Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to back up Azure Files from the Azure portal.
Azure Files backup is a native cloud solution that protects your data and eliminates on-premises maintenance overheads. Azure Backup seamlessly integrates with Azure File Sync, centralizing your file share data and backups. The simple, reliable, and secure solution allows you to protect your enterprise file shares using snapshot and vaulted backups, ensuring data recovery for accidental or malicious deletion.
Azure Backup supports configuring snapshot backups for Azure Files in your storage accounts. You can:
- Define backup schedules and retention settings.
- Store backup data in the Recovery Service vault, retaining it for up to 10 years.
Prerequisites
- Ensure the file share is present in one of the supported storage account types. Review the support matrix.
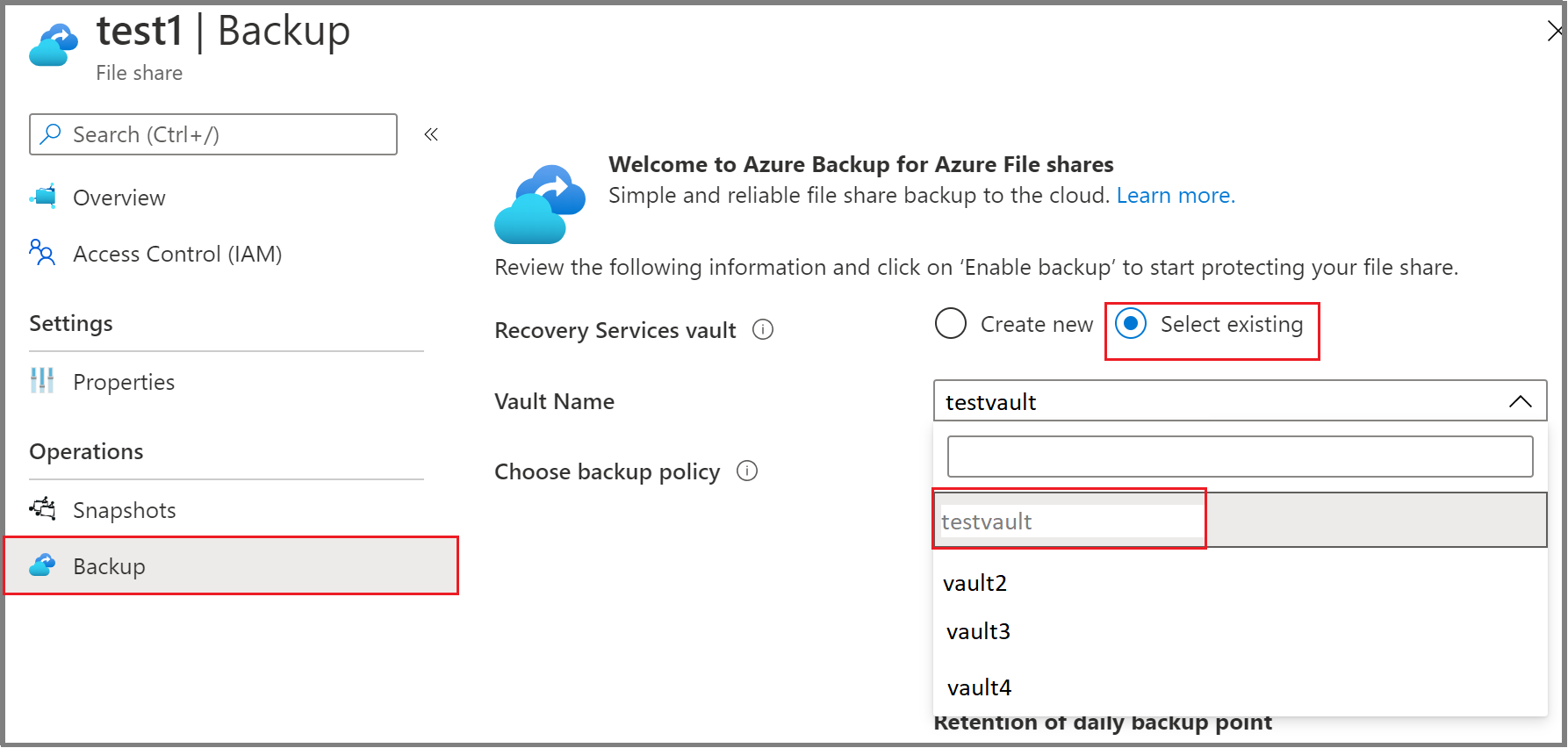
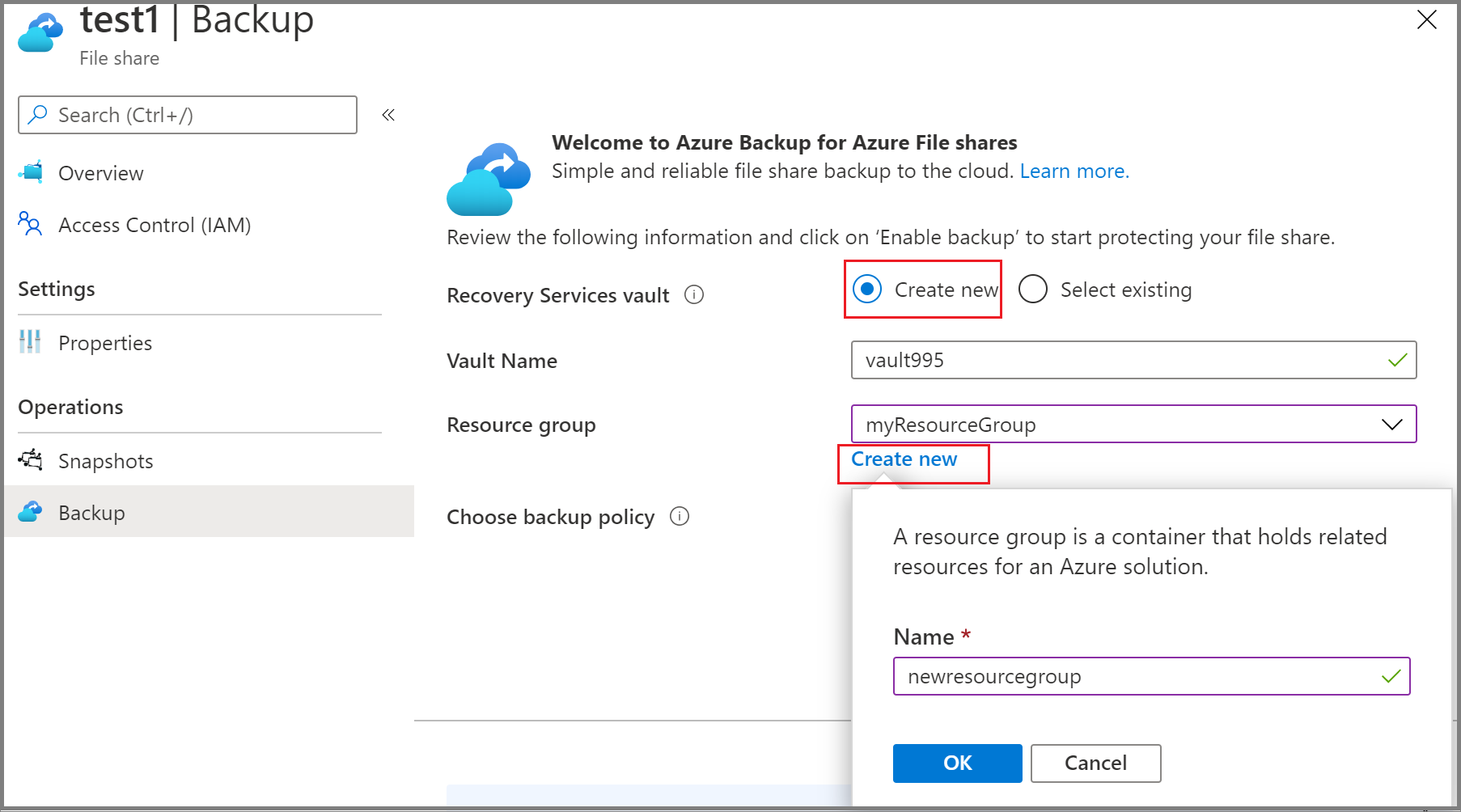
- Identify or create a Recovery Services vault in the same region and subscription as the storage account that hosts the file share.
- If the storage account access has restrictions, check the firewall settings of the account to ensure the exception Allow Azure services on the trusted services list to access this storage account is in grant state. You can refer to this link for the steps to grant an exception.
- Ensure that you allow the Storage account key access in the required storage account.
Configure the backup
You can configure snapshot backup and vaulted backup for Azure Files from the Recovery Services vault or File share pane.
Choose an entry point
To configure backup for multiple file shares from the Recovery Services vault, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, go to the Recovery Services vault and select +Backup.
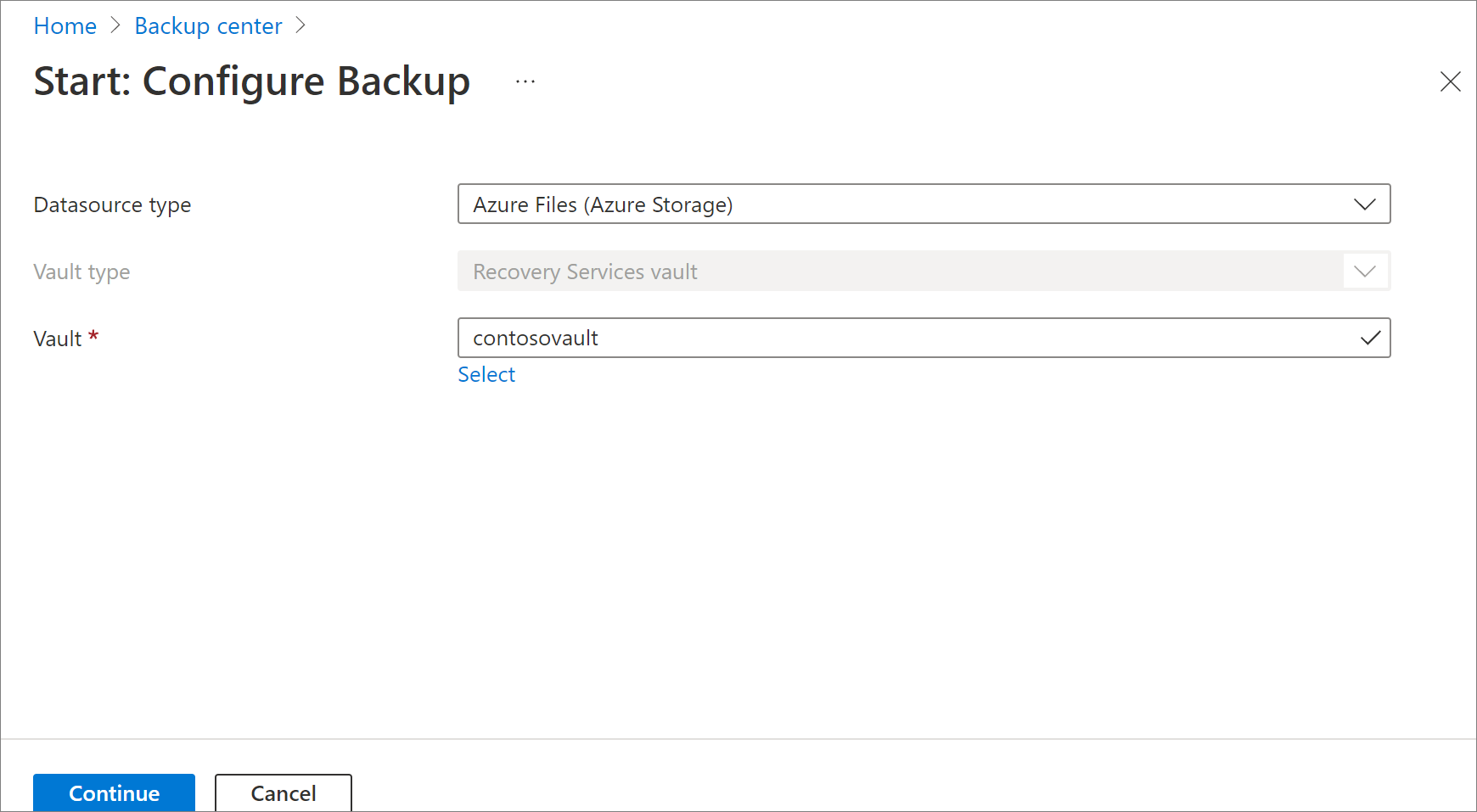
On the Backup Goal pane, select Azure Files (Azure Storage) as the datasource type, select the vault that you want to protect the file shares with, and then select Continue.
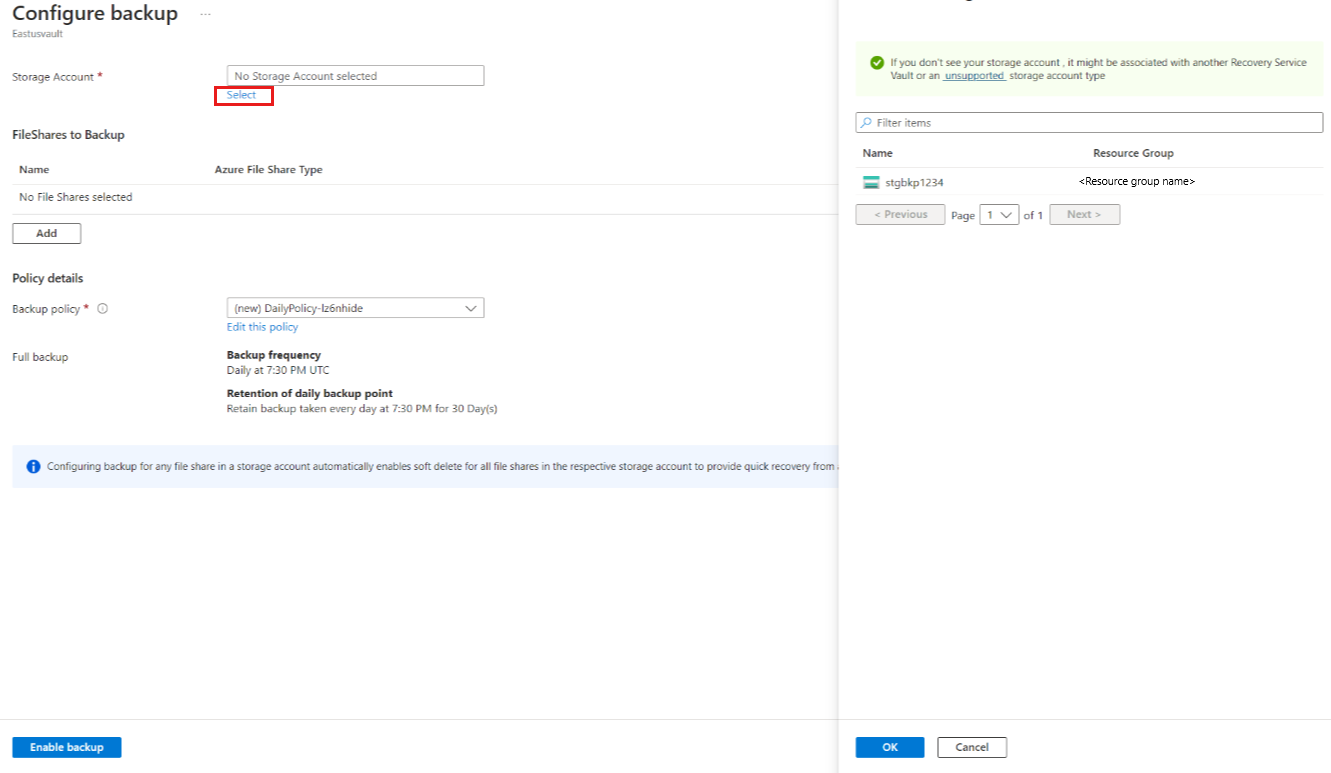
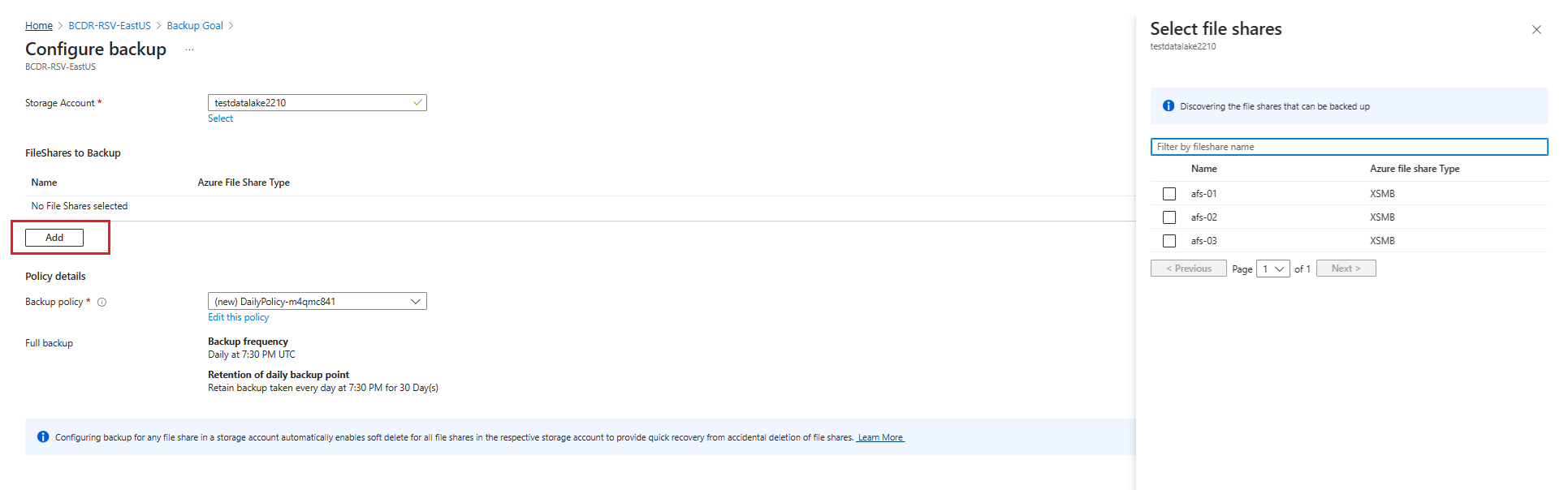
On the Configure backup pane, click Select to select the storage account that contains the file shares to be backed up.
The Select storage account pane opens, which lists a set of discovered supported storage accounts. They're either associated with this vault or present in the same region as the vault, but not yet associated with any Recovery Services vault.
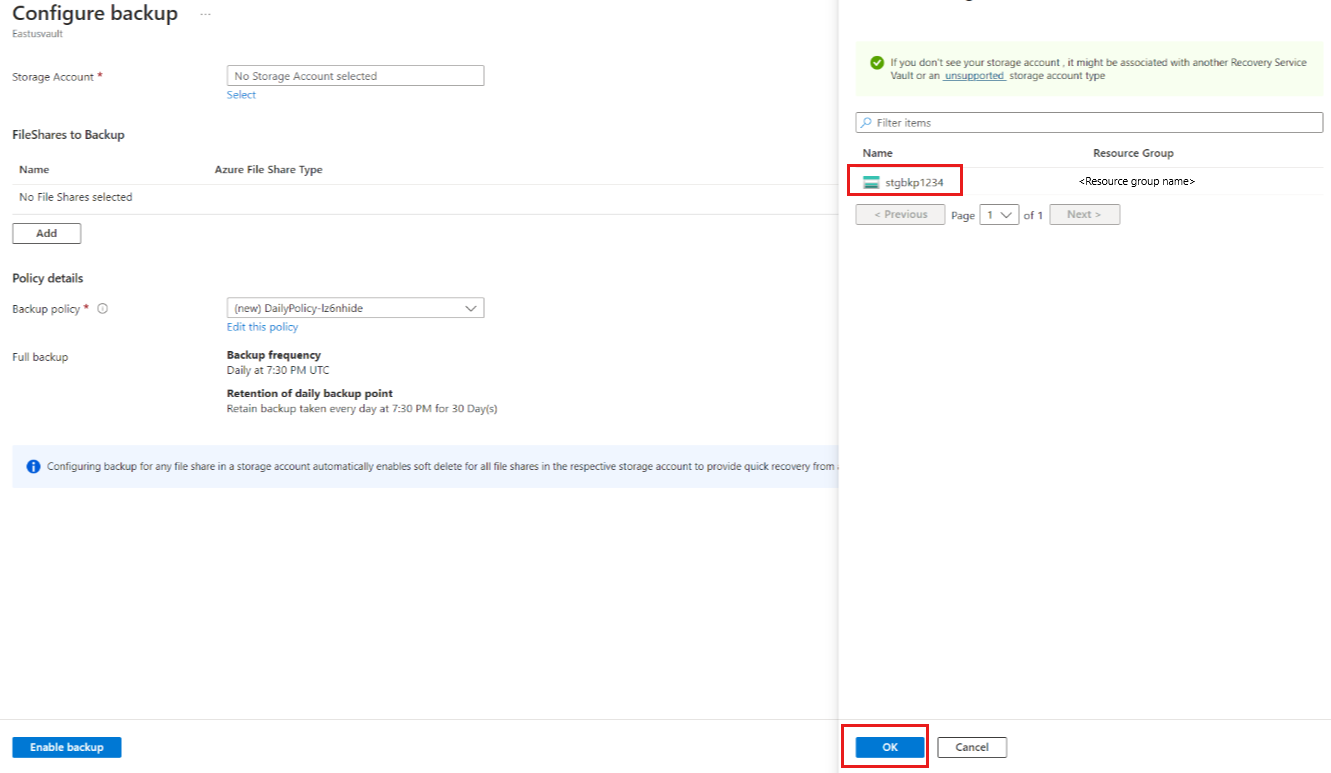
On the Select storage account pane, by default it list the storage accounts from the current subscription. Select an account, and select OK.
Note
If a storage account is present in a different region than the vault, then the storage account doesn't appear in the discovery list.
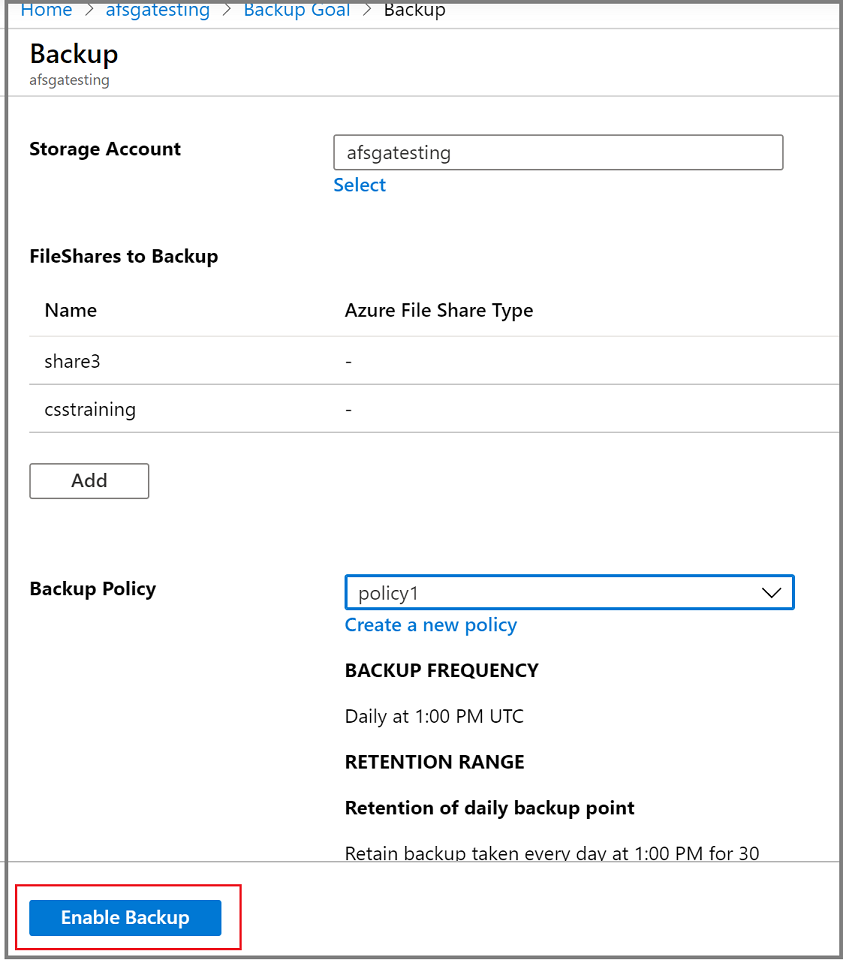
On the Configure Backup pane, under the FileShares to Backup section, select the file shares type you want to back up, and then select Add.
The Select file shares context pane opens. Azure searches the storage account for file shares that can be backed up. If you recently added your file shares and don't see them in the list, allow some time for the file shares to appear.
On the Select file shares pane, from the file shares list, select one or more file shares you want to back up, and then select OK.
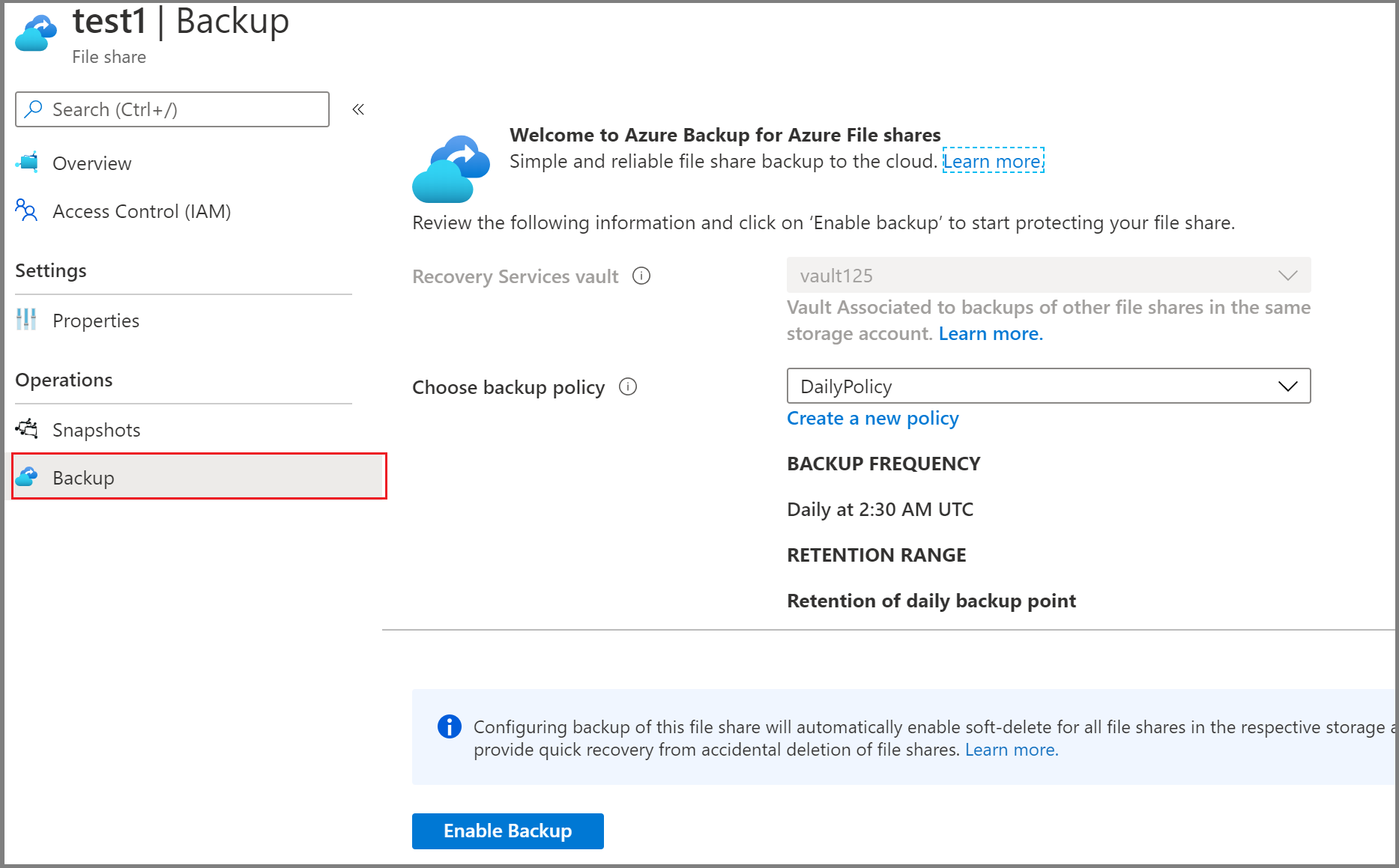
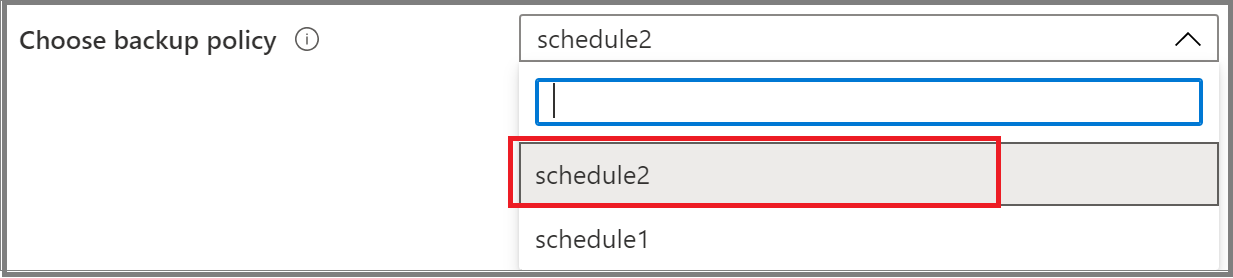
On the Configure Backup pane, under Policy Details, choose an existing backup policy from the list for your file share protection or create a new policy.
To create a new backup policy, you can configure the following attributes in the backup policy:
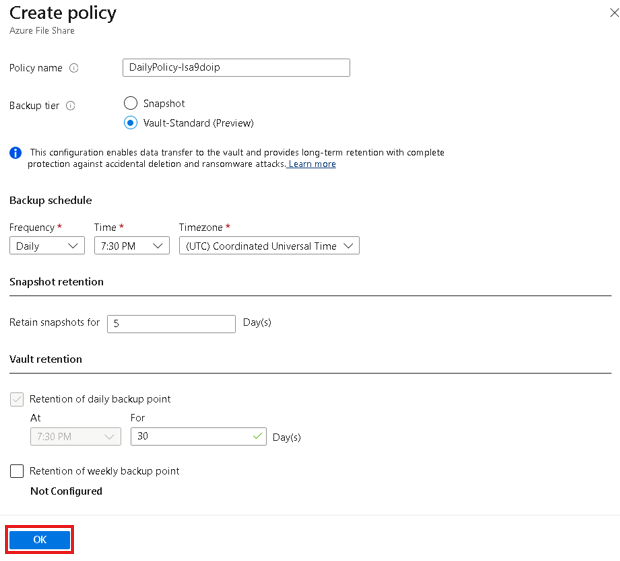
On the Configure Backup pane, select Create new under Policy Details.
On the Create policy pane, provide the policy name.
On Backup tier, select one of the following tiers:
- Snapshot: Enables only snapshot-based backups that are stored locally and can only provide protection during accidental deletions.
- Vault-Standard: Provides comprehensive data protection.
Configure the backup schedule as per the requirement. You can configure up to six backups per day. The snapshots are taken as per the schedule defined in the policy. For vaulted backup, the data from the last snapshot of the day is transferred to the vault.
Configure the Snapshot retention and Vault retention duration to determine the expiry date of the recovery points.
Note
The vault tier provides longer retention than the snapshot tier.
Select OK to create the backup policy.
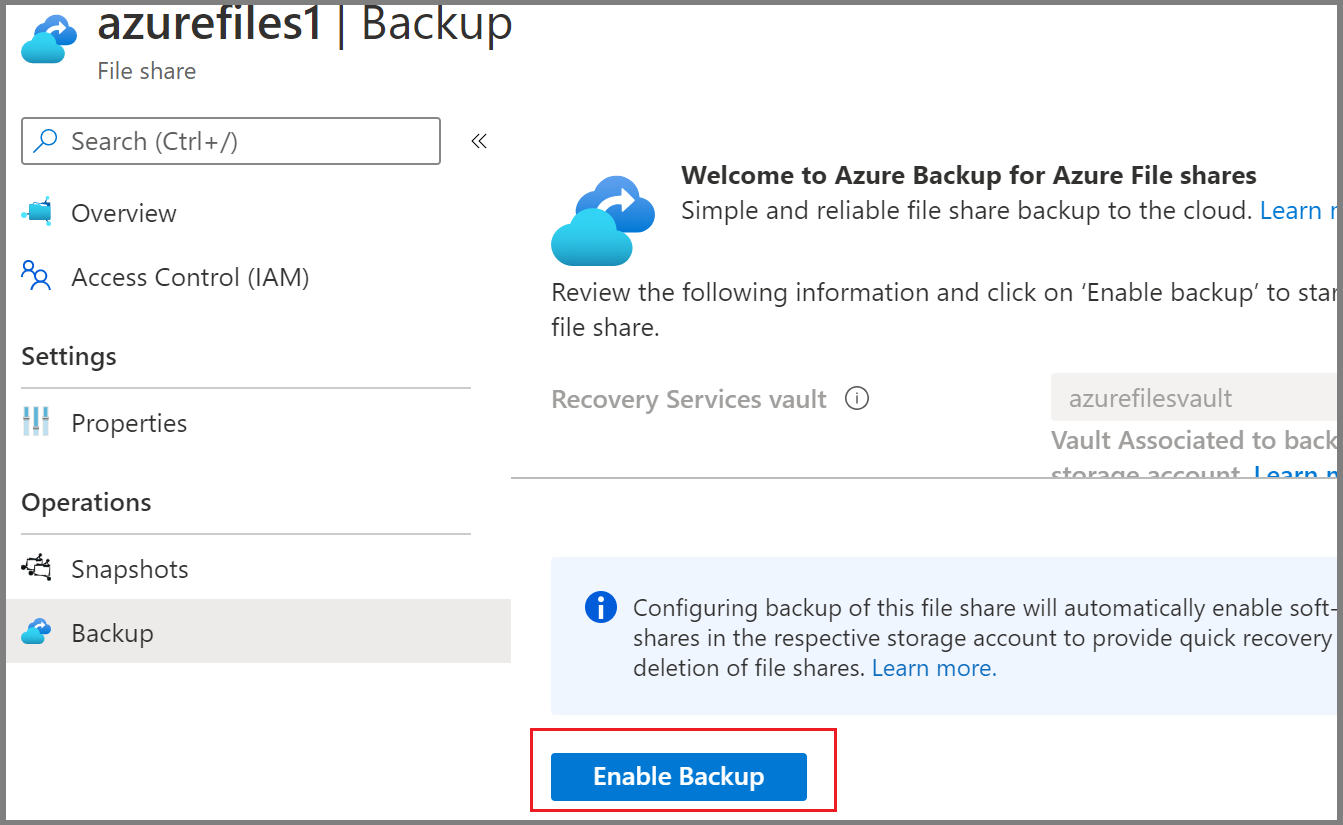
On the Configure Backup pane, select Enable Backup to start protecting the file share.
Run an on-demand backup job
Occasionally, you might want to generate a backup snapshot, or recovery point, outside of the times scheduled in the backup policy. A common reason to generate an on-demand backup is right after you've configured the backup policy. Based on the schedule in the backup policy, it might be hours or days until a snapshot is taken. To protect your data until the backup policy engages, initiate an on-demand backup. Creating an on-demand backup is often required before you make planned changes to your file shares.
Choose an entry point
To run an on-demand backup, follow these steps:
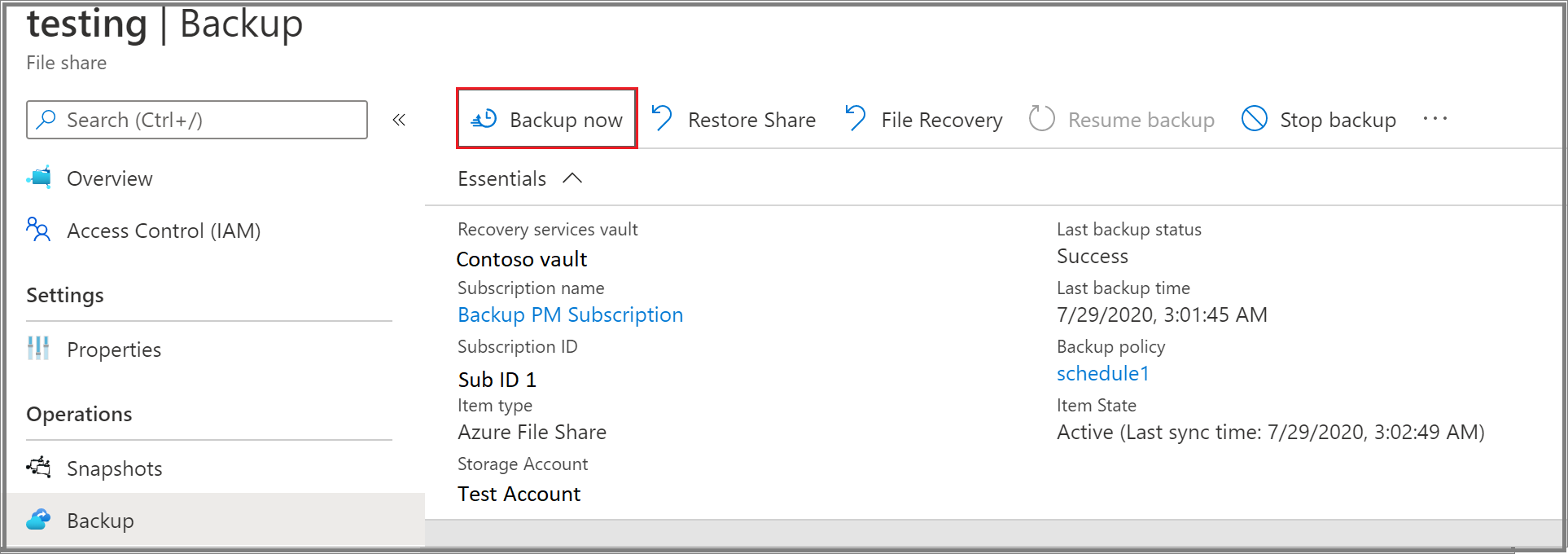
Go to the Recovery Services vault and select Backup items from the menu.
On the Backup items blade, select the Backup Management Type as Azure Storage (Azure Files).
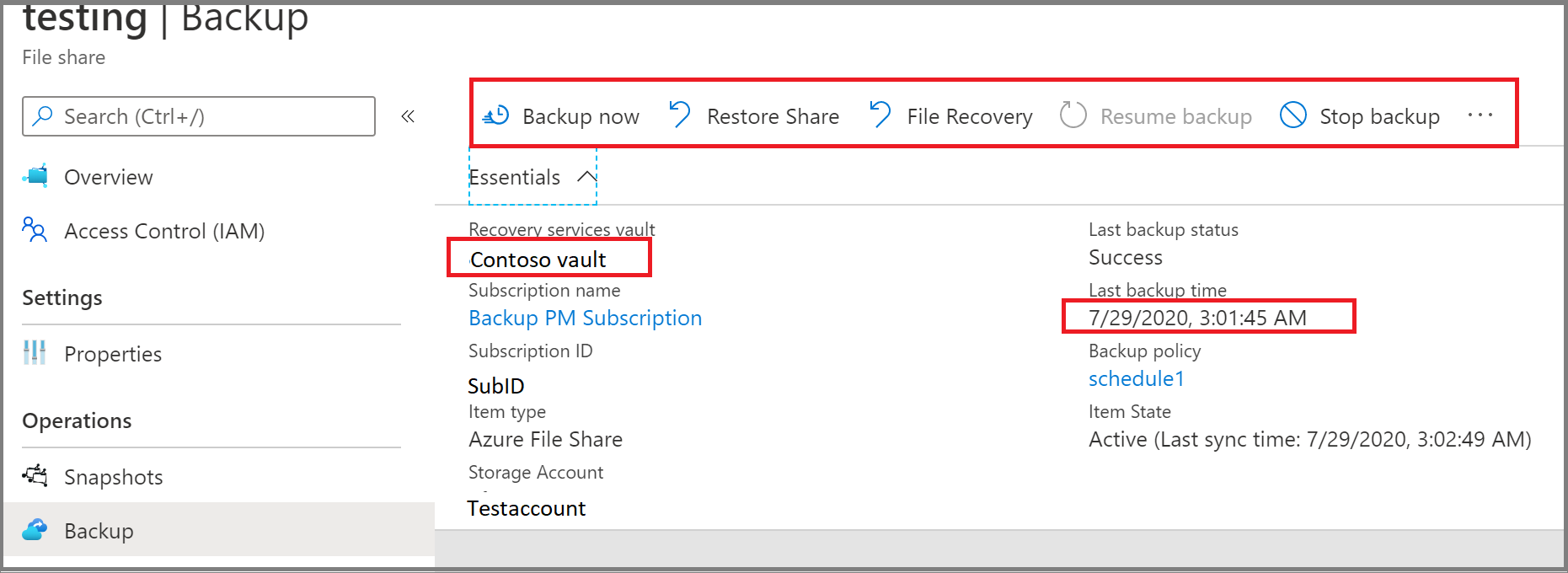
Select the item for which you want to run an on-demand backup job.
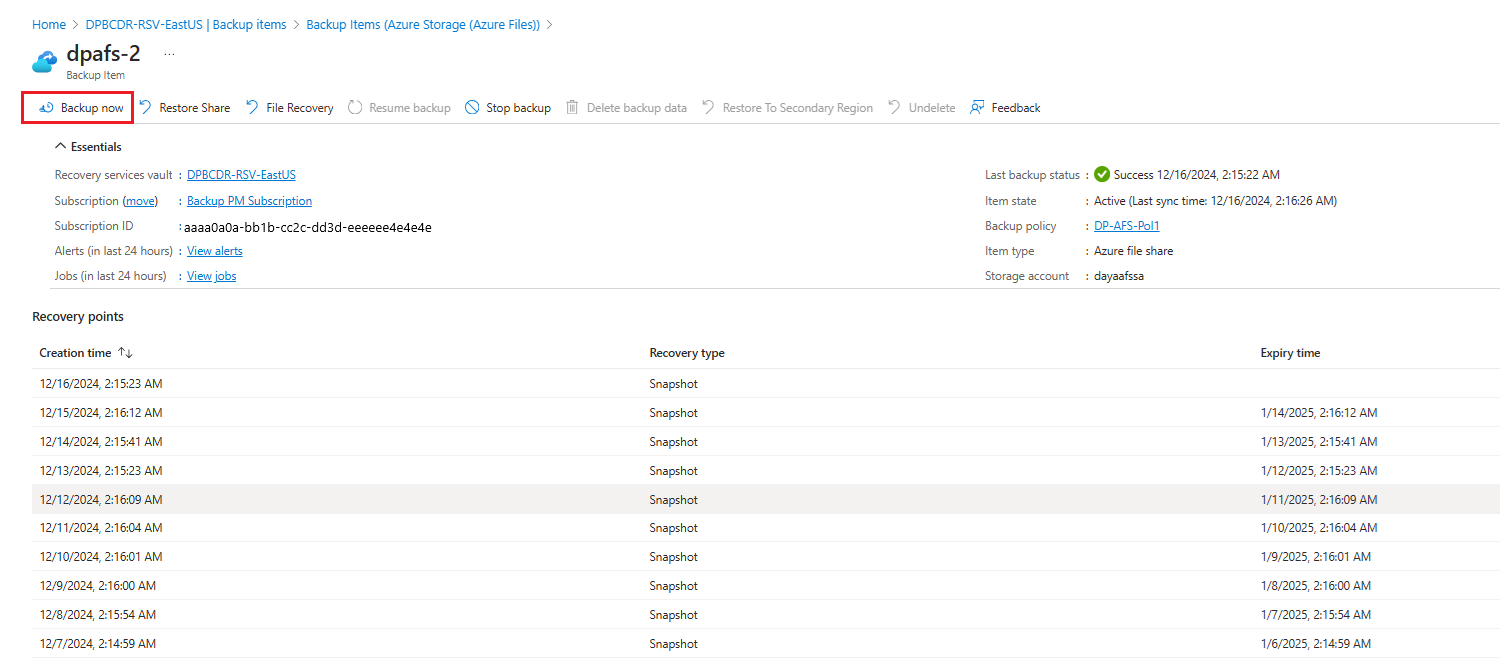
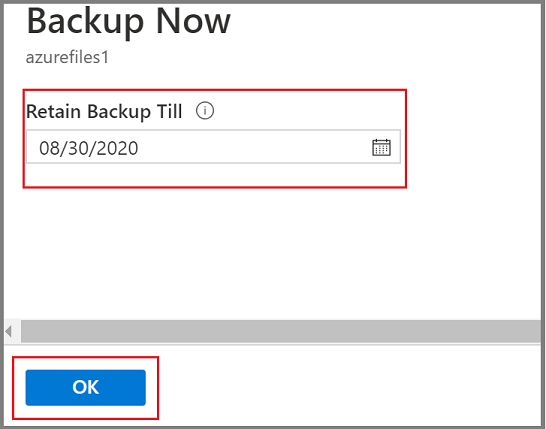
In the Backup Item menu, select Backup now. Because this backup job is on demand, there's no retention policy associated with the recovery point.
The Backup Now blade opens. Specify the last day you want to retain the recovery point. You can have a maximum retention of 10 years for an on-demand backup.
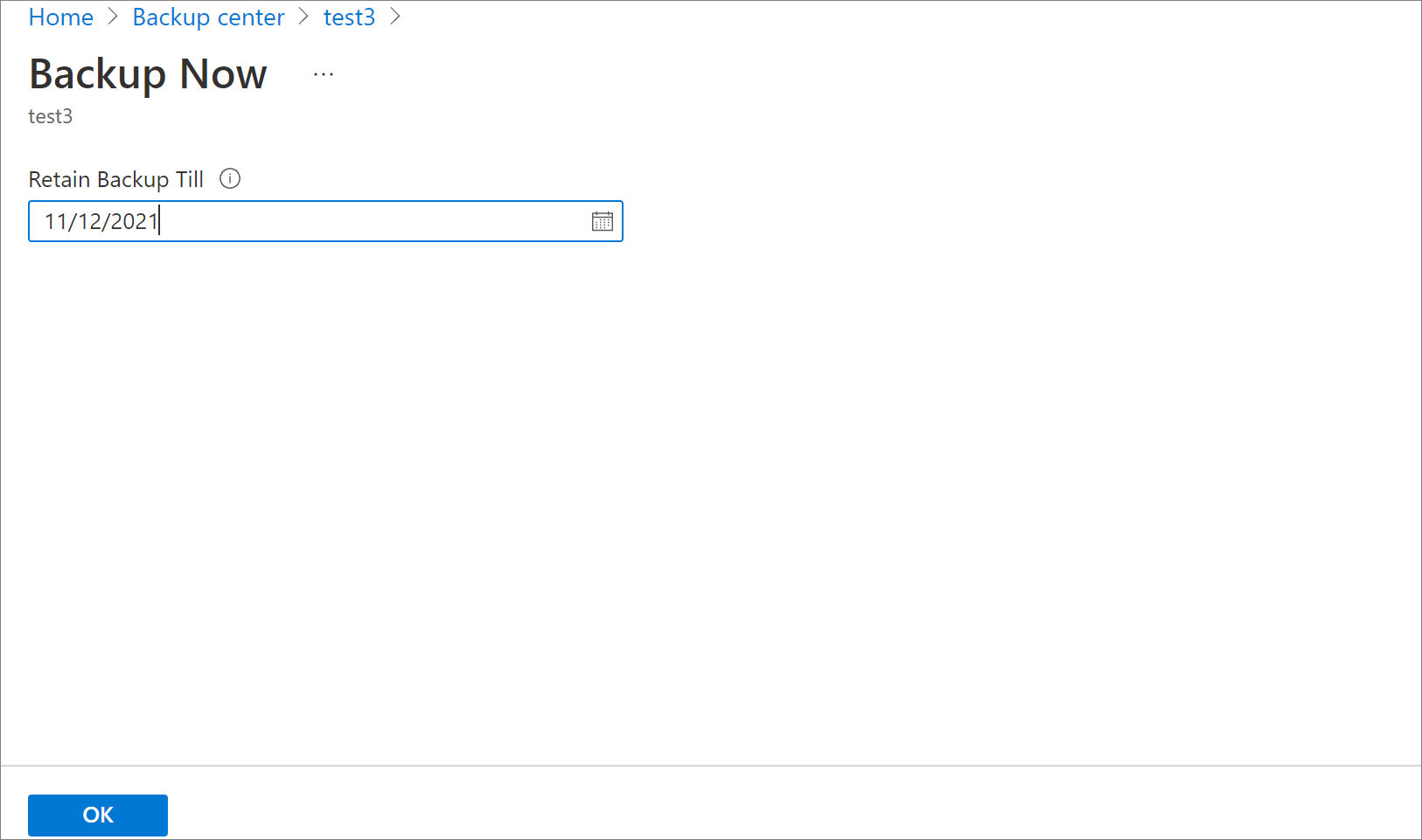
Select OK to confirm the on-demand backup job that runs.
Monitor the portal notifications to keep track of backup job run completion.
To monitor the job progress in the Recovery Services vault dashboard, go to Recovery Services vault > Backup Jobs > In progress.
Best practices
Don't delete snapshots created by Azure Backup. Deleting snapshots can result in loss of recovery points and/or restore failures.
Don't remove the lock taken on the storage account by Azure Backup. Deletion of the lock can make your storage account prone to accidental deletion. Learn more about protect your resources with lock.