geo_point_in_circle()
Applies to: ✅ Azure Data Explorer ✅ Azure Monitor ✅ Microsoft Sentinel
Calculates whether the geospatial coordinates are inside a circle on Earth.
Syntax
geo_point_in_circle(p_longitude, p_latitude, pc_longitude, pc_latitude, c_radius)
Learn more about syntax conventions.
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| p_longitude | real |
✔️ | Geospatial coordinate longitude value in degrees. Valid value is a real number and in the range [-180, +180]. |
| p_latitude | real |
✔️ | Geospatial coordinate latitude value in degrees. Valid value is a real number and in the range [-90, +90]. |
| pc_longitude | real |
✔️ | Circle center geospatial coordinate longitude value in degrees. Valid value is a real number and in the range [-180, +180]. |
| pc_latitude | real |
✔️ | circle center geospatial coordinate latitude value in degrees. Valid value is a real number and in the range [-90, +90]. |
| c_radius | real |
✔️ | Circle radius in meters. Valid value must be positive. |
Returns
Indicates whether the geospatial coordinates are inside a circle. If the coordinates or circle is invalid, the query produces a null result.
Note
- The geospatial coordinates are interpreted as represented by the WGS-84 coordinate reference system.
- The geodetic datum used to measure distance on Earth is a sphere.
- A circle is a spherical cap on Earth. The radius of the cap is measured along the surface of the sphere.
Examples
The following example finds all the places in the area defined by the following circle: Radius of 18 km, center at [-122.317404, 47.609119] coordinates.
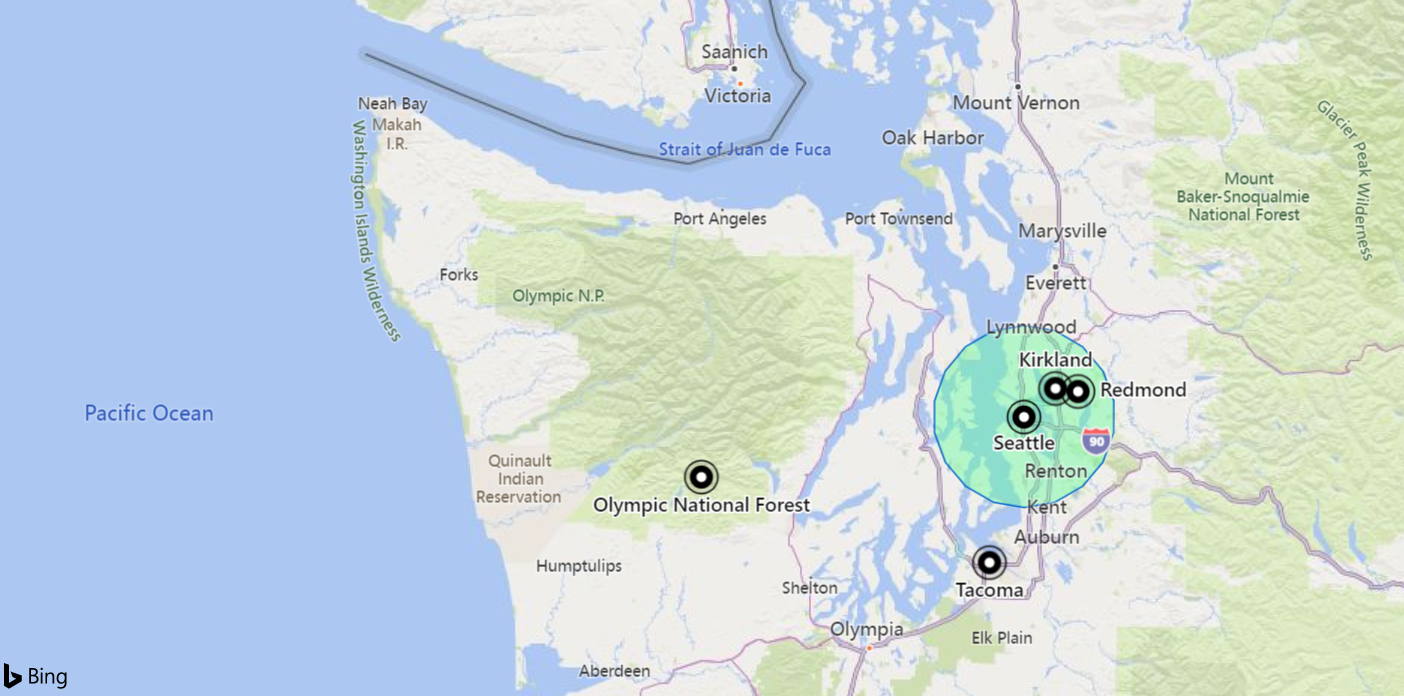
datatable(longitude:real, latitude:real, place:string)
[
real(-122.317404), 47.609119, 'Seattle', // In circle
real(-123.497688), 47.458098, 'Olympic National Forest', // In exterior of circle
real(-122.201741), 47.677084, 'Kirkland', // In circle
real(-122.443663), 47.247092, 'Tacoma', // In exterior of circle
real(-122.121975), 47.671345, 'Redmond', // In circle
]
| where geo_point_in_circle(longitude, latitude, -122.317404, 47.609119, 18000)
| project place
Output
| place |
|---|
| Seattle |
| Kirkland |
| Redmond |
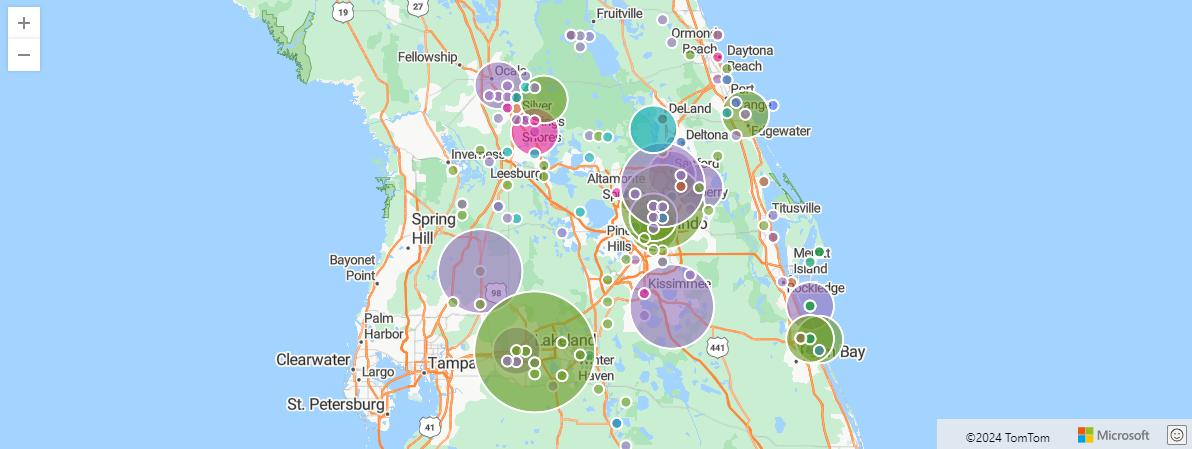
The following example finds storm events in Orlando. The events are filtered by 100 km within Orlando coordinates, and aggregated by event type and hash.
StormEvents
| project BeginLon, BeginLat, EventType
| where geo_point_in_circle(BeginLon, BeginLat, real(-81.3891), 28.5346, 1000 * 100)
| summarize count() by EventType, hash = geo_point_to_s2cell(BeginLon, BeginLat)
| project geo_s2cell_to_central_point(hash), EventType, count_
| render piechart with (kind=map) // map pie rendering available in Kusto Explorer desktop
Output
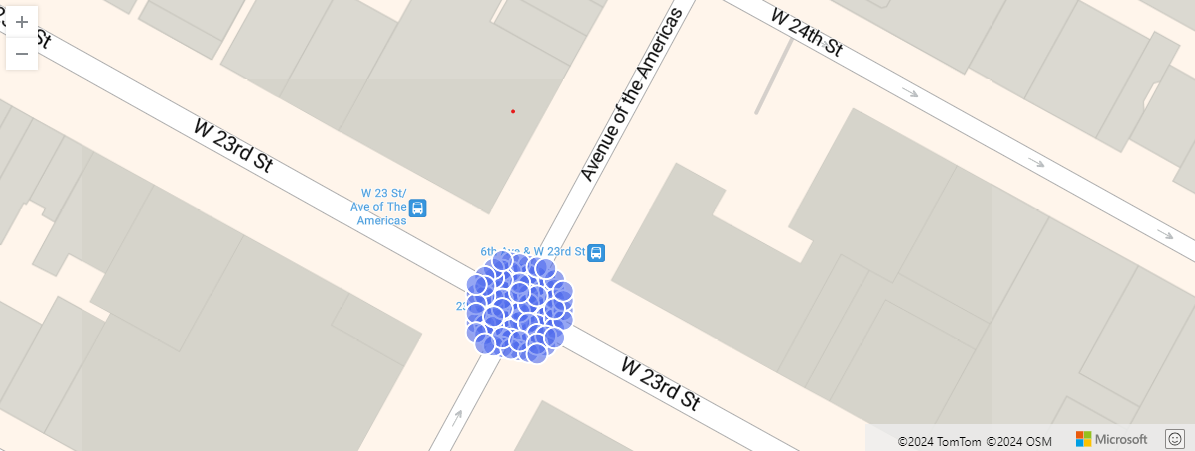
The following example shows New York city taxi pickups within 10 meters of a particular location. Relevant pickups are aggregated by hash.
nyc_taxi
| project pickup_longitude, pickup_latitude
| where geo_point_in_circle( pickup_longitude, pickup_latitude, real(-73.9928), 40.7429, 10)
| summarize by hash = geo_point_to_s2cell(pickup_longitude, pickup_latitude, 22)
| project geo_s2cell_to_central_point(hash)
| render scatterchart with (kind = map)
Output
The following example returns true.
print in_circle = geo_point_in_circle(-122.143564, 47.535677, -122.100896, 47.527351, 3500)
Output
| in_circle |
|---|
| true |
The following example returns false.
print in_circle = geo_point_in_circle(-122.137575, 47.630683, -122.100896, 47.527351, 3500)
Output
| in_circle |
|---|
| false |
The following example returns a null result because of the invalid coordinate input.
print in_circle = geo_point_in_circle(200, 1, 1, 1, 1)
Output
| in_circle |
|---|
The following example returns a null result because of the invalid circle radius input.
print in_circle = geo_point_in_circle(1, 1, 1, 1, -1)
Output
| in_circle |
|---|