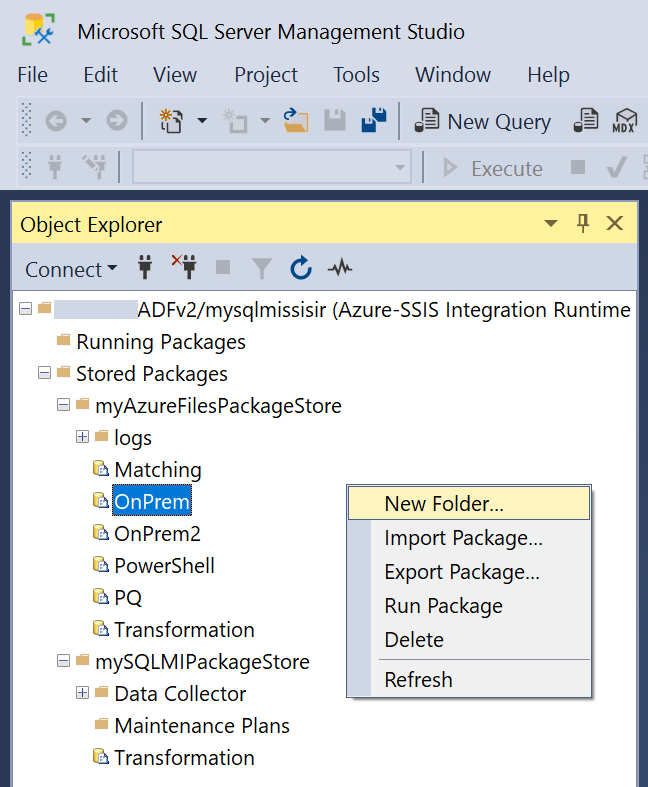
Select New Folder to create a new folder for imported packages.
Select Import Package to import packages from File System, SQL Server (MSDB), or the legacy SSIS Package Store into your package store.
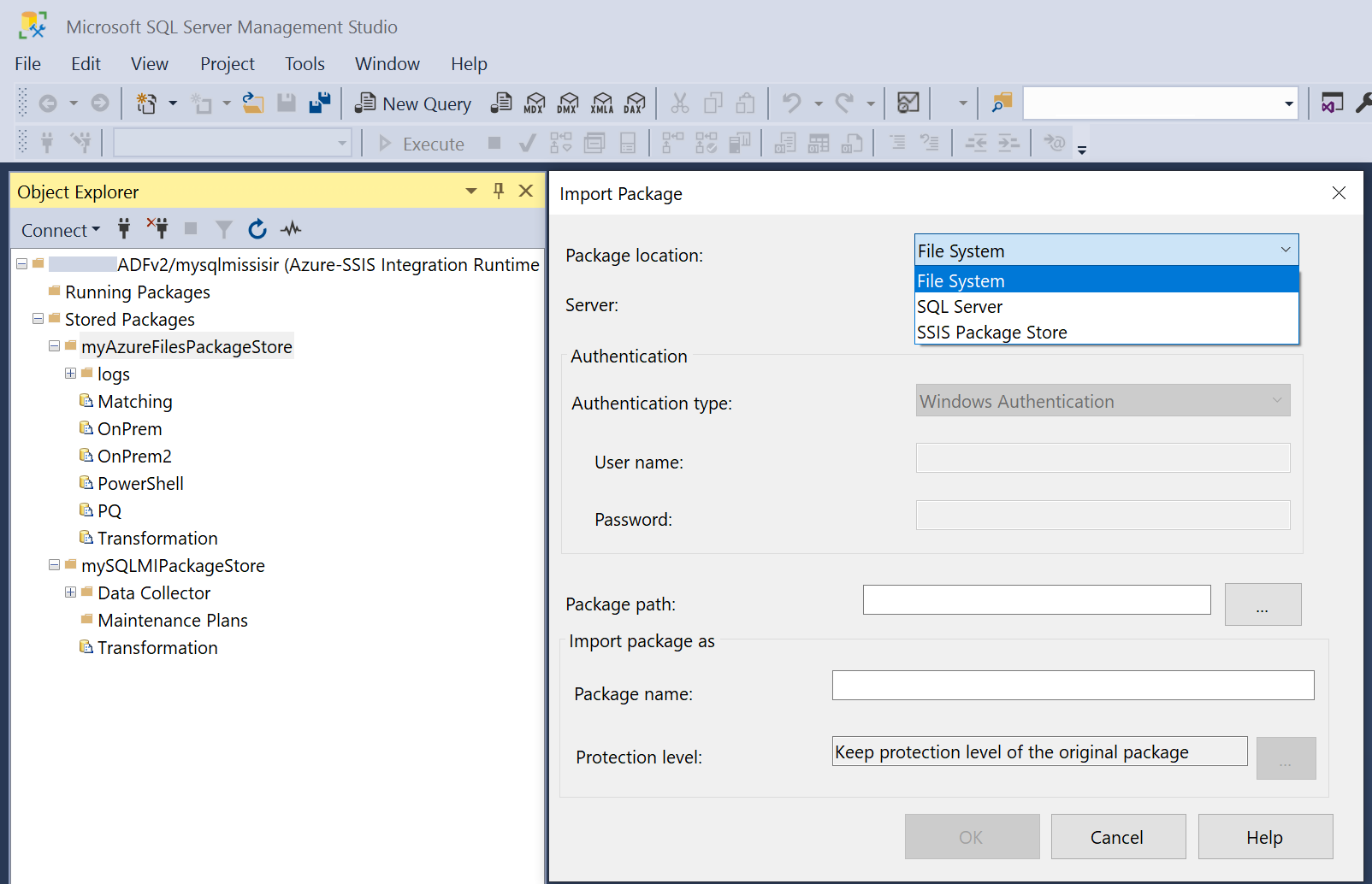
Depending on the Package location to import from, select the relevant Server/Authentication type, enter the access credentials if necessary, select the Package path, and enter the new Package name. When importing packages, their protection level can't be changed. To change it, use SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT) or
dtutilcommand-line utility.Note
Importing SSIS packages into Azure-SSIS IR package stores can only be done one-by-one and will simply copy them into the underlying MSDB/file system/Azure Files while preserving their SQL Server/SSIS version.
Since Azure-SSIS IR is currently based on SQL Server 2017, executing lower-version packages on it will upgrade them into SSIS 2017 packages at run-time. Executing higher-version packages is unsupported.
Additionally, since legacy SSIS package stores are bound to specific SQL Server version and accessible only on SSMS for that version, lower-version packages in legacy SSIS package stores need to be exported into file system first using the designated SSMS version before they can be imported into Azure-SSIS IR package stores using SSMS 2019 or later versions.
Alternatively, to import multiple SSIS packages into Azure-SSIS IR package stores while switching their protection level, you can use dtutil command line utility, see Deploying multiple packages with dtutil.
Select Export Package to export packages from your package store into File System, SQL Server (MSDB), or the legacy SSIS Package Store.
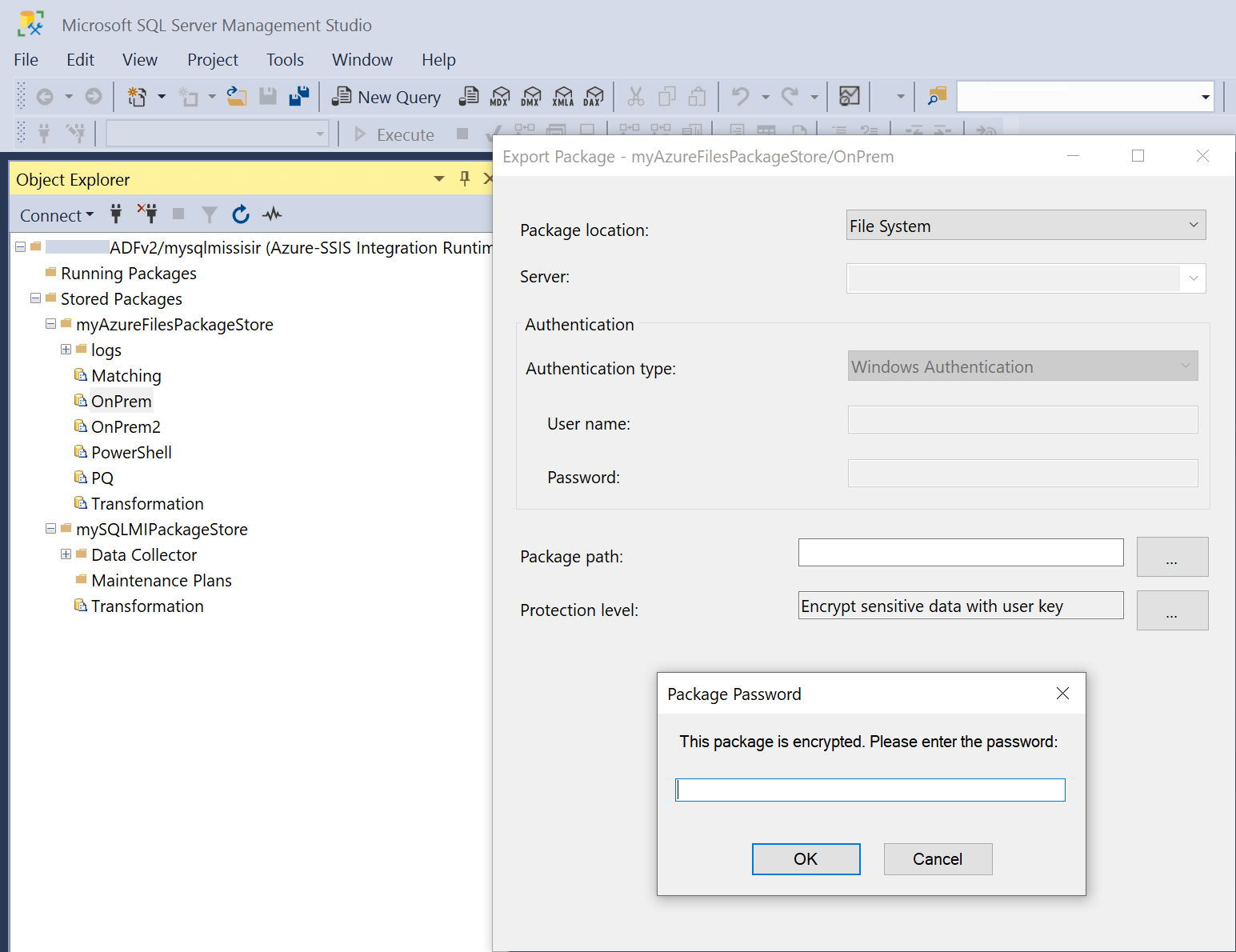
Depending on the Package location to export into, select the relevant Server/Authentication type, enter the access credentials if necessary, and select the Package path. When exporting packages, if they're encrypted, enter the passwords to decrypt them first and then you can change their protection level, for example to avoid storing any sensitive data or to encrypt it or all data with user key or password.
Note
Exporting SSIS packages from Azure-SSIS IR package stores can only be done one-by-one and doing so without switching their protection level will simply copy them while preserving their SQL Server/SSIS version, otherwise it will upgrade them into SSIS 2019 or later-version packages.
Since Azure-SSIS IR is currently based on SQL Server 2017, executing lower-version packages on it will upgrade them into SSIS 2017 packages at run-time. Executing higher-version packages is unsupported.
Alternatively, to export multiple SSIS packages from Azure-SSIS IR package stores while switching their protection level, you can use dtutil command line utility, see Deploying multiple packages with dtutil.
Select Delete to delete existing folders/packages from your package store.
Select Refresh to show newly added folders/packages in your package store.
Execute packages
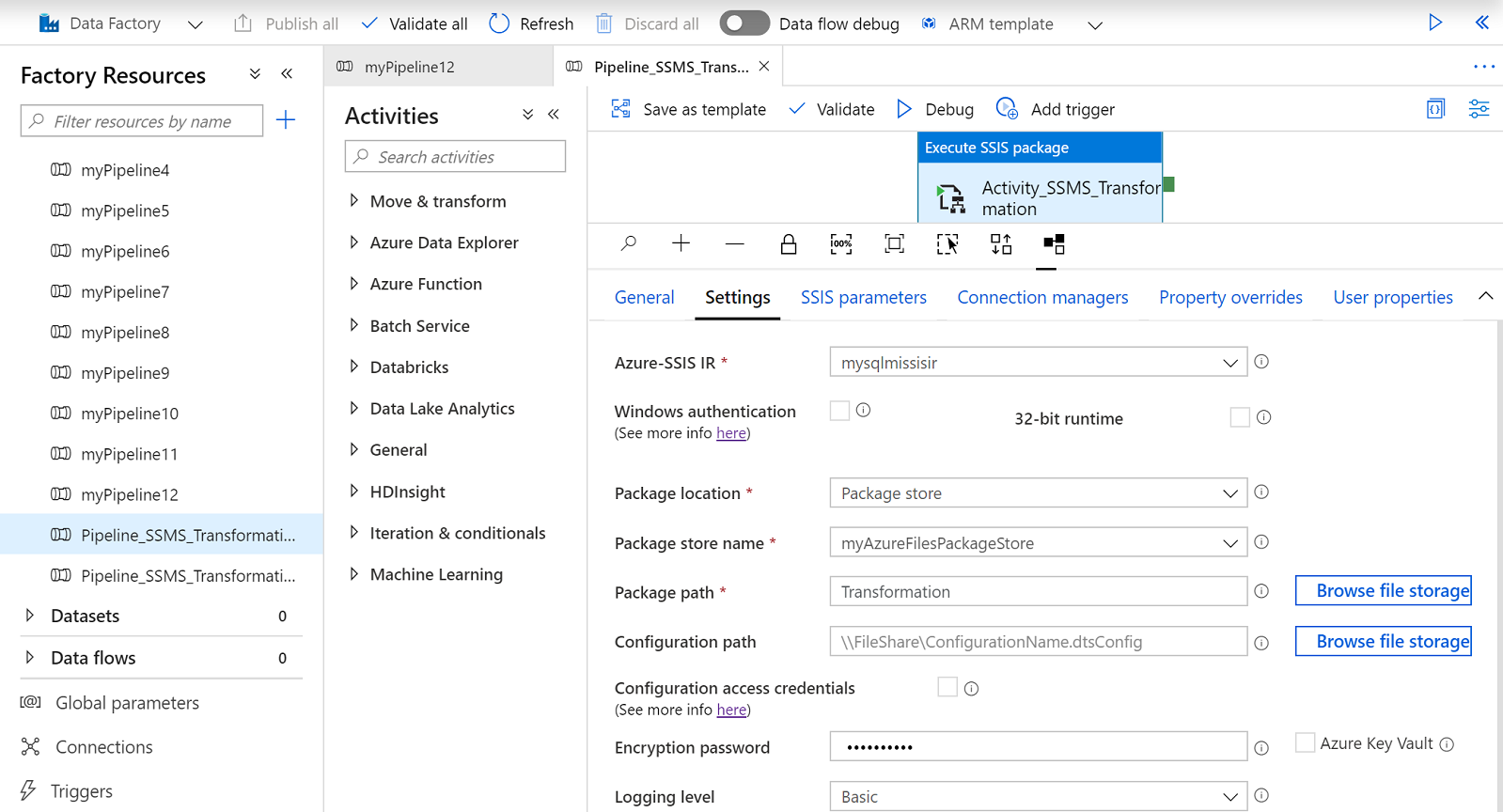
After you connect to your Azure-SSIS IR on SSMS, you can right-click on any stored packages to pop up a menu and select Run Package. This will open the Execute Package Utility dialog, where you can configure your package executions on Azure-SSIS IR as Execute SSIS Package activities in ADF pipelines.
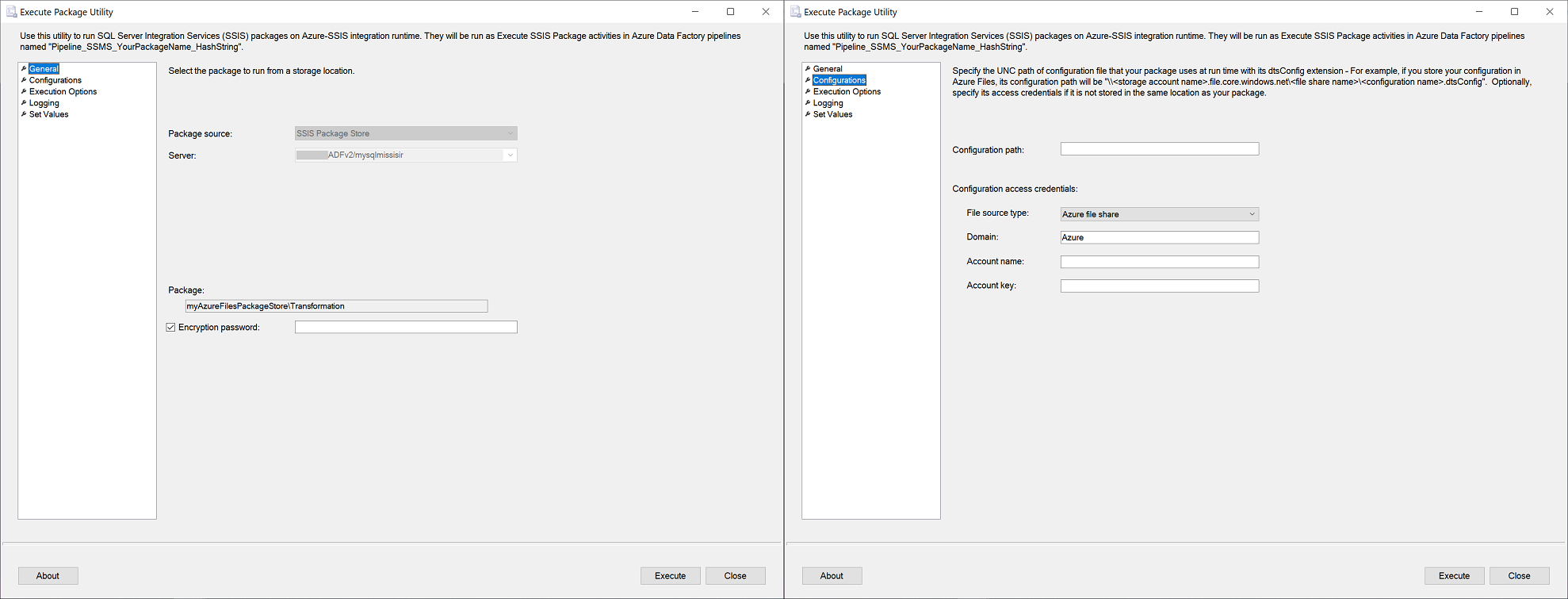
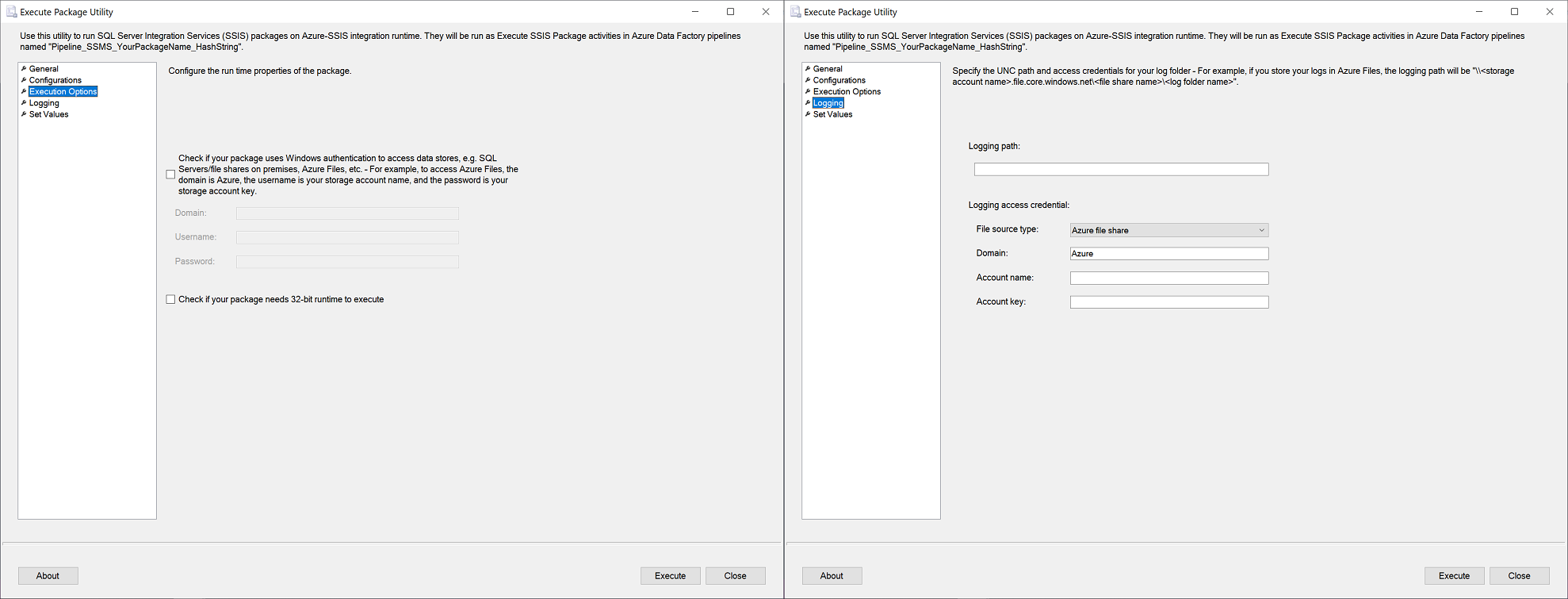
The General, Configurations, Execution Options, and Logging pages of Execute Package Utility dialog correspond to the Settings tab of Execute SSIS Package activity. On these pages, you can enter the encryption password for your package and access information for your package configuration file. You can also enter your package execution credentials and properties, as well as the access information for your log folder. The Set Values page of Execute Package Utility dialog corresponds to the Property Overrides tab of Execute SSIS Package activity, where you can enter your existing package properties to override. For more information, see Run SSIS packages as Execute SSIS Package activities in ADF pipelines.
When you select the Execute button, a new ADF pipeline with Execute SSIS Package activity will be automatically generated and triggered. If an ADF pipeline with the same settings already exists, it will be rerun and a new pipeline won't be generated. The ADF pipeline and Execute SSIS Package activity will be named Pipeline_SSMS_YourPackageName_HashString and Activity_SSMS_YourPackageName, respectively.
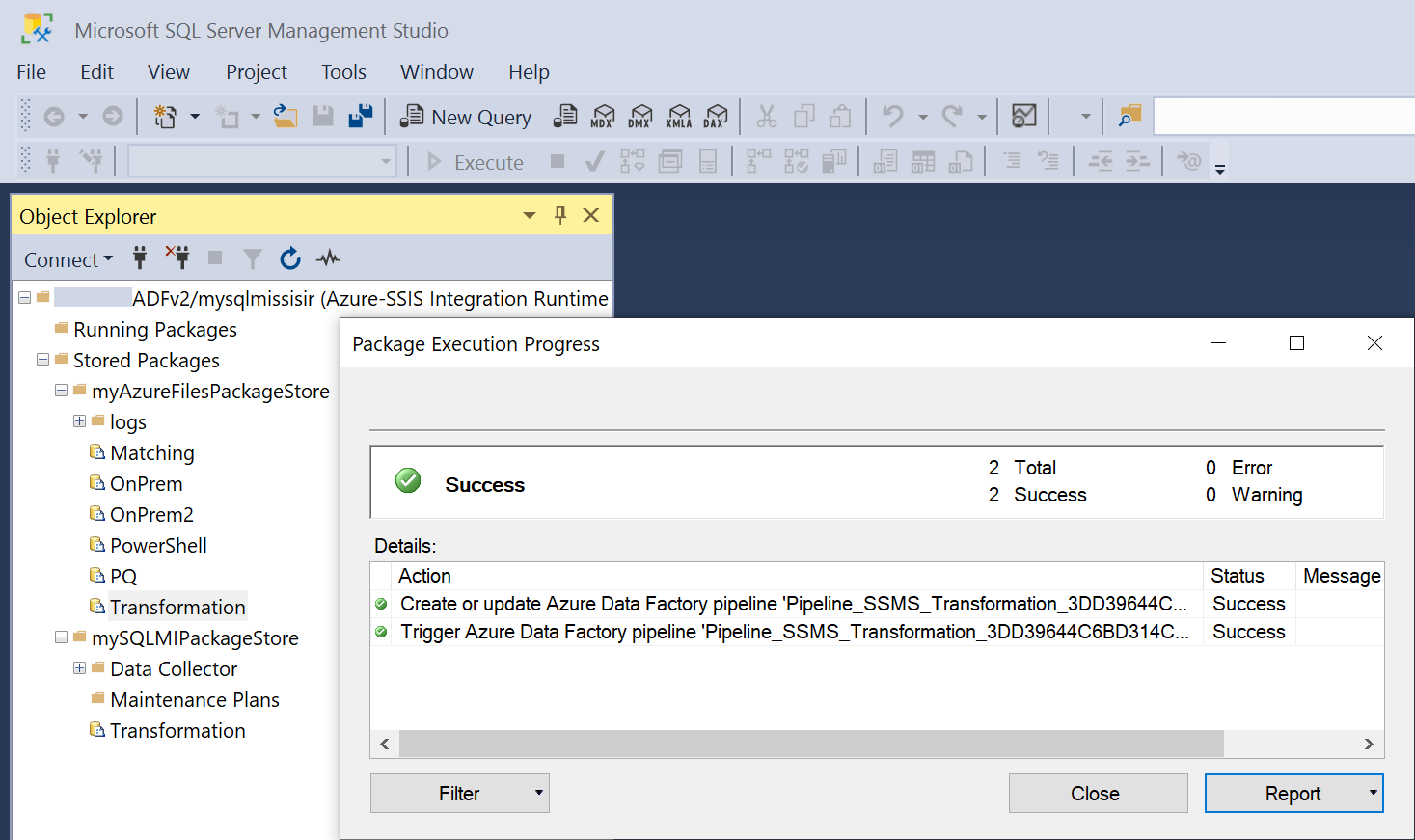
Monitor and stop running packages
After you connect to your Azure-SSIS IR on SSMS, you can expand the Running Packages node to see your currently running packages underneath. Right-click on any of them to pop up a menu and select Stop or Refresh.
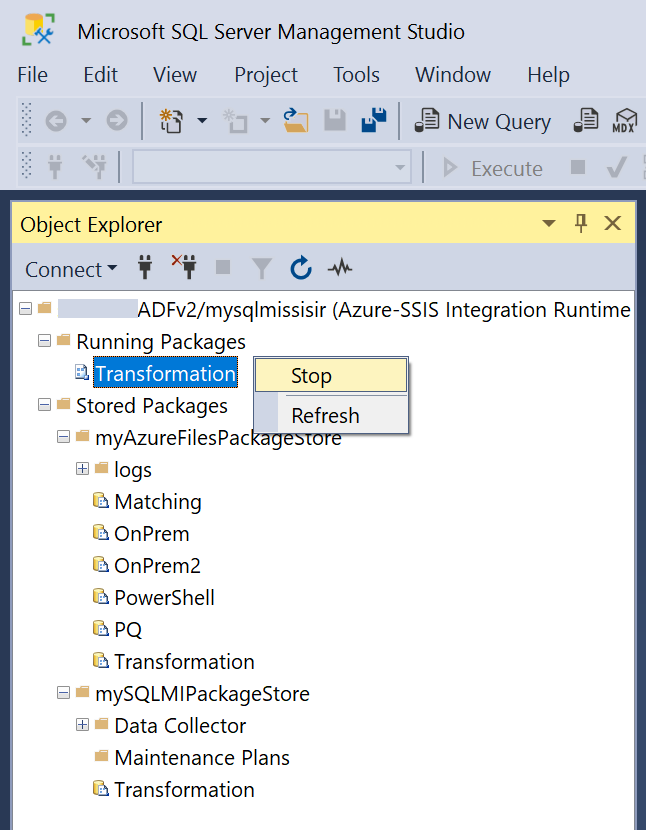
Select Stop to cancel the currently running ADF pipeline that runs the package as Execute SSIS Package activity.
Select Refresh to show newly running packages from your package stores.
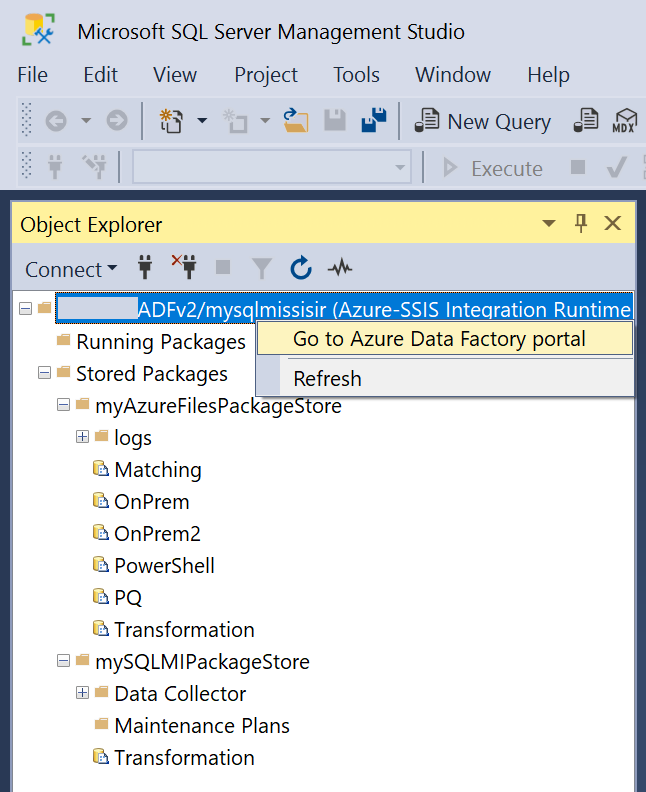
Monitor Azure-SSIS IR and edit package stores
After you connect to your Azure-SSIS IR on SSMS, you can right-click on it to pop up a menu and select Go to Azure Data Factory portal or Refresh.
Select Go to Azure Data Factory portal to open the Integration runtimes page of ADF monitoring hub, where you can monitor your Azure-SSIS IR. On the PACKAGE STORES tile, you can see the number of package stores that are attached to your Azure-SSIS IR. Selecting that number will pop up a window where you can edit ADF linked services that store the access information for your package stores.
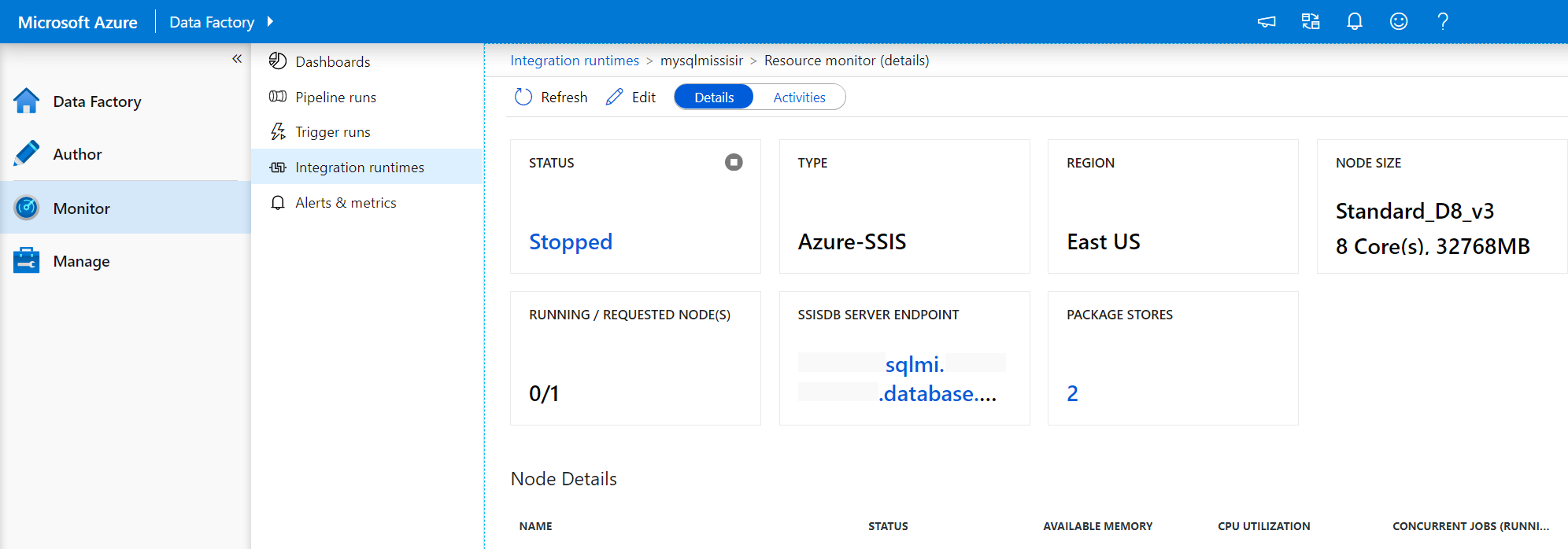
Select Refresh to show newly added folders/packages in your package stores and running packages from your package stores.
Deploying multiple packages with dtutil
To lift & shift your on-premises SSIS workloads onto SSIS in ADF while maintaining the legacy Package Deployment Model, you need to deploy your packages from file system, MSDB hosted by SQL Server, or legacy SSIS package stores into Azure Files, MSDB hosted by Azure SQL Managed Instance, or Azure-SSIS IR package stores. At the same time, you should also switch their protection level from encryption by user key to unencrypted or encryption by password if you haven't done so already.
You can use dtutil command line utility that comes with SQL Server/SSIS installation to deploy multiple packages in batches. It's bound to specific SSIS version, so if you use it to deploy lower-version packages without switching their protection level, it will simply copy them while preserving their SSIS version. If you use it to deploy them and switch their protection level at the same time, it will upgrade them into its SSIS version.
Since Azure-SSIS IR is currently based on SQL Server 2017, executing lower-version packages on it will upgrade them into SSIS 2017 packages at run-time. Executing higher-version packages is unsupported.
Consequently, to avoid run-time upgrades, deploying packages to run on Azure-SSIS IR in Package Deployment Model should use dtutil 2017 that comes with SQL Server/SSIS 2017 installation. You can download and install the free SQL Server/SSIS 2017 Developer Edition for this purpose. Once installed, you can find dtutil 2017 on this folder: YourLocalDrive:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\140\DTS\Binn.
Deploying multiple packages from file system on premises into Azure Files with dtutil
To deploy multiple packages from file system into Azure Files and switch their protection level at the same time, you can run the following commands at a command prompt. Please replace all strings that are specific to your case.
REM Persist the access credentials for Azure Files on your local machine
cmdkey /ADD:YourStorageAccountName.file.core.chinacloudapi.cn /USER:azure\YourStorageAccountName /PASS:YourStorageAccountKey
REM Connect Azure Files to a drive on your local machine
net use Z: \\YourStorageAccountName.file.core.chinacloudapi.cn\YourFileShare /PERSISTENT:Yes
REM Go to a local folder where you store your packages
cd YourLocalDrive:\...\YourPackageFolder
REM Run dtutil in a loop to deploy your packages from the local folder into Azure Files while switching their protection level
for %f in (*.dtsx) do dtutil.exe /FILE %f /ENCRYPT FILE;Z:\%f;2;YourEncryptionPassword
To run the above commands in a batch file, replace %f with %%f.
To deploy multiple packages from legacy SSIS package stores on top of file system into Azure Files and switch their protection level at the same time, you can use the same commands, but replace YourLocalDrive:\...\YourPackageFolder with a local folder used by legacy SSIS package stores: YourLocalDrive:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\YourSQLServerDefaultCompatibilityLevel\DTS\Packages\YourPackageFolder. For example, if your legacy SSIS package store is bound to SQL Server 2016, go to YourLocalDrive:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\130\DTS\Packages\YourPackageFolder. You can find the value for YourSQLServerDefaultCompatibilityLevel from a list of SQL Server default compatibility levels.
If you've configured Azure-SSIS IR package stores on top of Azure Files, your deployed packages will appear in them when you connect to your Azure-SSIS IR on SSMS 2019 or later versions.
Deploying multiple packages from MSDB on premises into MSDB in Azure with dtutil
To deploy multiple packages from MSDB hosted by SQL Server or legacy SSIS package stores on top of MSDB into MSDB hosted by Azure SQL Managed Instance and switch their protection level at the same time, you can connect to your SQL Server on SSMS, right-click on Databases->System Databases->msdb node on the Object Explorer of SSMS to open a New Query window, and run the following T-SQL script. Please replace all strings that are specific to your case:
BEGIN
SELECT 'dtutil /SQL '+f.foldername+'\'+NAME+' /ENCRYPT SQL;'+f.foldername+'\'+NAME+';2;YourEncryptionPassword /DestServer YourSQLManagedInstanceEndpoint /DestUser YourSQLAuthUsername /DestPassword YourSQLAuthPassword'
FROM msdb.dbo.sysssispackages p
inner join msdb.dbo.sysssispackagefolders f
ON p.folderid = f.folderid
END
To use the private/public endpoint of your Azure SQL Managed Instance, replace YourSQLManagedInstanceEndpoint with YourSQLMIName.YourDNSPrefix.database.chinacloudapi.cn/YourSQLMIName.public.YourDNSPrefix.database.chinacloudapi.cn,3342, respectively.
The script will generate dtutil command lines for all packages in MSDB that you can multiselect, copy & paste, and run at a command prompt.
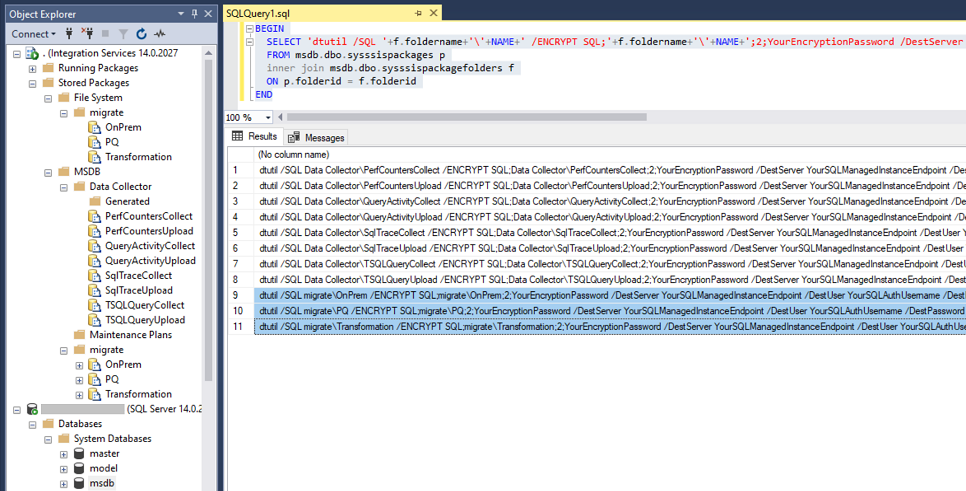
dtutil /SQL YourFolder\YourPackage1 /ENCRYPT SQL;YourFolder\YourPackage1;2;YourEncryptionPassword /DestServer YourSQLManagedInstanceEndpoint /DestUser YourUserName /DestPassword YourPassword
dtutil /SQL YourFolder\YourPackage2 /ENCRYPT SQL;YourFolder\YourPackage2;2;YourEncryptionPassword /DestServer YourSQLManagedInstanceEndpoint /DestUser YourUserName /DestPassword YourPassword
dtutil /SQL YourFolder\YourPackage3 /ENCRYPT SQL;YourFolder\YourPackage3;2;YourEncryptionPassword /DestServer YourSQLManagedInstanceEndpoint /DestUser YourUserName /DestPassword YourPassword
If you've configured Azure-SSIS IR package stores on top of MSDB, your deployed packages will appear in them when you connect to your Azure-SSIS IR on SSMS 2019 or later versions.
Deploying multiple packages from MSDB on premises into Azure Files with dtutil
To deploy multiple packages from MSDB hosted by SQL Server or legacy SSIS package stores on top of MSDB into Azure Files and switch their protection level at the same time, you can connect to your SQL Server on SSMS, right-click on Databases->System Databases->msdb node on the Object Explorer of SSMS to open a New Query window, and run the following T-SQL script. Please replace all strings that are specific to your case:
BEGIN
SELECT 'dtutil /SQL '+f.foldername+'\'+NAME+' /ENCRYPT FILE;Z:\'+f.foldername+'\'+NAME+'.dtsx;2;YourEncryptionPassword'
FROM msdb.dbo.sysssispackages p
inner join msdb.dbo.sysssispackagefolders f
ON p.folderid = f.folderid
END
The script will generate dtutil command lines for all packages in MSDB that you can multiselect, copy & paste, and run at a command prompt.
REM Persist the access credentials for Azure Files on your local machine
cmdkey /ADD:YourStorageAccountName.file.core.chinacloudapi.cn /USER:azure\YourStorageAccountName /PASS:YourStorageAccountKey
REM Connect Azure Files to a drive on your local machine
net use Z: \\YourStorageAccountName.file.core.chinacloudapi.cn\YourFileShare /PERSISTENT:Yes
REM Multiselect, copy & paste, and run the T-SQL-generated dtutil command lines to deploy your packages from MSDB on premises into Azure Files while switching their protection level
dtutil /SQL YourFolder\YourPackage1 /ENCRYPT FILE;Z:\YourFolder\YourPackage1.dtsx;2;YourEncryptionPassword
dtutil /SQL YourFolder\YourPackage2 /ENCRYPT FILE;Z:\YourFolder\YourPackage2.dtsx;2;YourEncryptionPassword
dtutil /SQL YourFolder\YourPackage3 /ENCRYPT FILE;Z:\YourFolder\YourPackage3.dtsx;2;YourEncryptionPassword
If you've configured Azure-SSIS IR package stores on top of Azure Files, your deployed packages will appear in them when you connect to your Azure-SSIS IR on SSMS 2019 or later versions.
Related content
You can rerun/edit the auto-generated ADF pipelines with Execute SSIS Package activities or create new ones on ADF portal. For more information, see Run SSIS packages as Execute SSIS Package activities in ADF pipelines.