Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This quickstart describes how to troubleshoot Bicep file deployment errors. You'll create a file with errors and learn how to fix the errors.
There are three types of errors that are related to a deployment:
- Validation errors occur before a deployment begins and are caused by syntax errors in your file. A code editor like Visual Studio Code can identify these errors.
- Preflight validation errors occur when a deployment command is run but resources aren't deployed. These errors are found without starting the deployment. For example, if a parameter value is incorrect, the error is found in preflight validation.
- Deployment errors occur during the deployment process and can only be found by assessing the deployment's progress in your Azure environment.
All types of errors return an error code that you use to troubleshoot the deployment. Validation and preflight errors are shown in the activity log but don't appear in your deployment history. A Bicep file with syntax errors doesn't compile into JSON and isn't shown in the activity log.
Prerequisites
To complete this quickstart, you need the following items:
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial subscription before you begin.
- Visual Studio Code with the latest Bicep extension.
- The latest version of either Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI.
Create a Bicep file with errors
Copy the following Bicep file and save it locally. You'll use this file to troubleshoot a validation error, a preflight error, and a deployment error. This quickstart assumes you've named the file troubleshoot.bicep but you can give it any name.
@description('SKU for the storage account')
@allowed([
'Standard_LRS'
'Standard_GRS'
'Standard_ZRS'
'Premium_LRS'
])
parameter storageAccountType string = 'Standard_LRS'
@description('Prefix for storage name.')
param prefixName string
var storageAccountName = '${prefixName}${uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)}'
resource storageAccount 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2021-06-01' = {
name: storageAccountName
location: resourceGroup().location
sku: {
name: storageAccountType
}
kind: 'StorageV2'
properties: {}
}
resource existingVNet 'Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks@2021-03-01' existing = {
name: 'doesnotexist'
}
output storageAccountName string = storageAccountName
output vnetResult object = existingVNet
Fix validation error
Open the file in Visual Studio Code. You'll notice that Visual Studio Code identifies a syntax error. The first parameter declaration is marked with red squiggles to indicate an error.
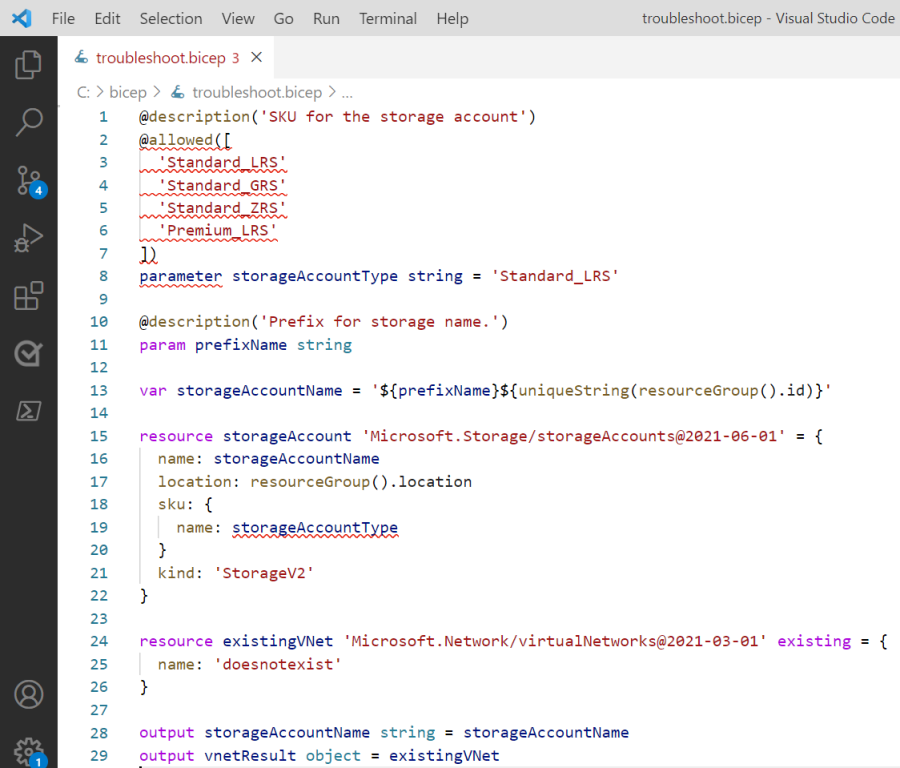
The lines marked with an error are:
@allowed([
'Standard_LRS'
'Standard_GRS'
'Premium_LRS'
])
parameter storageAccountType string = 'Standard_LRS'
When you hover over parameter, you see an error message.
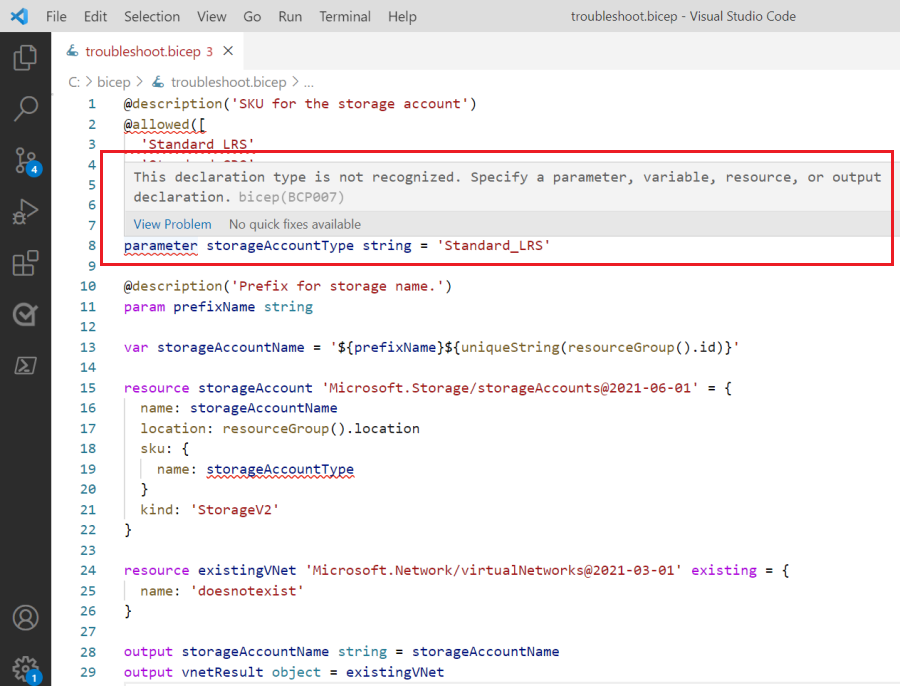
The message states: This declaration type is not recognized. Specify a parameter, variable, resource, or output declaration. If you attempt to deploy this file, you'll get the same error message from the deployment command.
If you look at the documentation for a parameter declaration, you'll see the keyword is actually param. When you change that syntax, the validation error disappears. The @allowed decorator was also marked as an error, but that error is also resolved by changing the parameter declaration. The decorator was marked as an error because it expects a parameter declaration after the decorator. This condition wasn't true when the declaration was incorrect.
The fixed line is:
param storageAccountType string = 'Standard_LRS'
Fix preflight error
Now that you've fixed the validation error, it's time to deploy the file. But, you'll provide a bad parameter value to see a preflight error.
az group create --name troubleshootRG --location chinanorth
az deployment group create \
--resource-group troubleshootRG \
--template-file troubleshoot.bicep \
--parameters prefixName=longNamewith!!Charactersthatarenotallowed
Azure Resource Manager determines that the name of the storage account contains characters that aren't allowed. It doesn't attempt the deployment.
You see an error message that indicates preflight validation failed. You also get a message that says the storage account name must be between 3 and 24 characters in length and use numbers and lower-case letters only. The prefix you provided didn't meet that requirement. For more information about this error code, see Resolve errors for storage account names.
Because the error was caught in preflight, no deployment exists in the history.
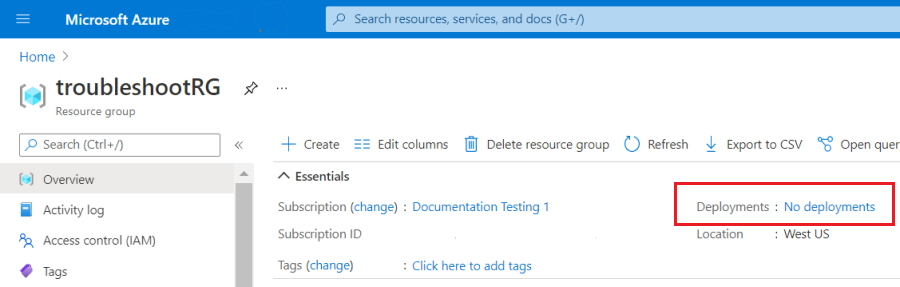
But, the failed deployment exists in the Activity Log.
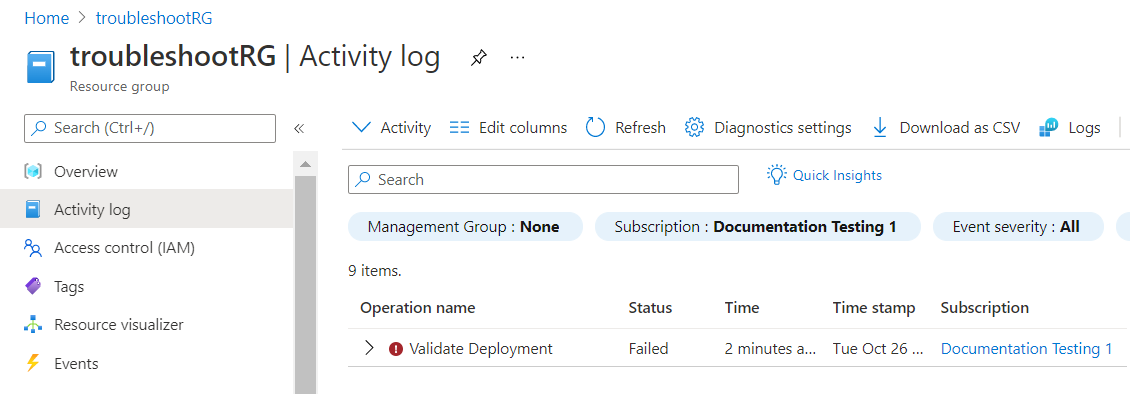
You can open details of the log entry to see the error message.
Fix deployment error
You'll deploy the file again and provide an allowed value for the name prefix parameter.
az group create --name troubleshootRG --location chinanorth
az deployment group create \
--resource-group troubleshootRG \
--template-file troubleshoot.bicep \
--parameters prefixName=stg
The deployment starts but fails with a message that the virtual network wasn't found. Typically, you would fix this error by changing the reference to the resource. In this quickstart, you'll delete the reference. For more information about this error code, see Resolve resource not found errors.
Notice in the portal that the deployment appears in the history.
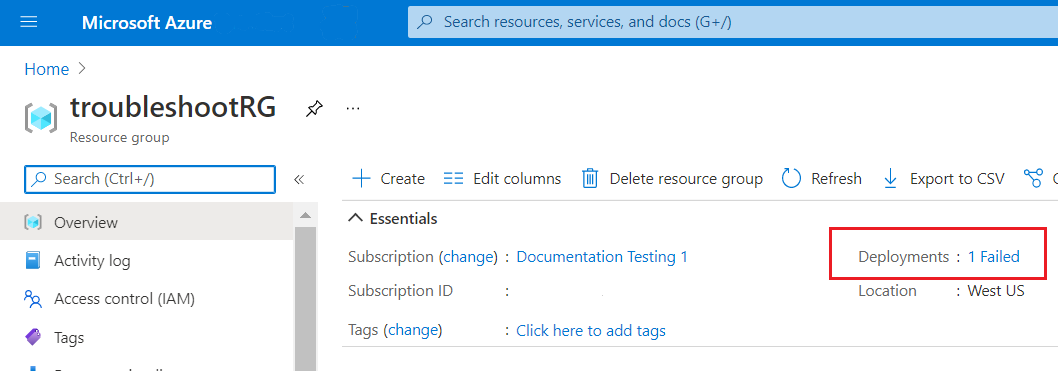
You can open the entry in the deployment history to get details about the error. The error also exists in the activity log.
The Bicep file attempts to reference a virtual network that doesn't exist in your resource group. Delete the reference to the existing virtual network to fix the error.
@description('SKU for the storage account')
@allowed([
'Standard_LRS'
'Standard_GRS'
'Standard_ZRS'
'Premium_LRS'
])
param storageAccountType string = 'Standard_LRS'
@description('Prefix for storage name.')
param prefixName string
var storageAccountName = '${prefixName}${uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)}'
resource storageAccount 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2021-06-01' = {
name: storageAccountName
location: resourceGroup().location
sku: {
name: storageAccountType
}
kind: 'StorageV2'
properties: {}
}
output storageAccountName string = storageAccountName
You can deploy that Bicep file without any errors.
Clean up resources
When the Azure resources are no longer needed, delete the resource group. You can delete the resource group from local Shell or the portal.
az group delete --name troubleshootRG
To delete the resource group from the portal, follow these steps:
- In the Azure portal, enter Resource groups in the search box.
- In the Filter by name field, enter the resource group name.
- Select the resource group name.
- Select Delete resource group.
- To confirm the deletion, enter the resource group name and select Delete.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to troubleshoot Bicep file deployment errors.