Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
MongoDB
Gremlin
Table
Azure Cosmos DB's point-in-time restore feature helps you to recover from an accidental change within a container, to restore a deleted account, database, or a container or to restore into any region (where backups existed). The continuous backup mode allows you to do restore to any point of time within the last 30 days.
This article describes how to identify the restore time and restore a live or deleted Azure Cosmos DB account. It shows how to restore the account using the Azure portal, PowerShell, CLI, or an Azure Resource Manager template.
Restore an account using Azure portal
Restore a live account from accidental modification
You can use Azure portal to restore an entire live account or selected databases and containers under it. Use the following steps to restore your data:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
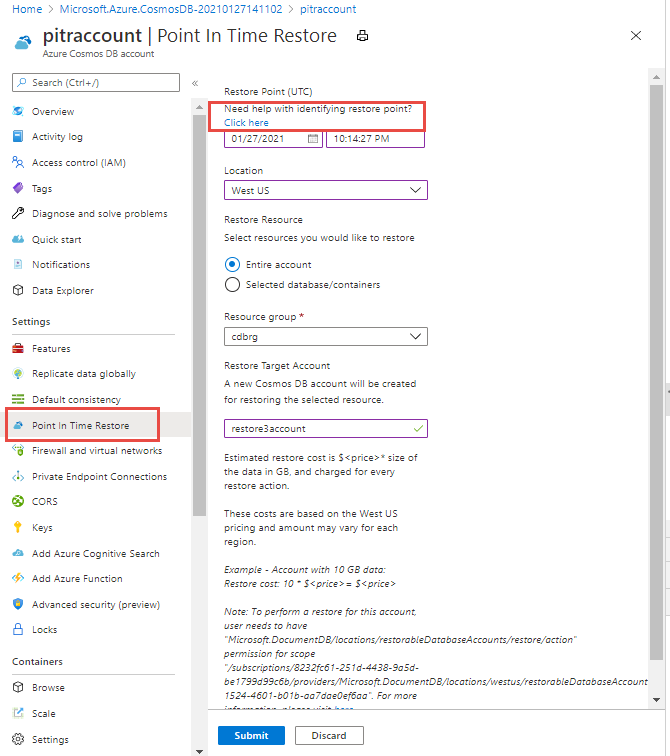
Navigate to your Azure Cosmos DB account and open the Point In Time Restore blade.
Note
The restore blade in Azure portal is only populated if you have the
Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts/*/readpermission. To learn more about how to set this permission, see the Backup and restore permissions article.Fill the following details to restore:
Restore Point (UTC) – A timestamp within the last 30 days. The account should exist at that timestamp. You can specify the restore point in UTC. It can be as close to the second when you want to restore it. Select the Click here link to get help on identifying the restore point.
Location - The destination region where the account is restored. The account should exist in this region at the given timestamp (for example, China North or China East). An account can be restored only to the regions in which the source account existed.
Restore Resource – You can either choose Entire account or a selected database/container to restore. The databases and containers should exist at the given timestamp. Based on the restore point and location selected, restore resources are populated, which allows user to select specific databases or containers that need to be restored.
Resource group - Resource group under which the target account will be created and restored. The resource group must already exist.
Restore Target Account – The target account name. The target account name needs to follow same guidelines as when you are creating a new account. This account will be created by the restore process in the same region where your source account exists.
After you select the above parameters, select the Submit button to kick off a restore. The restore cost is a one time charge, which is based on the size of data and the cost of backup storage in the selected region. To learn more, see the Pricing section.
Deleting source account while a restore is in-progress could result in failure of the restore.
Restorable timestamp for live accounts
To restore Azure Cosmos DB live accounts that are not deleted, it is a best practice to always identify the latest restorable timestamp for the container. You can then use this timestamp to restore the account to its latest version.
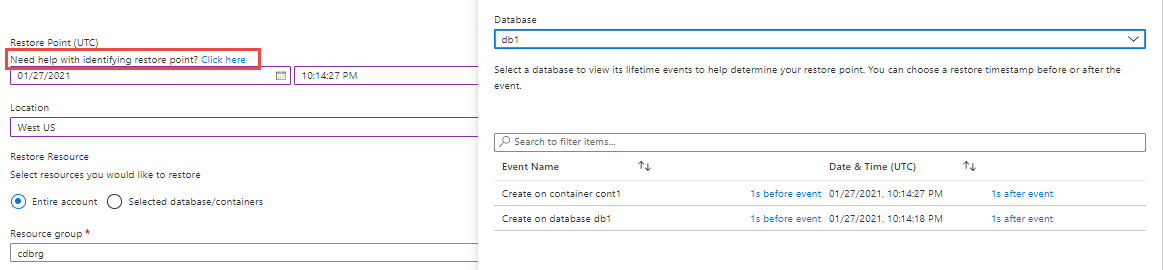
Use event feed to identify the restore time
When filling out the restore point time in the Azure portal, if you need help with identifying restore point, select the Click here link, it takes you to the event feed blade. The event feed provides a full fidelity list of create, replace, delete events on databases and containers of the source account.
For example, if you want to restore to the point before a certain container was deleted or updated, check this event feed. Events are displayed in chronologically descending order of time when they occurred, with recent events at the top. You can browse through the results and select the time before or after the event to further narrow your time.
Note
The event feed does not display the changes to the item resources. You can always manually specify any timestamp in the last 30 days (as long as account exists at that time) for restore.
Restore a deleted account
You can use Azure portal to completely restore a deleted account within 30 days of its deletion. Use the following steps to restore a deleted account:
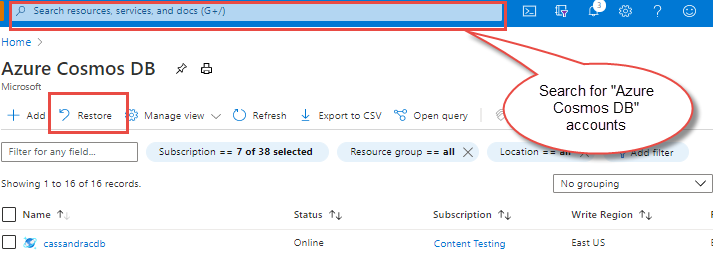
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Search for Azure Cosmos DB resources in the global search bar. It lists all your existing accounts.
Next select the Restore button. The Restore blade displays a list of deleted accounts that can be restored within the retention period, which is 30 days from deletion time.
Choose the account that you want to restore.
Note
The restore blade in Azure portal is only populated if you have the
Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts/*/readpermission. To learn more about how to set this permission, see the Backup and restore permissions article.Select an account to restore and input the following details to restore a deleted account:
Restore Point (UTC) – A timestamp within the last 30 days. The account should have existed at that timestamp. Specify the restore point in UTC. It can be as close to the second when you want to restore it.
Location - The destination region where the account needs to be restored. The source account should exist in this region at the given timestamp. Example China North or China East.
Resource group - Resource group under which the target account will be created and restored. The resource group must already exist.
Restore Target Account – The target account name needs to follow same guidelines as when you are creating a new account. This account will be created by the restore process in the same region where your source account exists.
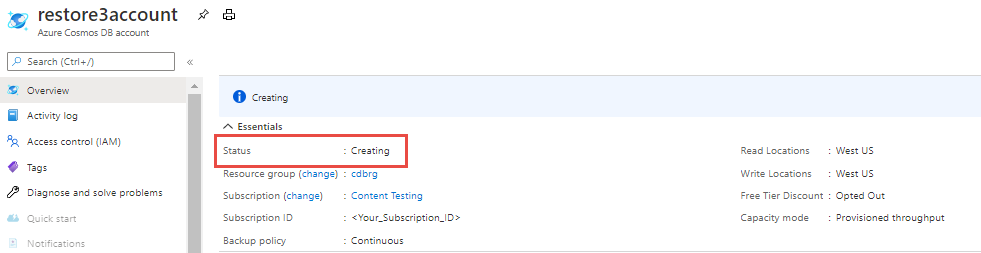
Track the status of restore operation
After initiating a restore operation, select the Notification bell icon at top-right corner of portal. It gives a link displaying the status of the account being restored. While restore is in progress, the status of the account will be Creating, after the restore operation completes, the account status will change to Online.
Get the restore details from the restored account
After the restore operation completes, you may want to know the source account details from which you restored or the restore time.
Use the following steps to get the restore details from Azure portal:
Sign in to the Azure portal and navigate to the restored account.
Navigate to the Export template pane. It opens a JSON template, corresponding to the restored account.
Restore an account using Azure PowerShell
Before restoring the account, install the latest version of Azure PowerShell or version higher than 9.6.0. Next connect to your Azure account and select the required subscription with the following commands:
Sign into Azure using the following command:
Connect-AzAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloudSelect a specific subscription with the following command:
Select-AzSubscription -Subscription <SubscriptionName>
Trigger a restore operation for API for NoSQL account
The following cmdlet is an example to trigger a restore operation with the restore command by using the target account, source account, location, resource group, PublicNetworkAccess, DisableTtl, and timestamp:
Restore-AzCosmosDBAccount `
-TargetResourceGroupName "MyRG" `
-TargetDatabaseAccountName "RestoredAccountName" `
-SourceDatabaseAccountName "SourceDatabaseAccountName" `
-RestoreTimestampInUtc "UTCTime" `
-Location "AzureRegionName" `
-PublicNetworkAccess Disabled `
-DisableTtl $true
Example 1: Restoring the entire account:
Restore-AzCosmosDBAccount `
-TargetResourceGroupName "MyRG" `
-TargetDatabaseAccountName "Pitracct" `
-SourceDatabaseAccountName "source-sql" `
-RestoreTimestampInUtc "2021-01-05T22:06:00" `
-Location "China North" `
-PublicNetworkAccess Disabled
-DisableTtl $false
If PublicNetworkAccess is not set, restored account is accessible from public network, please ensure to pass Disabled to the PublicNetworkAccess option to disable public network access for restored account. Setting DisableTtl to $true ensures TTL is disabled on restored account, not providing parameter restores the account with TTL enabled if it was set earlier.
Note
For restoring with public network access disabled, the minimum stable version of Az.CosmosDB required is 1.12.0.
Example 2: Restoring specific collections and databases. This example restores the collections MyCol1, MyCol2 from MyDB1 and the entire database MyDB2, which, includes all the containers under it.
$datatabaseToRestore1 = New-AzCosmosDBDatabaseToRestore -DatabaseName "MyDB1" -CollectionName "MyCol1", "MyCol2"
$datatabaseToRestore2 = New-AzCosmosDBDatabaseToRestore -DatabaseName "MyDB2"
Restore-AzCosmosDBAccount `
-TargetResourceGroupName "MyRG" `
-TargetDatabaseAccountName "Pitracct" `
-SourceDatabaseAccountName "SourceSql" `
-RestoreTimestampInUtc "2021-01-05T22:06:00" `
-DatabasesToRestore $datatabaseToRestore1, $datatabaseToRestore2 `
-Location "China North"
Example 3: Restoring API for Gremlin Account. This example restores the graphs graph1, graph2 from MyDB1 and the entire database MyDB2, which, includes all the containers under it.
$datatabaseToRestore1 = New-AzCosmosDBGremlinDatabaseToRestore -DatabaseName "MyDB1" -GraphName "graph1", "graph2"
$datatabaseToRestore2 = New-AzCosmosDBGremlinDatabaseToRestore -DatabaseName "MyDB2"
Restore-AzCosmosDBAccount `
-TargetResourceGroupName "MyRG" `
-TargetDatabaseAccountName "Pitracct" `
-SourceDatabaseAccountName "SourceGremlin" `
-RestoreTimestampInUtc "2022-04-05T22:06:00" `
-DatabasesToRestore $datatabaseToRestore1, $datatabaseToRestore2 `
-Location "China North"
Example 4: Restoring API for Table Account. This example restores the tables table1, table1 from MyDB1
$tablesToRestore = New-AzCosmosDBTableToRestore -TableName "table1", "table2"
Restore-AzCosmosDBAccount `
-TargetResourceGroupName "MyRG" `
-TargetDatabaseAccountName "Pitracct" `
-SourceDatabaseAccountName "SourceTable" `
-RestoreTimestampInUtc "2022-04-06T22:06:00" `
-TablesToRestore $tablesToRestore `
-Location "China North"
To restore a continuous account that is configured with managed identity using CLI
To restore Customer Managed Key (CMK) continuous account, please refer to the steps provided here
Get the restore details from the restored account
Import the Az.CosmosDB module version 1.12.0 and run the following command to get the restore details. The restoreTimestamp will be under the restoreParameters object:
Get-AzCosmosDBAccount -ResourceGroupName MyResourceGroup -Name MyCosmosDBDatabaseAccount
Enumerate restorable resources for API for NoSQL
The enumeration cmdlets help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account, database, and container resources.
List all the accounts that can be restored in the current subscription
Run the Get-AzCosmosDBRestorableDatabaseAccount PowerShell command to list all the accounts that can be restored in the current subscription.
The response includes all the database accounts (both live and deleted) that can be restored and the regions that they can be restored from.
{
"accountName": "SampleAccount",
"apiType": "Sql",
"creationTime": "2020-08-08T01:04:52.070190+00:00",
"deletionTime": null,
"id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/West US/restorableDatabaseAccounts/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e",
"identity": null,
"location": "China North",
"name": "aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e",
"restorableLocations": [
{
"creationTime": "2020-08-08T01:04:52.945185+00:00",
"deletionTime": null,
"location": "China North",
"regionalDatabaseAccountInstanceId": "30701557-ecf8-43ce-8810-2c8be01dccf9"
},
{
"creationTime": "2020-08-08T01:15:43.507795+00:00",
"deletionTime": null,
"location": "China East",
"regionalDatabaseAccountInstanceId": "8283b088-b67d-4975-bfbe-0705e3e7a599"
}
],
"tags": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts"
}
Just like the CreationTime or DeletionTime for the account, there is a CreationTime or DeletionTime for the region too. These times allow you to choose the right region and a valid time range to restore into that region.
List all the versions of SQL databases in a live database account
Listing all the versions of databases allows you to choose the right database in a scenario where the actual time of existence of database is unknown.
Run the following PowerShell command to list all the versions of databases. This command only works with live accounts. The DatabaseAccountInstanceId and the Location parameters are obtained from the name and location properties in the response of Get-AzCosmosDBRestorableDatabaseAccount cmdlet. The DatabaseAccountInstanceId attribute refers to instanceId property of source database account being restored:
Get-AzCosmosdbSqlRestorableDatabase `
-Location "China East" `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId <DatabaseAccountInstanceId>
List all the versions of SQL containers of a database in a live database account
Use the following command to list all the versions of SQL containers. This command only works with live accounts. The DatabaseRId parameter is the ResourceId of the database you want to restore. It is the value of ownerResourceid attribute found in the response of Get-AzCosmosdbSqlRestorableDatabase cmdlet. The response also includes a list of operations performed on all the containers inside this database.
Get-AzCosmosdbSqlRestorableContainer `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-DatabaseRId "AoQ13r==" `
-Location "China North"
Find databases or containers that can be restored at any given timestamp
Use the following command to get the list of databases or containers that can be restored at any given timestamp. This command only works with live accounts.
Get-AzCosmosdbSqlRestorableResource `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-Location "China North" `
-RestoreLocation "China East" `
-RestoreTimestamp "2020-07-20T16:09:53+0000"
Enumerate restorable resources in API for MongoDB
The enumeration commands described below help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account, database, and container resources. These commands only work for live accounts and they are similar to API for NoSQL commands but with MongoDB in the command name instead of sql.
List all the versions of MongoDB databases in a live database account
Get-AzCosmosdbMongoDBRestorableDatabase `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-Location "China North"
List all the versions of MongoDB collections of a database in a live database account
Get-AzCosmosdbMongoDBRestorableCollection `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-DatabaseRId "AoQ13r==" `
-Location "China North"
List all the resources of a MongoDB database account that are available to restore at a given timestamp and region
Get-AzCosmosdbMongoDBRestorableResource `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-Location "China North" `
-RestoreLocation "China North" `
-RestoreTimestamp "2020-07-20T16:09:53+0000"
Enumerate restorable resources for API for Gremlin
The enumeration cmdlets help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account, database, and graph resources.
List all the versions of Gremlin databases in a live database account
Listing all the versions of databases allows you to choose the right database in a scenario where the actual time of existence of database is unknown.
Run the following PowerShell command to list all the versions of databases. This command only works with live accounts. The DatabaseAccountInstanceId and the Location parameters are obtained from the name and location properties in the response of Get-AzCosmosDBRestorableDatabaseAccount cmdlet. The DatabaseAccountInstanceId attribute refers to instanceId property of source database account being restored:
Get-AzCosmosdbGremlinRestorableDatabase `
-Location "China East" `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId <DatabaseAccountInstanceId>
List all the versions of Gremlin graphs of a database in a live database account
Use the following command to list all the versions of API for Gremlin graphs. This command only works with live accounts. The DatabaseRId parameter is the ResourceId of the database you want to restore. It is the value of ownerResourceid attribute found in the response of Get-AzCosmosdbGremlinRestorableDatabase cmdlet. The response also includes a list of operations performed on all the graphs inside this database.
Get-AzCosmosdbGremlinRestorableGraph `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-DatabaseRId "AoQ13r==" `
-Location "China North"
Find databases or graphs that can be restored at any given timestamp
Use the following command to get the list of databases or graphs that can be restored at any given timestamp. This command only works with live accounts.
Get-AzCosmosdbGremlinRestorableResource `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-Location "China North" `
-RestoreLocation "China East" `
-RestoreTimestamp "2020-07-20T16:09:53+0000"
Enumerate restorable resources for API for Table
The enumeration cmdlets help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account and table resources.
List all the versions of tables of a database in a live database account
Use the following command to list all the versions of tables. This command only works with live accounts.
Get-AzCosmosdbTableRestorableTable `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68"
` -Location "China North"
Find tables that can be restored at any given timestamp
Use the following command to get the list of tables that can be restored at any given timestamp. This command only works with live accounts.
Get-AzCosmosdbTableRestorableResource `
-DatabaseAccountInstanceId "d056a4f8-044a-436f-80c8-cd3edbc94c68" `
-Location "China North" `
-RestoreLocation "China East" `
-RestoreTimestamp "2020-07-20T16:09:53+0000"
Restore an account using Azure CLI
Before restoring the account, install Azure CLI with the following steps:
Install the latest version of Azure CLI
- Install the latest version of Azure CLI or version higher than 2.52.0.
- If you have already installed CLI, run
az upgradecommand to update to the latest version. This command will only work with CLI version higher than 2.52.0. If you have an earlier version, use the above link to install the latest version.
Sign in and select your subscription
- Sign in to your Azure account with
az logincommand. - Select the required subscription using
az account set -s <subscriptionguid>command.
- Sign in to your Azure account with
Trigger a restore operation with Azure CLI
The simplest way to trigger a restore is by issuing the restore command with name of the target account, source account, location, resource group, timestamp (in UTC), and optionally the database and container names. The following are some examples to trigger the restore operation:
Create a new Azure Cosmos DB account by restoring from an existing account
az cosmosdb restore \
--target-database-account-name <MyRestoredCosmosDBDatabaseAccount> \
--account-name <MySourceAccount> \
--restore-timestamp 2020-07-13T16:03:41+0000 \
--resource-group <TargetResourceGroup> \
--location "China North"
--public-network-access Disabled \
If --public-network-access is not set, restored account is accessible from public network. Please ensure to pass Disabled to the --public-network-access option to prevent public network access for restored account.
Note
For restoring with public network access disabled, the minimum stable version of azure-cli is 2.52.0.
Create a new Azure Cosmos DB account by restoring only selected databases and containers from an existing database account
az cosmosdb restore \
--resource-group MyResourceGroup \
--target-database-account-name MyRestoredCosmosDBDatabaseAccount \
--account-name MySourceAccount \
--restore-timestamp 2020-07-13T16:03:41+0000 \
--location "China North" \
--databases-to-restore name=MyDB1 collections=Collection1 Collection2 \
--databases-to-restore name=MyDB2 collections=Collection3 Collection4
Create a new Azure Cosmos DB API for Gremlin account by restoring only selected databases and graphs from an existing API for Gremlin account
az cosmosdb restore \
--resource-group MyResourceGroup \
--target-database-account-name MyRestoredCosmosDBDatabaseAccount \
--account-name MySourceAccount \
--restore-timestamp 2022-04-13T16:03:41+0000 \
--location "China North" \
--gremlin-databases-to-restore name=MyDB1 graphs=graph1 graph2 \
--gremlin-databases-to-restore name=MyDB2 graphs =graph3 graph4
Create a new Azure Cosmos DB API for Table account by restoring only selected tables from an existing API for Table account
az cosmosdb restore \
--resource-group MyResourceGroup \
--target-database-account-name MyRestoredCosmosDBDatabaseAccount \
--account-name MySourceAccount \
--restore-timestamp 2022-04-14T06:03:41+0000 \
--location "China North" \
--tables-to-restore table1 table2
Get the restore details from the restored account
Run the following command to get the restore details. The az cosmosdb show command output shows the value of createMode property. If the value is set to Restore, it indicates that the account was restored from another account. The restoreParameters property has further details such as restoreSource, which has the source account ID. The last GUID in the restoreSource parameter is the instanceId of the source account. And the restoreTimestamp will be under the restoreParameters object:
az cosmosdb show --name MyCosmosDBDatabaseAccount --resource-group MyResourceGroup
Enumerate restorable resources for API for NoSQL
The enumeration commands described below help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account, database, and container resources.
List all the accounts that can be restored in the current subscription
Run the following Azure CLI command to list all the accounts that can be restored in the current subscription
az cosmosdb restorable-database-account list --account-name "Pitracct"
The response includes all the database accounts (both live and deleted) that can be restored, and the regions that they can be restored from:
{
"accountName": "Pitracct",
"apiType": "Sql",
"creationTime": "2021-01-08T23:34:11.095870+00:00",
"deletionTime": null,
"id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/West US/restorableDatabaseAccounts/abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234",
"identity": null,
"location": "China North",
"name": "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234",
"restorableLocations": [
{
"creationTime": "2021-01-08T23:34:11.095870+00:00",
"deletionTime": null,
"locationName": "China North",
"regionalDatabaseAccountInstanceId": "f02df26b-c0ec-4829-8bef-3482d36e6230"
}
],
"tags": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts"
}
Just like the CreationTime or DeletionTime for the account, there is a CreationTime or DeletionTime for the region too. These times allow you to choose the right region and a valid time range to restore into that region.
List all the versions of databases in a live database account
Listing all the versions of databases allows you to choose the right database in a scenario where the actual time of existence of database is unknown.
Run the following Azure CLI command to list all the versions of databases. This command only works with live accounts. The instance-id and the location parameters are obtained from the name and location properties in the response of az cosmosdb restorable-database-account list command. The instanceId attribute is also a property of source database account that is being restored:
az cosmosdb sql restorable-database list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--location "China North"
This command output now shows when a database was created and deleted.
[
{
"id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/chinanorth/restorableDatabaseAccounts/abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234/restorableSqlDatabases/bbbb1b1b-cc2c-dd3d-ee4e-ffffff5f5f5f",
"name": "bbbb1b1b-cc2c-dd3d-ee4e-ffffff5f5f5f",
"resource": {
"database": {
"id": "db1"
},
"eventTimestamp": "2021-01-08T23:27:25Z",
"operationType": "Create",
"ownerId": "db1",
"ownerResourceId": "YuZAAA=="
},
},
{
"id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/chinanorth/restorableDatabaseAccounts/abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234/restorableSqlDatabases/cccc2c2c-dd3d-ee4e-ff5f-aaaaaa6a6a6a",
"name": "cccc2c2c-dd3d-ee4e-ff5f-aaaaaa6a6a6a",
"resource": {
"database": {
"id": "spdb1"
},
"eventTimestamp": "2021-01-08T23:25:25Z",
"operationType": "Create",
"ownerId": "spdb1",
"ownerResourceId": "OIQ1AA=="
},
}
]
List all the versions of SQL containers of a database in a live database account
Use the following command to list all the versions of SQL containers. This command only works with live accounts. The database-rid parameter is the ResourceId of the database you want to restore. It is the value of ownerResourceid attribute found in the response of az cosmosdb sql restorable-database list command.
az cosmosdb sql restorable-container list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--database-rid "OIQ1AA==" \
--location "China North"
This command output shows includes list of operations performed on all the containers inside this database:
[
{
"eventTimestamp": "2021-01-08T23:25:29Z",
"operationType": "Replace",
"ownerId": "procol3",
"ownerResourceId": "OIQ1APZ7U18="
},
{
"eventTimestamp": "2021-01-08T23:25:26Z",
"operationType": "Create",
"ownerId": "procol3",
"ownerResourceId": "OIQ1APZ7U18="
},
]
Find databases or containers that can be restored at any given timestamp
Use the following command to get the list of databases or containers that can be restored at any given timestamp. This command only works with live accounts.
az cosmosdb sql restorable-resource list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--location "China North" \
--restore-location "China North" \
--restore-timestamp "2021-01-10T01:00:00+0000"
[
{
"collectionNames": [
"procol1",
"procol2"
],
"databaseName": "db1"
},
{
"collectionNames": [
"procol3",
"spcol1"
],
"databaseName": "spdb1"
}
]
Enumerate restorable resources for API for MongoDB account
The enumeration commands described below help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account, database, and container resources. These commands only work for live accounts.
List all the versions of MongoDB databases in a live database account
az cosmosdb mongodb restorable-database list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--location "China North"
List all the versions of MongoDB collections of a database in a live database account
az cosmosdb mongodb restorable-collection list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--database-rid "AoQ13r==" \
--location "China North"
List all the resources of a mongodb database account that are available to restore at a given timestamp and region
az cosmosdb mongodb restorable-resource list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--location "China North" \
--restore-location "China North" \
--restore-timestamp "2020-07-20T16:09:53+0000"
List all the versions of databases in a live database account
The enumeration commands described below help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account, database, and graph resources. These commands only work for live accounts.
az cosmosdb gremlin restorable-database list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--location "China North"
This command output now shows when a database was created and deleted.
[ {
"id": "/subscriptions/abcd1234-b6ac-4328-a753-abcd1234/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/chinaeast2euap/restorableDatabaseAccounts/abcd1234-4316-483b-8308-abcd1234/restorableGremlinDatabases/abcd1234-0e32-4036-ac9d-abcd1234",
"name": "abcd1234-0e32-4036-ac9d-abcd1234",
"resource": {
"eventTimestamp": "2022-02-09T17:10:18Z",
"operationType": "Create",
"ownerId": "db1",
"ownerResourceId": "1XUdAA==",
"rid": "ymn7kwAAAA=="
},
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts/restorableGremlinDatabases"
}
]
List all the versions of Gremlin graphs of a database in a live database account
az cosmosdb gremlin restorable-graph list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--database-rid "OIQ1AA==" \
--location "China North"
This command output shows includes list of operations performed on all the containers inside this database:
[ {
"id": "/subscriptions/dddd3d3d-ee4e-ff5f-aa6a-bbbbbb7b7b7b/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/chinanorth/restorableDatabaseAccounts/eeee4efe-ff5f-aa6a-bb7b-cccccc8c8c8c/restorableGraphs/ffff5f5f-aa6a-bb7b-cc8c-dddddd9d9d9d",
"name": "ffff5f5f-aa6a-bb7b-cc8c-dddddd9d9d9d",
"resource": {
"eventTimestamp": "2022-02-09T17:10:31Z",
"operationType": "Create",
"ownerId": "graph1",
"ownerResourceId": "1XUdAPv9duQ=",
"rid": "IcWqcQAAAA=="
},
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts/restorableGraphs"
}
]
Find databases or graphs that can be restored at any given timestamp
az cosmosdb gremlin restorable-resource list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--location "China North" \
--restore-location "China North" \
--restore-timestamp "2021-01-10T01:00:00+0000"
This command output shows the graphs which are restorable:
[
{
"databaseName": "db1",
"graphNames": [ "graph1", "graph3", "graph2" ]
}
]
Enumerate restorable resources for API for Table account
The enumeration commands described below help you discover the resources that are available for restore at various timestamps. Additionally, they also provide a feed of key events on the restorable account and API for Table resources. These commands only work for live accounts.
List all the versions of tables in a live database account
az cosmosdb table restorable-table list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234"
--location "China North"
[ {
"id": "/subscriptions/dddd3d3d-ee4e-ff5f-aa6a-bbbbbb7b7b7b/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/WestUS/restorableDatabaseAccounts/aaaa6a6a-bb7b-cc8c-dd9d-eeeeee0e0e0e/restorableTables/bbbb1b1b-cc2c-dd3d-ee4e-ffffff5f5f5f",
"name": "bbbb1b1b-cc2c-dd3d-ee4e-ffffff5f5f5f",
"resource": {
"eventTimestamp": "2022-02-09T17:09:54Z",
"operationType": "Create",
"ownerId": "table1",
"ownerResourceId": "tOdDAKYiBhQ=",
"rid": "9pvDGwAAAA=="
},
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts/restorableTables"
},
{"id": "/subscriptions/dddd3d3d-ee4e-ff5f-aa6a-bbbbbb7b7b7b/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/eastus2euap/restorableDatabaseAccounts/aaaa6a6a-bb7b-cc8c-dd9d-eeeeee0e0e0e/restorableTables/cccc2c2c-dd3d-ee4e-ff5f-aaaaaa6a6a6a",
"name": "cccc2c2c-dd3d-ee4e-ff5f-aaaaaa6a6a6a",
"resource": {
"eventTimestamp": "2022-02-09T20:47:53Z",
"operationType": "Create",
"ownerId": "table3",
"ownerResourceId": "tOdDALBwexw=",
"rid": "01DtkgAAAA=="
},
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/restorableDatabaseAccounts/restorableTables"
},
]
List all the resources of a API for Table account that are available to restore at a given timestamp and region
az cosmosdb table restorable-resource list \
--instance-id "abcd1234-d1c0-4645-a699-abcd1234" \
--location "China North" \
--restore-location "China North" \
--restore-timestamp "2020-07-20T16:09:53+0000"
Following is the result of the command.
{
"tableNames": [
"table1",
"table3",
"table2"
]
}
Restore using the Azure Resource Manager template
You can also restore an account using Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template. When defining the template, include the following parameters:
Restore API for NoSQL or MongoDB account using ARM template
- Set the
createModeparameter to Restore. - Define the
restoreParameters, notice that therestoreSourcevalue is extracted from the output of theaz cosmosdb restorable-database-account listcommand for your source account. The Instance ID attribute for your account name is used to do the restore. - Set the
restoreModeparameter to PointInTime and configure therestoreTimestampInUtcvalue.
Use the following ARM template to restore an account for the Azure Cosmos DB API for NoSQL or MongoDB. Examples for other APIs are provided next.
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources": [
{
"name": "vinhpitrarmrestore-kal3",
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts",
"apiVersion": "2023-04-15",
"location": "China North",
"properties": {
"locations": [
{
"locationName": "China North"
}
],
"databaseAccountOfferType": "Standard",
"createMode": "Restore",
"restoreParameters": {
"restoreSource": "/subscriptions/dddd3d3d-ee4e-ff5f-aa6a-bbbbbb7b7b7b/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/chinanorth/restorableDatabaseAccounts/eeee4efe-ff5f-aa6a-bb7b-cccccc8c8c8c",
"restoreMode": "PointInTime",
"restoreTimestampInUtc": "6/24/2020 4:01:48 AM",
"restoreWithTtlDisabled": "true"
}
}
}
]
}
Restore API for Gremlin account using ARM template
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources": [
{
"name": "ademo-pitr1",
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts",
"apiVersion": "2023-04-15",
"location": "China North",
"properties": {
"locations": [
{
"locationName": "China North"
}
],
"backupPolicy": {
"type": "Continuous"
},
"databaseAccountOfferType": "Standard",
"createMode": "Restore",
"restoreParameters": {
"restoreSource": "/subscriptions/dddd3d3d-ee4e-ff5f-aa6a-bbbbbb7b7b7b/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/chinanorth/restorableDatabaseAccounts/ffff5f5f-aa6a-bb7b-cc8c-dddddd9d9d9d",
"restoreMode": "PointInTime",
"restoreTimestampInUtc": "2021-10-27T23:20:46Z",
"gremlinDatabasesToRestore": [{
"databaseName": "db1",
"graphNames": [
"graph1", "graph2"
]
}]
}
}
}
]
}
Restore API for Table account using ARM template
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources": [
{
"name": "ademo-pitr1",
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts",
"apiVersion": "2023-04-15",
"location": "China North",
"properties": {
"locations": [
{
"locationName": "China North"
}
],
"backupPolicy": {
"type": "Continuous"
},
"databaseAccountOfferType": "Standard",
"createMode": "Restore",
"restoreParameters": {
"restoreSource": "/subscriptions/aaaa6a6a-bb7b-cc8c-dd9d-eeeeee0e0e0e/providers/Microsoft.DocumentDB/locations/chinanorth/restorableDatabaseAccounts/4bcb9d82e-ec71-430b-b977-cd6641db85ad",
"restoreMode": "PointInTime",
"restoreTimestampInUtc": "2022-04-13T10:20:46Z",
"tablesToRestore": [
"table1", "table2"
]
}
}
}
]
}
Next, deploy the template by using Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI. The following example shows how to deploy the template with an Azure CLI command:
az deployment group create -g <ResourceGroup> --template-file <RestoreTemplateFilePath>
Next steps
- Provision continuous backup using the Azure portal, PowerShell, CLI, or Azure Resource Manager.
- How to migrate to an account from periodic backup to continuous backup.
- Continuous backup mode resource model.
- Manage permissions required to restore data with continuous backup mode.