Quickstart: Use Azure Redis in Node.js
In this quickstart, you incorporate Azure Cache for Redis into a Node.js app. The app has access to a secure, dedicated cache that is accessible from any application within Azure.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription - create one
- Node.js installed - To install Node.js, see Install Node.js on Windows for instructions on how to install Node and npm on a Windows computer.
Create an Azure Cache for Redis instance
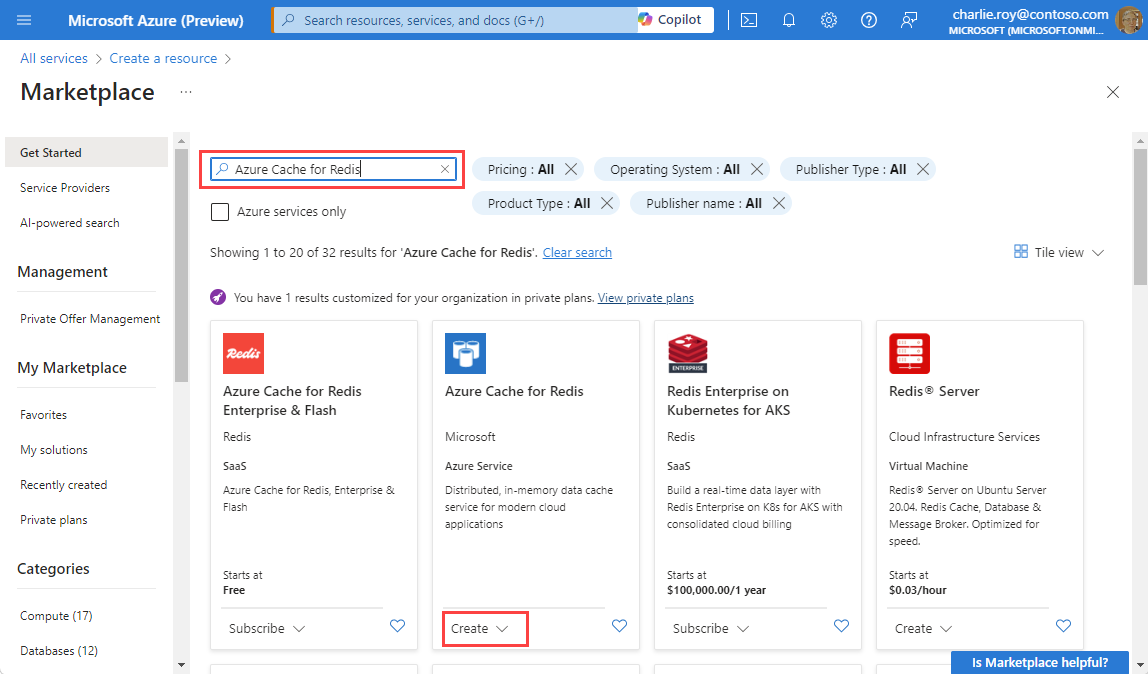
To create a cache, sign in to the Azure portal and select Create a resource.

On the Get Started page, type Azure Cache for Redis in the search box. Then, select Create.
On the New Redis Cache page, configure the settings for your cache.
Setting Choose a value Description Subscription Drop down and select your subscription. The subscription under which to create this new Azure Cache for Redis instance. Resource group Drop down and select a resource group, or select Create new and enter a new resource group name. Name for the resource group in which to create your cache and other resources. By putting all your app resources in one resource group, you can easily manage or delete them together. DNS name Enter a unique name. The cache name must be a string between 1 and 63 characters that contain only numbers, letters, or hyphens. The name must start and end with a number or letter, and can't contain consecutive hyphens. Your cache instance's host name is <DNS name>.redis.cache.chinacloudapi.cn. Location Drop down and select a location. Select a region near other services that use your cache. Cache SKU Drop down and select a SKU. The SKU determines the size, performance, and features parameters that are available for the cache. For more information, see Azure Cache for Redis Overview. Cache size Drop down and select a size of your cache For more information, see Azure Cache for Redis Overview. Select the Networking tab or select the Networking button at the bottom of the page.
In the Networking tab, select your connectivity method.
Select the Next: Advanced tab or select the Next: Advanced button on the bottom of the page to see the Advanced tab.
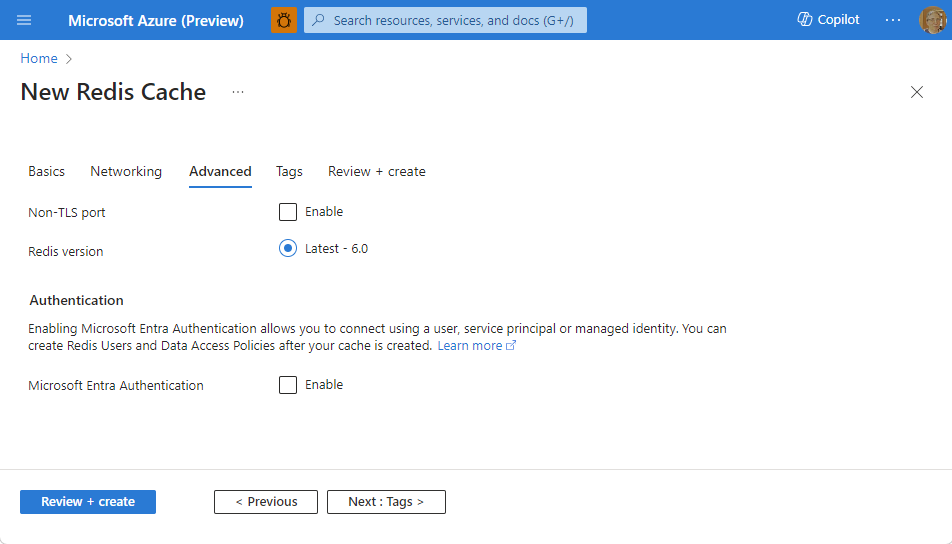
- For Basic or Standard caches, toggle the selection for a non-TLS port. You can also select if you want to enable Microsoft Entra Authentication.
- For a Premium cache, configure the settings for non-TLS port, clustering, managed identity, and data persistence. You can also select if you want to enable Microsoft Entra Authentication.
Select the Next: Tags tab or select the Next: Tags button at the bottom of the page.
Optionally, in the Tags tab, enter the name and value if you wish to categorize the resource.
Select Review + create. You're taken to the Review + create tab where Azure validates your configuration.
After the green Validation passed message appears, select Create.
It takes a while for a cache to create. You can monitor progress on the Azure Cache for Redis Overview page. When Status shows as Running, the cache is ready to use.
Install the node-redis client library
The node-redis library is the primary Node.js client for Redis. You can install the client with npm by using the following command:
npm install redis
Create a Node.js app to access a cache
Create a Node.js app that uses either Microsoft Entra ID or access keys to connect to an Azure Cache for Redis. We recommend you use Microsoft Entra ID.
Use Microsoft Entra ID authentication on your cache
Azure Redis caches have Microsoft Entra Authentication enabled by default. Access keys are disabled by default.
Important
Microsoft recommends using Microsoft Entra ID authentication for the most secure authentication experience instead of using passwords or access keys. The authentication described in this section of the article uses access keys, which require a very high degree of trust in the application and carries risks not present when using Microsoft Entra ID. Use the approach in this document only when Microsoft Entra ID authentication is not viable.
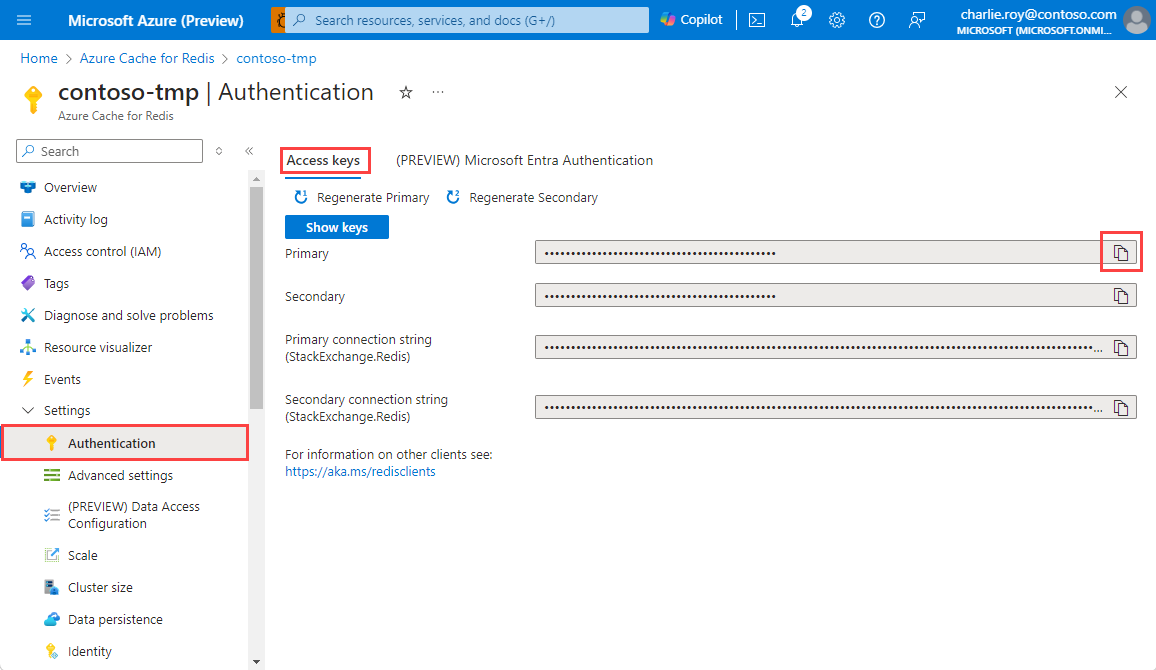
In the Azure portal, select the cache where you'd like to use Microsoft Entra token-based authentication.
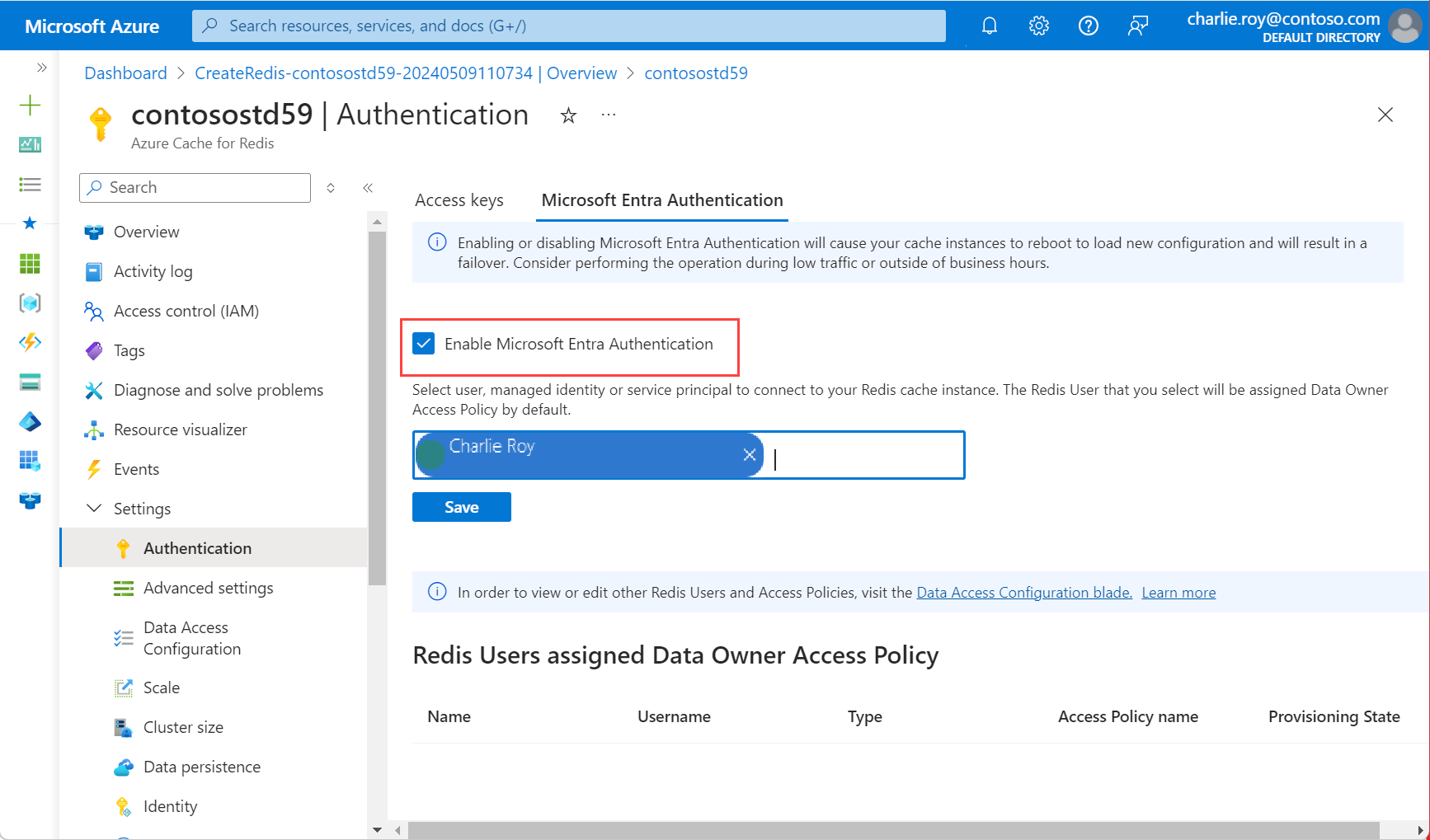
Select Authentication from the Resource menu.
Select Select member and enter the name of a valid user. The user you enter is automatically assigned Data Owner Access Policy by default when you select Save. You can also enter a managed identity or service principal to connect to your cache instance.
For information on using Microsoft Entra ID with Azure CLI, see the reference pages for identity.
Install the JavaScript Azure Identity client library
The Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) allows you to acquire security tokens from Microsoft identity to authenticate users. There's a JavaScript Azure identity client library available that uses MSAL to provide token authentication support. Install this library using npm:
npm install @azure/identity
Create a new Node.js app using Microsoft Entra ID
Add environment variables for your Host name and Service Principal ID, which is the object ID of your Microsoft Entra ID service principal or user. In the Azure portal, look for the Username.
set AZURE_CACHE_FOR_REDIS_HOST_NAME=contosoCache set REDIS_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_ID=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXCreate a new script file named redistest.js.
Add the following example JavaScript to the file. This code shows you how to connect to an Azure Cache for Redis instance using the cache host name and key environment variables. The code also stores and retrieves a string value in the cache. The
PINGandCLIENT LISTcommands are also executed. For more examples of using Redis with the node-redis client, see https://redis.js.org/.const { createClient } = require("redis"); const { DefaultAzureCredential } = require("@azure/identity"); async function main() { // Construct a Token Credential from Identity library, e.g. ClientSecretCredential / ClientCertificateCredential / ManagedIdentityCredential, etc. const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential(); const redisScope = "https://redis.azure.com/.default"; // Fetch a Microsoft Entra token to be used for authentication. This token will be used as the password. let accessToken = await credential.getToken(redisScope); console.log("access Token", accessToken); // Create redis client and connect to the Azure Cache for Redis over the TLS port using the access token as password. const cacheConnection = createClient({ username: process.env.REDIS_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_ID, password: accessToken.token, url: `redis://${process.env.AZURE_CACHE_FOR_REDIS_HOST_NAME}:6380`, pingInterval: 100000, socket: { tls: true, keepAlive: 0 }, }); cacheConnection.on("error", (err) => console.log("Redis Client Error", err)); await cacheConnection.connect(); // PING command console.log("\nCache command: PING"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.ping()); // SET console.log("\nCache command: SET Message"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.set("Message", "Hello! The cache is working from Node.js!")); // GET console.log("\nCache command: GET Message"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.get("Message")); // Client list, useful to see if connection list is growing... console.log("\nCache command: CLIENT LIST"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.sendCommand(["CLIENT", "LIST"])); cacheConnection.disconnect(); return "Done" } main().then((result) => console.log(result)).catch(ex => console.log(ex));Run the script with Node.js.
node redistest.jsThe output of your code looks like this.
Cache command: PING Cache response : PONG Cache command: GET Message Cache response : Hello! The cache is working from Node.js! Cache command: SET Message Cache response : OK Cache command: GET Message Cache response : Hello! The cache is working from Node.js! Cache command: CLIENT LIST Cache response : id=10017364 addr=76.22.73.183:59380 fd=221 name= age=1 idle=0 flags=N db=0 sub=0 psub=0 multi=-1 qbuf=26 qbuf-free=32742 argv-mem=10 obl=0 oll=0 omem=0 tot-mem=61466 ow=0 owmem=0 events=r cmd=client user=default numops=6 Done
Create a sample JavaScript app with reauthentication
Microsoft Entra ID access tokens have a limited lifespan, averaging 75 minutes. In order to maintain a connection to your cache, you need to refresh the token. This example demonstrates how to do this using JavaScript.
Create a new script file named redistestreauth.js.
Add the following example JavaScript to the file.
const { createClient } = require("redis"); const { DefaultAzureCredential } = require("@azure/identity"); async function returnPassword(credential) { const redisScope = "https://redis.azure.com/.default"; // Fetch a Microsoft Entra token to be used for authentication. This token will be used as the password. return credential.getToken(redisScope); } async function main() { // Construct a Token Credential from Identity library, e.g. ClientSecretCredential / ClientCertificateCredential / ManagedIdentityCredential, etc. const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential(); let accessToken = await returnPassword(credential); // Create redis client and connect to the Azure Cache for Redis over the TLS port using the access token as password. let cacheConnection = createClient({ username: process.env.REDIS_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_ID, password: accessToken.token, url: `redis://${process.env.AZURE_CACHE_FOR_REDIS_HOST_NAME}:6380`, pingInterval: 100000, socket: { tls: true, keepAlive: 0 }, }); cacheConnection.on("error", (err) => console.log("Redis Client Error", err)); await cacheConnection.connect(); for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) { try { // PING command console.log("\nCache command: PING"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.ping()); // SET console.log("\nCache command: SET Message"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.set("Message", "Hello! The cache is working from Node.js!")); // GET console.log("\nCache command: GET Message"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.get("Message")); // Client list, useful to see if connection list is growing... console.log("\nCache command: CLIENT LIST"); console.log("Cache response : " + await cacheConnection.sendCommand(["CLIENT", "LIST"])); break; } catch (e) { console.log("error during redis get", e.toString()); if ((accessToken.expiresOnTimestamp <= Date.now())|| (redis.status === "end" || "close") ) { await redis.disconnect(); accessToken = await returnPassword(credential); cacheConnection = createClient({ username: process.env.REDIS_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_ID, password: accessToken.token, url: `redis://${process.env.AZURE_CACHE_FOR_REDIS_HOST_NAME}:6380`, pingInterval: 100000, socket: { tls: true, keepAlive: 0 }, }); } } } } main().then((result) => console.log(result)).catch(ex => console.log(ex));Run the script with Node.js.
node redistestreauth.jsThe output of your code looks like this.
Cache command: PING Cache response : PONG Cache command: GET Message Cache response : Hello! The cache is working from Node.js! Cache command: SET Message Cache response : OK Cache command: GET Message Cache response : Hello! The cache is working from Node.js! Cache command: CLIENT LIST Cache response : id=10017364 addr=76.22.73.183:59380 fd=221 name= age=1 idle=0 flags=N db=0 sub=0 psub=0 multi=-1 qbuf=26 qbuf-free=32742 argv-mem=10 obl=0 oll=0 omem=0 tot-mem=61466 ow=0 owmem=0 events=r cmd=client user=default numops=6
Note
For additional examples of using Microsoft Entra ID to authenticate to Redis using the node-redis library, please see this GitHub repo
Clean up resources
If you want to continue to use the resources you created in this article, keep the resource group.
Otherwise, if you're finished with the resources, you can delete the Azure resource group that you created to avoid charges.
Important
Deleting a resource group is irreversible. When you delete a resource group, all the resources in it are permanently deleted. Make sure that you do not accidentally delete the wrong resource group or resources. If you created the resources inside an existing resource group that contains resources you want to keep, you can delete each resource individually instead of deleting the resource group.
To delete a resource group
Sign in to the Azure portal, and then select Resource groups.
Select the resource group you want to delete.
If there are many resource groups, use the Filter for any field... box, type the name of your resource group you created for this article. Select the resource group in the results list.
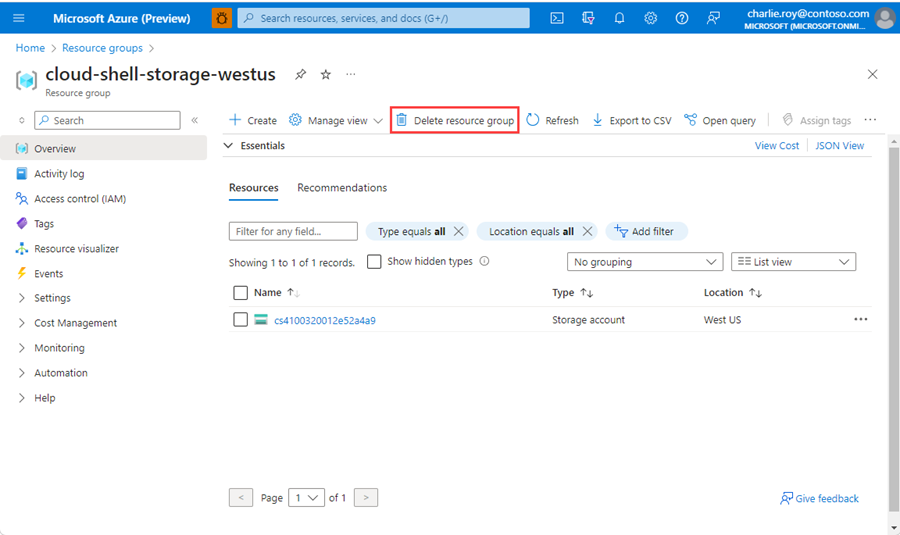
Select Delete resource group.
You're asked to confirm the deletion of the resource group. Type the name of your resource group to confirm, and then select Delete.
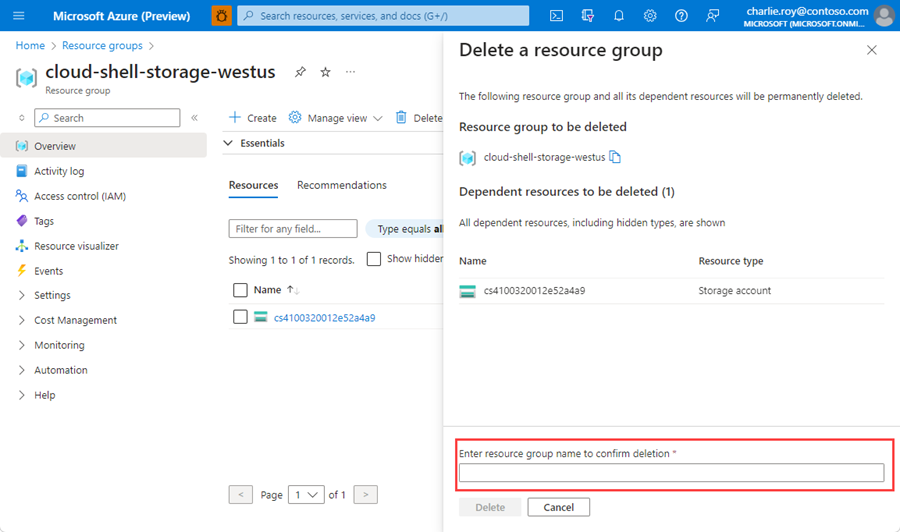
After a few moments, the resource group and all of its resources are deleted.
Get the sample code
Get the Node.js quickstart on GitHub.
Related content
In this quickstart, you learned how to use Azure Cache for Redis from a Node.js application. Learn more about the Azure Redis offerings: