Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes runbook issues that might occur and how to resolve them. For general information, see Runbook execution in Azure Automation.
It is no longer possible to use cmdlets from imported non-default modules in graphical PowerShell runbooks
Issue
When you import a PowerShell module you will not be able to use its cmdlets in graphical PowerShell runbooks.
Cause
To improve the security posture of PowerShell runbooks, the service no longer processes the module manifest file to export the cmdlets and functions. This means that they cannot be used when authoring graphical PowerShell runbooks.
Resolution
There is no impact on the execution of existing runbooks. For new runbooks using non-default PowerShell modules we recommend using textual runbooks instead of graphical PowerShell runbooks to overcome this issue. You can use the Azure Automation extension for VScode for authoring and editing PowerShell runbooks, that leverages GitHub Copilot to simplify the runbook authoring experience.
Start-AzAutomationRunbook fails with "runbookName does not match expected pattern" error message
Issue
When you run Start-AzAutomationRunbook to start specific runbooks:
start-azautomationRunbook -Name "Test_2" -AutomationAccountName "AutomationParent" -ResourceGroupName "AutomationAccount"
It fails with the following error:
Start-AzAutomationRunbook: "runbookname" does not match expected pattern '^[a-zA-Z]*-*[a-zA-Z0-9]*$'
Cause
Code that was introduced in 1.9.0 version of the Az.Automation module verifies the names of the runbooks to start and incorrectly flags runbooks with multiple "-" characters or with an "_" character in the name as invalid.
Workaround
We recommend that you revert to 1.8.0 version of the module.
Resolution
Currently, we are working to deploy a fix to address this issue.
Diagnose runbook issues
When you receive errors during runbook execution in Azure Automation, you can use the following steps to help diagnose the issues:
Ensure that your runbook script executes successfully on your local machine.
For language reference and learning modules, see the PowerShell Docs or Python Docs. Running your script locally can discover and resolve common errors, such as:
- Missing modules
- Syntax errors
- Logic errors
Investigate runbook error streams.
Look at these streams for specific messages, and compare them to the errors documented in this article.
Ensure that your nodes and Automation workspace have the required modules.
If your runbook imports any modules, verify that they're available to your Automation account by using the steps in Import modules. Update your PowerShell modules to the latest version by following the instructions in Update Azure PowerShell modules in Azure Automation. For more troubleshooting information, see Troubleshoot modules.
If your runbook is suspended or unexpectedly fails:
- Renew the webhook if you're trying to use an expired webhook to start the runbook.
- Check job statuses to determine current runbook statuses and some possible causes of the issue.
- Add additional output to the runbook to identify what happens before the runbook is suspended.
- Handle any exceptions that are thrown by your job.
Do this step if the runbook job or the environment on Hybrid Runbook Worker doesn't respond.
If you're running your runbooks on a Hybrid Runbook Worker instead of in Azure Automation, you might need to troubleshoot the hybrid worker itself.
Scenario: Runbook fails with "this.Client.SubscriptionId cannot be null." error message
Issue
Your runbook using a managed identity Connect-AzAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloud -Identity which attempts to manage Azure objects, fails to work successfully and logs the following error - this.Client.SubscriptionId cannot be null.
get-azvm : 'this.Client.SubscriptionId' cannot be null. At line:5 char:1 + get-azvm + ~~~~~~~~ + CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Get-AzVM], ValidationException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.GetAzureVMCommand
Cause
This can happen when the Managed Identity (or other account used in the runbook) has not been granted any permissions to access the subscription.
Resolution
Grant the Managed Identity (or other account used in the runbook) an appropriate role membership in the subscription. Learn more
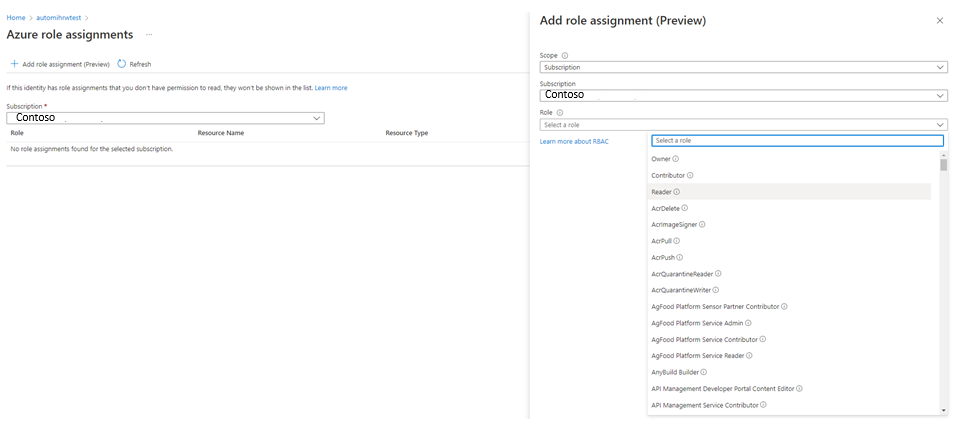
Scenario: Access blocked to Azure Storage, or Azure Key Vault, or Azure SQL
This scenario uses Azure Storage as an example; however, the information is equally applicable to Azure Key Vault and Azure SQL.
Issue
Attempting to access Azure Storage from a Runbook results in an error similar to the following message: The remote server returned an error: (403) Forbidden. HTTP Status Code: 403 - HTTP Error Message: This request is not authorized to perform this operation.
Cause
The Azure Firewall on Azure Storage is enabled.
Resolution
Enabling the Azure Firewall on Azure Storage, Azure Key Vault, or Azure SQL blocks access from Azure Automation runbooks for those services. Access will be blocked even when the firewall exception to allow trusted Microsoft services is enabled, as Automation is not a part of the trusted services list. With an enabled firewall, access can only be made by using a Hybrid Runbook Worker and a virtual network service endpoint.
Scenario: Runbook fails with a No permission or Forbidden 403 error
Issue
Your runbook fails with a No permission or Forbidden 403 error, or equivalent.
Cause
Run As accounts might not have the same permissions against Azure resources as your current Automation account.
Resolution
Ensure that your Run As account has permissions to access any resources used in your script.
Scenario: Sign-in to Azure account failed
Issue
You receive one of the following errors when you work with the Connect-AzAccount cmdlet:
Unknown_user_type: Unknown User Type
No certificate was found in the certificate store with thumbprint
Cause
These errors occur if the credential asset name isn't valid. They might also occur if the user name and password that you used to set up the Automation credential asset aren't valid.
Resolution
To determine what's wrong, follow these steps:
Make sure that you don't have any special characters. These characters include the
\@character in the Automation credential asset name that you're using to connect to Azure.Check to see if you can use the user name and password that are stored in the Azure Automation credential in your local PowerShell ISE editor. Run the following cmdlets in the PowerShell ISE.
$Cred = Get-Credential #Using Azure Service Management Add-AzureAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloud -Credential $Cred #Using Azure Resource Manager Connect-AzAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloud -Credential $CredIf the error appears to be transient, try adding retry logic to your authentication routine to make authenticating more robust.
$logonAttempt = 0 $logonResult = $False while(!($connectionResult) -And ($logonAttempt -le 10)) { $LogonAttempt++ #Logging in to Azure... $connectionResult = Connect-AzAccount ` Start-Sleep -Seconds 30 if($connectionResult) { $logonResult = $True } }
Scenario: Run Login-AzureRMAccount to log in
Issue
You receive the following error when you run a runbook:
Run Login-AzureRMAccount to login.
Cause
This error can occur when you're not using a Run As account or the Run As account has expired.
This error has two primary causes:
- There are different versions of the AzureRM or Az module.
- You're trying to access resources in a separate subscription.
Resolution
If you receive this error after you update one AzureRM or Az module, update all your modules to the same version.
If you're trying to access resources in another subscription, follow these steps to configure permissions:
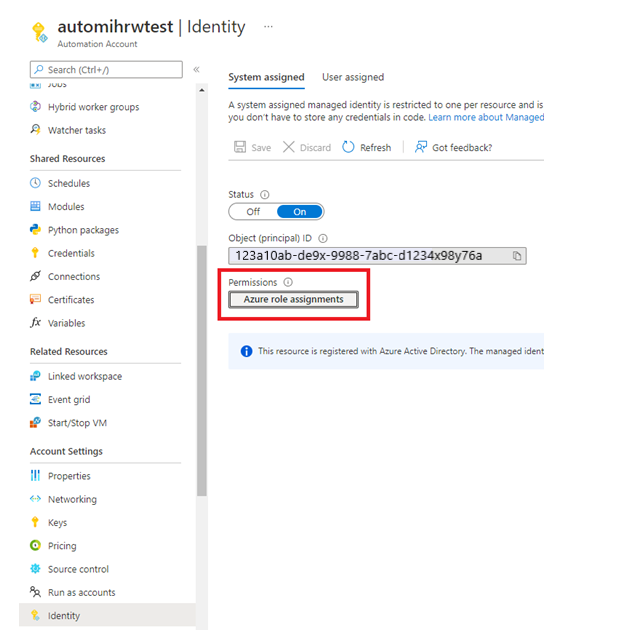
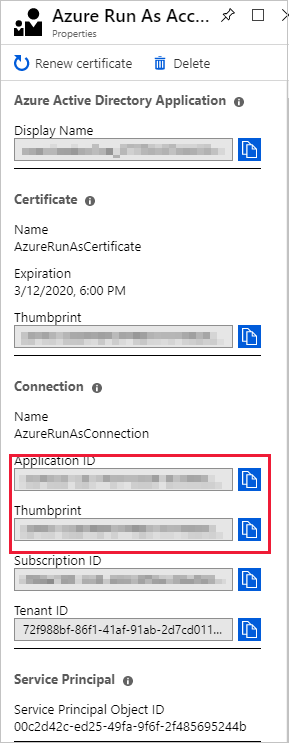
Go to the Automation Run As account, and copy the Application ID and Thumbprint.
Go to the subscription's Access control where the Automation account is not hosted, and add a new role assignment.
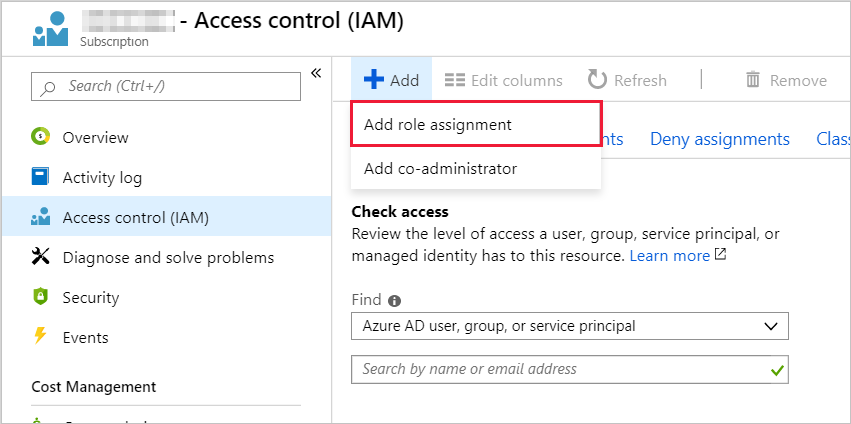
Add the Application ID collected earlier. Select Contributor permissions.
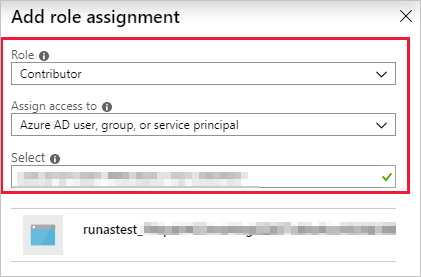
Copy the name of the subscription.
You can now use the following runbook code to test the permissions from your Automation account to the other subscription. Replace
<CertificateThumbprint>with the value copied in step 1. Replace"<SubscriptionName>"with the value copied in step 4.$Conn = Get-AutomationConnection -Name AzureRunAsConnection Connect-AzAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloud -ServicePrincipal -Tenant $Conn.TenantID -ApplicationId $Conn.ApplicationID -CertificateThumbprint "<CertificateThumbprint>" #Select the subscription you want to work with Select-AzSubscription -SubscriptionName '<YourSubscriptionNameGoesHere>' #Test and get outputs of the subscriptions you granted access. $subscriptions = Get-AzSubscription foreach($subscription in $subscriptions) { Set-AzContext $subscription Write-Output $subscription.Name }
Scenario: Unable to find the Azure subscription
Issue
You receive the following error when you work with the Select-AzureSubscription, Select-AzureRMSubscription, or Select-AzSubscription cmdlet:
The subscription named <subscription name> cannot be found.
Error
This error can occur if:
- The subscription name isn't valid.
- The Microsoft Entra user who's trying to get the subscription details isn't configured as an administrator of the subscription.
- The cmdlet isn't available.
- Context switching occurred.
Resolution
For context switching, see Context switching in Azure Automation.
Scenario: Runbooks fail when dealing with multiple subscriptions
Issue
When executing runbooks, the runbook fails to manage Azure resources.
Cause
The runbook isn't using the correct context when running. This may be because the runbook is accidentally trying to access the incorrect subscription.
You may see errors like this one:
Get-AzVM : The client '<client-id>' with object id '<object-id> does not have authorization to perform action 'Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/read' over scope '/subscriptions/<subscriptionIdOfSubscriptionWhichDoesntContainTheVM>/resourceGroups/REsourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/VMName '.
ErrorCode: AuthorizationFailed
StatusCode: 403
ReasonPhrase: Forbidden Operation
ID : <AGuidRepresentingTheOperation> At line:51 char:7 + $vm = Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -Name $UNBV... +
or like this one:
Get-AzureRmResource : Resource group "SomeResourceGroupName" could not be found.
... resources = Get-AzResource -ResourceGroupName $group.ResourceGro ...
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Get-AzResource], CloudException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.ResourceManager.Cmdlets.Implementation.GetAzureResourceCmdlet
Resolution
To avoid accidentally trying to access the incorrect subscription, see Context switching in Azure Automation.
Scenario: Authentication to Azure fails because multifactor authentication is enabled
Issue
You receive the following error when authenticating to Azure with your Azure user name and password:
Add-AzureAccount: AADSTS50079: Strong authentication enrollment (proof-up) is required
Cause
If you have multifactor authentication on your Azure account, you can't use a Microsoft Entra user to authenticate to Azure. Instead, you need to use a certificate or a service principal to authenticate.
Resolution
To use a service principal with Azure Resource Manager cmdlets, see Creating service principal using Azure portal and Authenticating a service principal with Azure Resource Manager.
Scenario: Runbook fails with "A task was canceled" error message
Issue
Your runbook fails with an error similar to the following example:
Exception: A task was cancelled.
Cause
This error can be caused by using outdated Azure modules.
Resolution
You can resolve this error by updating your Azure modules to the latest version:
- In your Automation account, select Modules, and then select Update Azure modules.
- The update takes roughly 15 minutes. After it's finished, rerun the runbook that failed.
To learn more about updating your modules, see Update Azure modules in Azure Automation.
Scenario: Term not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, or script
Issue
Your runbook fails with an error similar to the following example:
The term 'Connect-AzAccount' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if the path was included verify that the path is correct and try again.
Cause
This error can happen for the following reasons:
- The module that contains the cmdlet isn't imported into the Automation account.
- The module that contains the cmdlet is imported but is out of date.
Resolution
Do one of the following tasks to resolve this error:
- For an Azure module, see How to update Azure PowerShell modules in Azure Automation to learn how to update your modules in your Automation account.
- For a non-Azure module, make sure that the module is imported into your Automation account.
Scenario: Cmdlet fails in PnP PowerShell runbook on Azure Automation
Issue
When a runbook writes a PnP PowerShell-generated object to the Azure Automation output directly, cmdlet output can't stream back to Automation.
Cause
This issue most commonly occurs when Azure Automation processes runbooks that invoke PnP PowerShell cmdlets, for example, add-pnplistitem, without catching the return objects.
Resolution
Edit your scripts to assign any return values to variables so that the cmdlets don't attempt to write whole objects to the standard output. A script can redirect the output stream to a cmdlet, as shown here.
$null = add-pnplistitem
If your script parses cmdlet output, the script must store the output in a variable and manipulate the variable instead of simply streaming the output.
$SomeVariable = add-pnplistitem ....
if ($SomeVariable.someproperty -eq ....
Scenario: Cmdlet not recognized when executing a runbook
Issue
Your runbook job fails with the error:
<cmdlet name>: The term <cmdlet name> is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program.
Cause
This error is caused when the PowerShell engine can't find the cmdlet you're using in your runbook. It's possible that the module containing the cmdlet is missing from the account, there's a name conflict with a runbook name, or the cmdlet also exists in another module and Automation can't resolve the name.
Resolution
Use any of the following solutions to fix the problem:
- Make sure that you've entered the cmdlet name correctly.
- Ensure that the cmdlet exists in your Automation account and that there are no conflicts. To verify if the cmdlet is present, open a runbook in edit mode and search for the cmdlet you want to find in the library, or run
Get-Command <CommandName>. After you've validated that the cmdlet is available to the account, and that there are no name conflicts with other cmdlets or runbooks, add the cmdlet to the canvas. Make sure that you're using a valid parameter set in your runbook. - If you do have a name conflict and the cmdlet is available in two different modules, resolve the issue by using the fully qualified name for the cmdlet. For example, you can use
ModuleName\CmdletName. - If you're executing the runbook on-premises in a hybrid worker group, ensure that the module and cmdlet are installed on the machine that hosts the hybrid worker.
Scenario: Incorrect object reference on call to Add-AzAccount
Issue
You receive this error when you work with Add-AzAccount, which is an alias for the Connect-AzAccount cmdlet:
Add-AzAccount : Object reference not set to an instance of an object
Cause
This error can occur if the runbook doesn't do the proper steps before calling Add-AzAccount to add the Automation account. An example of one of the necessary steps is signing in with a Run As account. For the correct operations to use in your runbook, see Runbook execution in Azure Automation.
Scenario: Object reference not set to an instance of an object
Issue
You receive the following error when you invoke a child runbook with the Wait parameter and the Output stream contains an object:
Object reference not set to an instance of an object
Cause
If the stream contains objects, Start-AzAutomationRunbook doesn't handle the Output stream correctly.
Resolution
Implement a polling logic, and use the Get-AzAutomationJobOutput cmdlet to retrieve the output. A sample of this logic is defined here:
$AutomationAccountName = "ContosoAutomationAccount"
$RunbookName = "ChildRunbookExample"
$ResourceGroupName = "ContosoRG"
function IsJobTerminalState([string]$Status) {
$TerminalStates = @("Completed", "Failed", "Stopped", "Suspended")
return $Status -in $TerminalStates
}
$StartAzAutomationRunbookParameters = @{
Name = $RunbookName
AutomationAccountName = $AutomationAccountName
ResourceGroupName = $ResourceGroupName
}
$Job = Start-AzAutomationRunbook @StartAzAutomationRunBookParameters
$PollingSeconds = 5
$MaxTimeout = New-TimeSpan -Hours 3 | Select-Object -ExpandProperty TotalSeconds
$WaitTime = 0
while(-NOT (IsJobTerminalState $Job.Status) -and $WaitTime -lt $MaxTimeout) {
Start-Sleep -Seconds $PollingSeconds
$WaitTime += $PollingSeconds
$Job = $Job | Get-AzAutomationJob
}
$Job | Get-AzAutomationJobOutput | Get-AzAutomationJobOutputRecord | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Value
Scenario: Runbook fails because of deserialized object
Issue
Your runbook fails with the error:
Cannot bind parameter <ParameterName>.
Cannot convert the <ParameterType> value of type Deserialized <ParameterType> to type <ParameterType>.
Cause
If your runbook is a PowerShell Workflow, it stores complex objects in a deserialized format to persist your runbook state if the workflow is suspended.
Resolution
Use any of the following solutions to fix this problem:
- If you're piping complex objects from one cmdlet to another, wrap these cmdlets in an
InlineScriptactivity. - Pass the name or value that you need from the complex object instead of passing the entire object.
- Use a PowerShell runbook instead of a PowerShell Workflow runbook.
Scenario: 400 Bad Request status when calling a webhook
Issue
When you try to invoke a webhook for an Azure Automation runbook, you receive the following error:
400 Bad Request : This webhook has expired or is disabled
Cause
The webhook that you're trying to call is either disabled or is expired.
Resolution
If the webhook is disabled, you can re-enable it through the Azure portal. If the webhook has expired, you must delete and then re-create it. You can only renew a webhook if it hasn't already expired.
Scenario: 429: The request rate is currently too large
Issue
You receive the following error message when running the Get-AzAutomationJobOutput cmdlet:
429: The request rate is currently too large. Please try again
Cause
This error can occur when retrieving job output from a runbook that has many verbose streams.
Resolution
Do one of the following to resolve this error:
- Edit the runbook, and reduce the number of job streams that it emits.
- Reduce the number of streams to be retrieved when running the cmdlet. To do this, you can set the value of the
Streamparameter for the Get-AzAutomationJobOutput cmdlet to retrieve only Output streams.
Scenario: Runbook output stream greater than 1 MB
Issue
Your runbook running in the Azure sandbox fails with the following error:
The runbook job failed due to a job stream being larger than 1MB, this is the limit supported by an Azure Automation sandbox.
Cause
This error occurs because your runbook attempted to write too much exception data to the output stream.
Resolution
There's a 1 MB limit on the job output stream. Ensure that your runbook encloses calls to an executable or subprocess by using try and catch blocks. If the operations throw an exception, have the code write the message from the exception into an Automation variable. This technique prevents the message from being written into the job output stream. For Hybrid Runbook Worker jobs executed, the output stream truncated to 1 MB is displayed with no error message.
Scenario: Runbook job start attempted three times, but fails to start each time
Issue
Your runbook fails with the following error:
The job was tried three times but it failed
Cause
This error occurs because of one of the following issues:
Memory limit. A job might fail if it's using more than 400 MB of memory. The documented limits on memory allocated to a sandbox are found at Automation service limits.
Network sockets. Azure sandboxes are limited to 1,000 concurrent network sockets. For more information, see Automation service limits.
Module incompatible. Module dependencies might not be correct. In this case, your runbook typically returns a
Command not foundorCannot bind parametermessage.No authentication with Active Directory for sandbox. Your runbook attempted to call an executable or subprocess that runs in an Azure sandbox. Configuring runbooks to authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID by using the Azure Active Directory Authentication Library (ADAL) isn't supported.
Resolution
Memory limit, network sockets. Suggested ways to work within the memory limits are to split the workload among multiple runbooks, process less data in memory, avoid writing unnecessary output from your runbooks, and consider how many checkpoints are written into your PowerShell workflow runbooks. Use the clear method, such as
$myVar.clear, to clear out variables and use[GC]::Collectto run garbage collection immediately. These actions reduce the memory footprint of your runbook during runtime.Module incompatible. Update your Azure modules by following the steps in How to update Azure PowerShell modules in Azure Automation.
No authentication with Active Directory for sandbox. When you authenticate to Microsoft Entra ID with a runbook, ensure that the Azure AD module is available in your Automation account. Be sure to grant the Run As account the necessary permissions to perform the tasks that the runbook automates.
If your runbook can't call an executable or subprocess running in an Azure sandbox, use the runbook on a Hybrid Runbook Worker. Hybrid workers aren't limited by the memory and network limits that Azure sandboxes have.
Scenario: PowerShell job fails with "Cannot invoke method" error message
Issue
You receive the following error message when you start a PowerShell job in a runbook that runs in Azure:
Exception was thrown - Cannot invoke method. Method invocation is supported only on core types in this language mode.
Cause
This error might indicate that runbooks that run in an Azure sandbox can't run in the Full Language mode.
Resolution
There are two ways to resolve this error:
- Instead of using Start-Job, use Start-AzAutomationRunbook to start the runbook.
- Try running the runbook on a Hybrid Runbook Worker.
To learn more about this behavior and other behaviors of Azure Automation runbooks, see Runbook execution in Azure Automation.
Scenario: A long-running runbook fails to complete
Issue
Your runbook shows in a Stopped state after running for three hours. You might also receive this error:
The job was evicted and subsequently reached a Stopped state. The job cannot continue running.
This behavior is by design in Azure sandboxes because of the fair share monitoring of processes within Azure Automation. If a process executes longer than three hours, fair share automatically stops a runbook. The status of a runbook that goes past the fair share time limit differs by runbook type. PowerShell and Python runbooks are set to a Stopped status. PowerShell Workflow runbooks are set to Failed.
Cause
The runbook ran over the three-hour limit allowed by fair share in an Azure sandbox.
Resolution
One recommended solution is to run the runbook on a Hybrid Runbook Worker. Hybrid workers aren't limited by the three-hour fair share runbook limit that Azure sandboxes have. Runbooks that run on Hybrid Runbook Workers should be developed to support restart behaviors if there are unexpected local infrastructure issues.
Another solution is to optimize the runbook by creating child runbooks. If your runbook loops through the same function on several resources, for example, in a database operation on several databases, you can move the function to a child runbook. Each child runbook executes in parallel in a separate process. This behavior decreases the total amount of time for the parent runbook to complete.
The PowerShell cmdlets that enable the child runbook scenario are:
- Start-AzAutomationRunbook. This cmdlet allows you to start a runbook and pass parameters to the runbook.
- Get-AzAutomationJob. If there are operations that need to be performed after the child runbook completes, this cmdlet allows you to check the job status for each child.
Scenario: Error in job streams about the get_SerializationSettings method
Issue
You see the following error in your job streams for a runbook:
Connect-AzAccount : Method 'get_SerializationSettings' in type
'Microsoft.Azure.Management.Internal.Resources.ResourceManagementClient' from assembly
'Microsoft.Azure.Commands.ResourceManager.Common, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35'
does not have an implementation.
At line:16 char:1
+ Connect-AzAccount -ServicePrincipal -Tenant $Conn.TenantID -Appl ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Connect-AzAccount], TypeLoadException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : System.TypeLoadException,Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Profile.ConnectAzAccountCommand
Cause
This error is probably caused by using an incomplete migration from AzureRM to Az modules in your runbook. This situation can cause Azure Automation to start a runbook job by using only AzureRM modules, and then start another job by using only Az modules, which leads to a sandbox crash.
Resolution
We don't recommend the use of Az and AzureRM cmdlets in the same runbook. To learn more about the correct use of the modules, see Migrate to Az modules.
Scenario: Access denied when using Azure sandbox for runbook or application
Issue
When your runbook or application attempts to run in an Azure sandbox, the environment denies access.
Cause
This issue can occur because Azure sandboxes prevent access to all out-of-process COM servers. For example, a sandboxed application or runbook can't call into Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) or into the Windows Installer service (msiserver.exe).
Resolution
For details about the use of Azure sandboxes, see Runbook execution environment.
Scenario: Invalid Forbidden status code when using Key Vault inside a runbook
Issue
When you try to access Azure Key Vault through an Azure Automation runbook, you get the following error:
Operation returned an invalid status code 'Forbidden'
Cause
Possible causes for this issue are:
- Not using a Run As account.
- Insufficient permissions.
Resolution
Not using a Run As account
Follow Step 5 - Add authentication to manage Azure resources to ensure that you are using a Run As account to access Key Vault.
Insufficient permissions
Add permissions to Key Vault to ensure that your Run As account has sufficient permissions to access Key Vault.
Scenario: Runbook fails with "Parameter length exceeded" error
Issue
Your runbook uses parameters and fails with the following error:
Total Length of Runbook Parameter names and values exceeds the limit of 30,000 characters. To avoid this issue, use Automation Variables to pass values to runbook.
Cause
There is a limit to the total length of characters of all Parameters that can be provided in Python 2.7, Python 3.8, and PowerShell 7.1 runbooks. The total length of all Parameter names, and Parameter values must not exceed 30,000 characters.
Resolution
To overcome this issue, you can use Azure Automation Variables to pass values to runbook. You can alternatively reduce the number of characters in Parameter names and Parameter values to ensure that the total length does not exceed 30,000 characters.
Recommended documents
Next steps
If you don't see your problem here or you're unable to resolve your issue, try one of the following channels for more support:
- Get answers from Azure experts through Azure Forums
- If you need more help, you can file an Azure support incident. Go to the Azure support site.